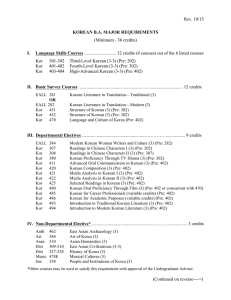
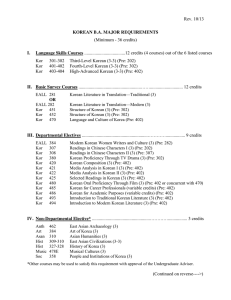
major requirements
... Asian Humanities (3) East Asian Civilizations (3-3) History of Korea (3) Musical Cultures (3) People and Institutions of Korea (3) ...
... Asian Humanities (3) East Asian Civilizations (3-3) History of Korea (3) Musical Cultures (3) People and Institutions of Korea (3) ...
B.A. in Korean Requirements
... Asian Humanities (3) East Asian Civilizations (3-3) History of Korea (3) Musical Cultures (3) People and Institutions of Korea (3) ...
... Asian Humanities (3) East Asian Civilizations (3-3) History of Korea (3) Musical Cultures (3) People and Institutions of Korea (3) ...
Korean Morphology
... ☞ The Korean language is considered to be a highly agglutinative language. Although Korean restricts the order of words in the way English does, its grammar imposes other types of requirements. Korean speakers should place the case markers at the end of noun and pronoun. In English, by contrast, thi ...
... ☞ The Korean language is considered to be a highly agglutinative language. Although Korean restricts the order of words in the way English does, its grammar imposes other types of requirements. Korean speakers should place the case markers at the end of noun and pronoun. In English, by contrast, thi ...
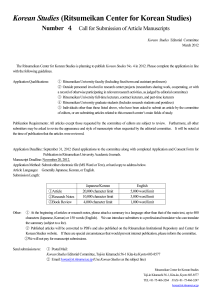
Korean Studies (Ritsumeikan Center for Korean Studies)
... Number 4 Call for Submission of Article Manuscripts Korean Studies Editorial Committee ...
... Number 4 Call for Submission of Article Manuscripts Korean Studies Editorial Committee ...
Required/Recommended Dictionaries for Korean Language Students
... There are also hanja dictionaries made for native Korean speakers, which are much more comprehensive. It is difficult, however, to buy these in the U.S. unless you go through a store that caters to Korean clientele (see below for “Where does one buy these things?”) ...
... There are also hanja dictionaries made for native Korean speakers, which are much more comprehensive. It is difficult, however, to buy these in the U.S. unless you go through a store that caters to Korean clientele (see below for “Where does one buy these things?”) ...
Korean name
A Korean name consists of a family name followed by a given name, as used by the Korean people in both North Korea and South Korea. In the Korean language, ireum or seong-myeong usually refers to the family name (seong) and given name (ireum in a narrow sense) together. Traditional Korean names typically consist of only one syllable. There is no middle name in the English language sense. Many Koreans have their given names made of a generational name syllable and an individually distinct syllable, while this practice is declining in the younger generations. The generational name syllable is shared by siblings in North Korea, and by all members of the same generation of an extended family in South Korea. Married men and women usually keep their full personal names, and children inherit the father's family name.The family names are subdivided into bon-gwan (clans), i.e. extended families which originate in the lineage system used in previous historical periods. Each clan is identified by a specific place, and traces its origin to a common patrilineal ancestor.Early names based on the Korean language were recorded in the Three Kingdoms period (57 BCE – 668 CE), but with the growing adoption of the Chinese writing system, these were gradually replaced by names based on Chinese characters (hanja). During periods of Mongol influence, the ruling class supplemented their Korean names with Mongolian names. Because of the many changes in Korean romanization practices over the years, modern Koreans, when using languages written in Latin script, romanize their names in various ways, most often approximating the pronunciation in English orthography. Some keep the original order of names, while others reverse the names to match the usual Western pattern.