Stellar Metamorphosis as Alternative to Nebular Hypothesis
... formation because these stars should have already squeezed together to make one single star. According to the mainstream dogma solar systems have a central star which centralizes the majority of the material that forms the theorized disk surrounding it, therefore these stars should not be separate, ...
... formation because these stars should have already squeezed together to make one single star. According to the mainstream dogma solar systems have a central star which centralizes the majority of the material that forms the theorized disk surrounding it, therefore these stars should not be separate, ...
Chapter 14 Neutron Stars and Black holes
... jumped into a Schwarzschild black hole. From what you have read, what do you think would happen to you if you jumped into a Kerr black hole? ...
... jumped into a Schwarzschild black hole. From what you have read, what do you think would happen to you if you jumped into a Kerr black hole? ...
The DBV stars: Progress and problems
... shows the helium layer mass should be about 10-3.5M, in order to explain the “carbon pollution” trace abundances seen in helium rich white dwarfs below 15,000 K. If the Dehner & Kawaler calculations can be extended down to 12,000 K or below, they should be able to show the total helium layer mass of ...
... shows the helium layer mass should be about 10-3.5M, in order to explain the “carbon pollution” trace abundances seen in helium rich white dwarfs below 15,000 K. If the Dehner & Kawaler calculations can be extended down to 12,000 K or below, they should be able to show the total helium layer mass of ...
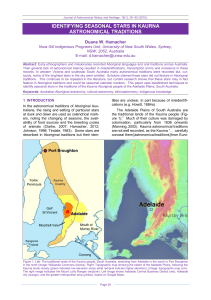
identifying seasonal stars in kaurna astronomical traditions
... Abstract: Early ethnographers and missionaries recorded Aboriginal languages and oral traditions across Australia. Their general lack of astronomical training resulted in misidentifications, transcription errors and omissions in these records. In western Victoria and southeast South Australia many a ...
... Abstract: Early ethnographers and missionaries recorded Aboriginal languages and oral traditions across Australia. Their general lack of astronomical training resulted in misidentifications, transcription errors and omissions in these records. In western Victoria and southeast South Australia many a ...
Astro Physics Notes and Study Guide 2015-17
... distance of about 800 pc from Earth. Apparent brightness of the Sun Apparent brightness of star A Mean distance of Sun from Earth 1 pc Use ratios ( see # 2 p. 7 of packet) b = ...
... distance of about 800 pc from Earth. Apparent brightness of the Sun Apparent brightness of star A Mean distance of Sun from Earth 1 pc Use ratios ( see # 2 p. 7 of packet) b = ...
Galaxies (and stars) in the far infrared: results from the AKARI All
... bright stars, mostly evolved stars and pulsating variables (often Mira-type) a smaller branch overlapping galaxies contains few bright stars with known IR excess (due to, e.g. dusty disks) – most notable among them is Vega, some faint (poorly known) stars and a certain number of planetary nebulae ...
... bright stars, mostly evolved stars and pulsating variables (often Mira-type) a smaller branch overlapping galaxies contains few bright stars with known IR excess (due to, e.g. dusty disks) – most notable among them is Vega, some faint (poorly known) stars and a certain number of planetary nebulae ...
The Probability and Effects of an Asteroid Impact with Earth
... of a comparison chart with star magnitudes adjusted for dark adaption is inappropriate. Observations near the visual limit are also more accurate than those made of bright stars using telescopes, so the ideal observations of δ Cephei are made by eye or binoculars before the eye becomes dark adapted. ...
... of a comparison chart with star magnitudes adjusted for dark adaption is inappropriate. Observations near the visual limit are also more accurate than those made of bright stars using telescopes, so the ideal observations of δ Cephei are made by eye or binoculars before the eye becomes dark adapted. ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... supernovae—stars exploding in cataclysmic stellar suicide—but did not act like familiar supernovae. Instead of brightening over a period of maybe three weeks (about 20 days), they seemed to take nearly three months (about 80 days). At first, no host galaxy could be found, so Howell and his colleague ...
... supernovae—stars exploding in cataclysmic stellar suicide—but did not act like familiar supernovae. Instead of brightening over a period of maybe three weeks (about 20 days), they seemed to take nearly three months (about 80 days). At first, no host galaxy could be found, so Howell and his colleague ...
The Stars - Springer
... class F0 star. Further prefixes and suffixes can be used to illustrate additional features: A star with emission lines (also called f in some O-type stars) Metallic lines A peculiar spectrum A variable spectrum A star with a blue or red shift in the line (for example P-Cygni stars) ...
... class F0 star. Further prefixes and suffixes can be used to illustrate additional features: A star with emission lines (also called f in some O-type stars) Metallic lines A peculiar spectrum A variable spectrum A star with a blue or red shift in the line (for example P-Cygni stars) ...
Chapter 12: The Life Cycle of Stars
... greater luminosity. However, never gets hot enough to burn carbon core: end of the line. • Star collapses to a dense, small, hot object: white dwarf. ...
... greater luminosity. However, never gets hot enough to burn carbon core: end of the line. • Star collapses to a dense, small, hot object: white dwarf. ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
s-process
... Significant production of r-process elements began when the metallicity of the Galaxy reached [Fe/H] = -3. The heavy n-capture elements were formed predominantly by the r-process at metallicities below [Fe/H] = -2.1. Elements from the s-process appear at a metallicity of [Fe/H] = -2.1, when low-mass ...
... Significant production of r-process elements began when the metallicity of the Galaxy reached [Fe/H] = -3. The heavy n-capture elements were formed predominantly by the r-process at metallicities below [Fe/H] = -2.1. Elements from the s-process appear at a metallicity of [Fe/H] = -2.1, when low-mass ...
Ch 13 Death of Stars(4-5?-13)
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
ppt - SLAC
... 1. Black-body temperature sets the star's color and determines its surface brightness: 2. Atmospheric pressure depends on the star's surface gravity and so, roughly, on its size —a giant, dwarf, or in between. The size and surface brightness yield the star's luminosity and often its evolutionary sta ...
... 1. Black-body temperature sets the star's color and determines its surface brightness: 2. Atmospheric pressure depends on the star's surface gravity and so, roughly, on its size —a giant, dwarf, or in between. The size and surface brightness yield the star's luminosity and often its evolutionary sta ...
Ch. 13 Death of Stars(11-16-10)-3
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
Temperate Earth-sized planets transiting a nearby ultracool dwarf star
... (b) and TRAPPIST-1d (c). The best-fit transit models, as derived from a global analysis of the data, are overplotted (red lines). The light curves are shifted along the y axis for the sake of clarity. For the HCT/Hanle faint object spectrograph camera (HFOSC) light curve, the data are unbinned and t ...
... (b) and TRAPPIST-1d (c). The best-fit transit models, as derived from a global analysis of the data, are overplotted (red lines). The light curves are shifted along the y axis for the sake of clarity. For the HCT/Hanle faint object spectrograph camera (HFOSC) light curve, the data are unbinned and t ...
The Dimensions Program - Asnuntuck Community College
... From telescopes, astronomers can find out many things about stars. In addition to the size and distance from the Earth, astronomers can also determine how bright they are, what they are made of, and approximately how much longer they will exist. When they do die out, astronomers can also tell how th ...
... From telescopes, astronomers can find out many things about stars. In addition to the size and distance from the Earth, astronomers can also determine how bright they are, what they are made of, and approximately how much longer they will exist. When they do die out, astronomers can also tell how th ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... The results from actual star counts in various Galactic fields are: i. Bright stars are nearly uniformly distributed between the pole and the plane of the Galaxy, but faint stars are clearly concentrated towards the Galactic plane. ii. Most of the light from the region of the Galactic poles comes f ...
... The results from actual star counts in various Galactic fields are: i. Bright stars are nearly uniformly distributed between the pole and the plane of the Galaxy, but faint stars are clearly concentrated towards the Galactic plane. ii. Most of the light from the region of the Galactic poles comes f ...
June 2010 - Denver Astronomical Society
... ball of Sirius has set in the west but the cool red giant Arcturus, magnitude 0.0, is overhead. The bright spark south of that is mag 1.0 Spica in Virgo, a hot blue star. Check out the color difference in your scope. If you stay up later, Vega will appear in the little constellation Lyra. Vega is an ...
... ball of Sirius has set in the west but the cool red giant Arcturus, magnitude 0.0, is overhead. The bright spark south of that is mag 1.0 Spica in Virgo, a hot blue star. Check out the color difference in your scope. If you stay up later, Vega will appear in the little constellation Lyra. Vega is an ...
Satellities - stoweschools.com
... Bipolar Star System Two stars 8x1010m apart rotate about a point 4x1010 m from each other in a circular path in 12.6 years. The two stars have the same mass. What is the mass of the stars? Fg causes the centripetal acceleration therefore Fg = Fc ...
... Bipolar Star System Two stars 8x1010m apart rotate about a point 4x1010 m from each other in a circular path in 12.6 years. The two stars have the same mass. What is the mass of the stars? Fg causes the centripetal acceleration therefore Fg = Fc ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.