Basic Properties of Stars
... If the Doppler shift of a star’s absorption lines changes with time (redshift, then blueshift, then redshift, etc.), it’s a spectroscopic binary. If one star is much fainter than the other, you may not see its lines. The object is then a singleline spectroscopic binary. If both sets of lines are see ...
... If the Doppler shift of a star’s absorption lines changes with time (redshift, then blueshift, then redshift, etc.), it’s a spectroscopic binary. If one star is much fainter than the other, you may not see its lines. The object is then a singleline spectroscopic binary. If both sets of lines are see ...
Quiz on Chapter 11
... red giant burning helium in its core. b) red supergiant burning helium in its core. c) red supergiant burning helium in a shell around its core. X d) red giant that has just finished fusing helium and no longer has any nuclear fusion occurring in it. 11-15. White dwarfs are not referred to as stars ...
... red giant burning helium in its core. b) red supergiant burning helium in its core. c) red supergiant burning helium in a shell around its core. X d) red giant that has just finished fusing helium and no longer has any nuclear fusion occurring in it. 11-15. White dwarfs are not referred to as stars ...
Planets Beyond the Solar System
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to account for this water. ...
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to account for this water. ...
Second
... • Determine the variables that define a star, e.g., L, P(r), r(r). • Using physics, establish an equal number of equations that relate the variables. Using boundary conditions, these equations can be solved exactly and uniquely. • Observe some of the boundary conditions, e.g. L, R…. and use the eqns ...
... • Determine the variables that define a star, e.g., L, P(r), r(r). • Using physics, establish an equal number of equations that relate the variables. Using boundary conditions, these equations can be solved exactly and uniquely. • Observe some of the boundary conditions, e.g. L, R…. and use the eqns ...
Document
... • That was a mistake because the room was locked but unguarded; this was a perfect opportunity for the gods to discuss their plan against Mt. Olympus. “We need to come up with a plan,” Hephaestus said grimly. • “We need revenge on Mt.Olympus” Hades said, his gray, dark eyes signing no emotion. • The ...
... • That was a mistake because the room was locked but unguarded; this was a perfect opportunity for the gods to discuss their plan against Mt. Olympus. “We need to come up with a plan,” Hephaestus said grimly. • “We need revenge on Mt.Olympus” Hades said, his gray, dark eyes signing no emotion. • The ...
Unit 1 - UW Madison Astronomy Department
... What causes the core of a s tar to contract during the main sequence phase of the star’s life? a. Helium has a larger atomic weight than hydrogen and exerts a stronger gravitational pull on the core. b. Convection in the outer layers carries energy out of the core more efficiently as the star ages c ...
... What causes the core of a s tar to contract during the main sequence phase of the star’s life? a. Helium has a larger atomic weight than hydrogen and exerts a stronger gravitational pull on the core. b. Convection in the outer layers carries energy out of the core more efficiently as the star ages c ...
How Bright is that star?
... The Stefan-Boltzmann Law Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity ...
... The Stefan-Boltzmann Law Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity ...
The fantastic journey of that ring on your finger: From
... example. Clouds of gas and dust condensed to form a star, our Sun, and from the debris, planets formed in a state of liquid rock, with the heaviest elements (like gold) concentrated at their cores. More’s the pity. But if nearly all of the planet’s original gold is in the core, again, where does the ...
... example. Clouds of gas and dust condensed to form a star, our Sun, and from the debris, planets formed in a state of liquid rock, with the heaviest elements (like gold) concentrated at their cores. More’s the pity. But if nearly all of the planet’s original gold is in the core, again, where does the ...
Cluster and Association Members
... are physically related groups of stars held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Therefore, they populate a limited region of space, which is typically much smaller than their distance from the Sun, so that the members are all approximately at the same distance. They are believed to originat ...
... are physically related groups of stars held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Therefore, they populate a limited region of space, which is typically much smaller than their distance from the Sun, so that the members are all approximately at the same distance. They are believed to originat ...
Educator Guide: Starlab (Grades 6-8)
... and its outer layers cool and take on a reddish hue. Red Supergiant – an especially large red giant star. Red supergiant stars can have dimeters greater than 500 times that of the Sun. Betelgeuse in the constellation Orion and Antares in Scorpius are red supergiant stars. Rotation – spinning on a ...
... and its outer layers cool and take on a reddish hue. Red Supergiant – an especially large red giant star. Red supergiant stars can have dimeters greater than 500 times that of the Sun. Betelgeuse in the constellation Orion and Antares in Scorpius are red supergiant stars. Rotation – spinning on a ...
CURRICULUM COMMITTEE COURSE PROPOSAL FORM
... WILL THIS COURSE REQUIRE SPECIAL FACILITIES AND/OR EQUIPMENT? IF YES, PLEASE CONTACT THE VICE PRESIDENT OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS. ...
... WILL THIS COURSE REQUIRE SPECIAL FACILITIES AND/OR EQUIPMENT? IF YES, PLEASE CONTACT THE VICE PRESIDENT OF ACADEMIC AFFAIRS. ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... outlining the form of a lion), Scorpius (a scorpion), and Crux (a cross). The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these ...
... outlining the form of a lion), Scorpius (a scorpion), and Crux (a cross). The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Indeed, the team of 15 astronomers from seven institutions on four continents had picked Tau Ceti specifically because meticulous observations strongly suggested the star had no planetary system. From the earliest days of the hunt for exoplanets almost 20 years ago, astronomers suspected that eviden ...
... Indeed, the team of 15 astronomers from seven institutions on four continents had picked Tau Ceti specifically because meticulous observations strongly suggested the star had no planetary system. From the earliest days of the hunt for exoplanets almost 20 years ago, astronomers suspected that eviden ...
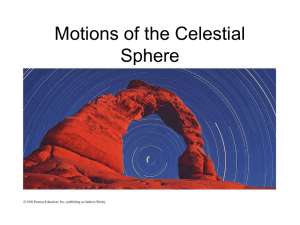
Motions of the Celestial Sphere
... Stars are not a same distances. So, constellations are not real places. ...
... Stars are not a same distances. So, constellations are not real places. ...
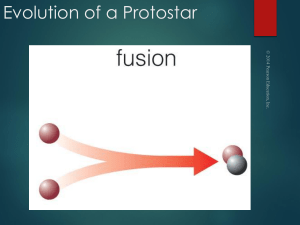
Evolution of a Protostar
... A life track illustrates a star's surface temperature and luminosity at different moments in time. ...
... A life track illustrates a star's surface temperature and luminosity at different moments in time. ...
Practice Questions for Exam 3
... A. The diagram shows main-sequence stars of all the spectral types except O and B, along with a few giants and supergiants. B. The diagram shows no main-sequence stars at all, but it has numerous supergiants and white dwarfs. C. The diagram shows main-sequence stars of spectral types G, K, and M, al ...
... A. The diagram shows main-sequence stars of all the spectral types except O and B, along with a few giants and supergiants. B. The diagram shows no main-sequence stars at all, but it has numerous supergiants and white dwarfs. C. The diagram shows main-sequence stars of spectral types G, K, and M, al ...
2. - Quia
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on your chart? Why or why not? 2. The Voyager spacecraft were equipped with CDs that contain pictures and sounds depicting our world. One of the Voyager spacecraft is actually headed towards Sirius. If there is an inte ...
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on your chart? Why or why not? 2. The Voyager spacecraft were equipped with CDs that contain pictures and sounds depicting our world. One of the Voyager spacecraft is actually headed towards Sirius. If there is an inte ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.