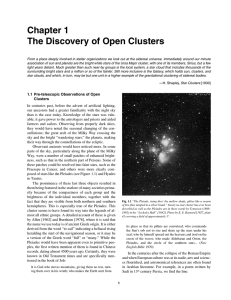
When we look at a neighboring galaxy (such as M31, the
... star could be a dwarf like our own sun, located maybe 3,000 parcsecs (10,000 light years) away in our own galaxy, or it could be a massive yellow supergiant 65,000 times more luminous, and located in the Andromeda Galaxy, at a distance of 760,000 parsecs (2.5 million light-years). Either would have ...
... star could be a dwarf like our own sun, located maybe 3,000 parcsecs (10,000 light years) away in our own galaxy, or it could be a massive yellow supergiant 65,000 times more luminous, and located in the Andromeda Galaxy, at a distance of 760,000 parsecs (2.5 million light-years). Either would have ...
Using color photometry to separate transiting exoplanets from false
... the degree to which they match reality is poorly known. It is an observational challenge to measure limb-darkening, especially for solar-type (and later) stars. The limb darkening for only one such star (besides the Sun) has been observed, from a high-magnification microlensing event (Abe et al. 200 ...
... the degree to which they match reality is poorly known. It is an observational challenge to measure limb-darkening, especially for solar-type (and later) stars. The limb darkening for only one such star (besides the Sun) has been observed, from a high-magnification microlensing event (Abe et al. 200 ...
Additional Cosmology Images
... within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus. Located at a distance of 2,450 light-years, the globule is a condensation of dense gas that is barely surviving the strong ionizing radiation from a nearby massive star. The globule is being compressed by the surrounding ionized gas ...
... within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus. Located at a distance of 2,450 light-years, the globule is a condensation of dense gas that is barely surviving the strong ionizing radiation from a nearby massive star. The globule is being compressed by the surrounding ionized gas ...
The Sun and Stars 4.1 Energy formation and layers of the Sun 4.2
... from Sol to reach the Earth. Stars are made primarily of hydrogen and helium with trace amounts of other elements. The gravity and heat of the sun cause all of those atoms to be very hot, so hot they are continuously in the plasma phase. Atoms in the plasma are also known as ions and they behave dif ...
... from Sol to reach the Earth. Stars are made primarily of hydrogen and helium with trace amounts of other elements. The gravity and heat of the sun cause all of those atoms to be very hot, so hot they are continuously in the plasma phase. Atoms in the plasma are also known as ions and they behave dif ...
D ASTROPHYSICS
... gives the distance d in parsecs when p is the parallax angle in arcsecond. This simple relationship is used for defining the parsec: when a star is at a distance of 1 pc from the Earth the parallax angle given by the equation will be one arcsecond. In a circle there are 360 degrees. In every degree ...
... gives the distance d in parsecs when p is the parallax angle in arcsecond. This simple relationship is used for defining the parsec: when a star is at a distance of 1 pc from the Earth the parallax angle given by the equation will be one arcsecond. In a circle there are 360 degrees. In every degree ...
structure and evolution of white dwarfs and their
... with masses below about eight times that of the Sun will pass through one or more red giant phases before losing most of their original mass to form a planetary nebula. The remnant object, a white dwarf, is the core of the progenitor star. In the absence of any internal source of energy, the tempera ...
... with masses below about eight times that of the Sun will pass through one or more red giant phases before losing most of their original mass to form a planetary nebula. The remnant object, a white dwarf, is the core of the progenitor star. In the absence of any internal source of energy, the tempera ...
Age Aspects of Habitability
... sufficiently to change its environment on a planetary scale, for instance, through the production of an oxygen atmosphere by photosynthetic organisms. Photosynthesis is currently the only geologically documented biogenic process (see e.g. Lyons and Reinhard, 2011; Fomina and Biel, 2014 and reference ...
... sufficiently to change its environment on a planetary scale, for instance, through the production of an oxygen atmosphere by photosynthetic organisms. Photosynthesis is currently the only geologically documented biogenic process (see e.g. Lyons and Reinhard, 2011; Fomina and Biel, 2014 and reference ...
“White Hot” Star Lab
... 3) Put a small piece of tape on the table blow the hole. Use a pen to make a mark on the tape directly below the hole. This mark represents the position of the telescope when Earth is on one side of its orbit. 4) Take the piece of paper labeled STAR 1 and place it inside the box with two paper clips ...
... 3) Put a small piece of tape on the table blow the hole. Use a pen to make a mark on the tape directly below the hole. This mark represents the position of the telescope when Earth is on one side of its orbit. 4) Take the piece of paper labeled STAR 1 and place it inside the box with two paper clips ...
The physics of white dwarfs
... knowledge of the white dwarfs. In the past two decades, other large telescopes have been constructed in various parts of the world, and several other groups have also begun white-dwarf observations. As a result, detailed spectroscopic information has now been acquired for more than 400 of these star ...
... knowledge of the white dwarfs. In the past two decades, other large telescopes have been constructed in various parts of the world, and several other groups have also begun white-dwarf observations. As a result, detailed spectroscopic information has now been acquired for more than 400 of these star ...
Chapter15- Our Galaxy-pptx - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... The Milky Way Galaxy appears in our sky as a faint band of light. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy appears in our sky as a faint band of light. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
AR2013 - Vatican Observatory
... star systems. Solar Studies: One way the VATT can contribute to studies of our own Sun is by continued spectroscopic and photometric monitoring of activity in solar analogues. A decade of such monitoring, added to the existing data from several years, will allow analysis of such activity over a peri ...
... star systems. Solar Studies: One way the VATT can contribute to studies of our own Sun is by continued spectroscopic and photometric monitoring of activity in solar analogues. A decade of such monitoring, added to the existing data from several years, will allow analysis of such activity over a peri ...
Isaac Newton
... experiment on the objects they study. Space probes sent to other worlds have changed this a little, but stars and galaxies are so far away that, for the most ...
... experiment on the objects they study. Space probes sent to other worlds have changed this a little, but stars and galaxies are so far away that, for the most ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... shown the importance of dust absorption and scattering, and Rayleigh scattering in the determination of the true size of the Galaxy • distances to object in the Galaxy • mapping distances to other galaxies • determination of the total light, hence luminous matter • apart from being the ingredient in ...
... shown the importance of dust absorption and scattering, and Rayleigh scattering in the determination of the true size of the Galaxy • distances to object in the Galaxy • mapping distances to other galaxies • determination of the total light, hence luminous matter • apart from being the ingredient in ...
Accuracy of spectroscopy-based radioactive dating of stars
... usually provides rather precise absolute ages (e.g. Vandenberg et al. 1996). However, for stellar clusters (especially globular clusters), radioactive dating could produce an age estimate of comparable or even higher precision if applied to a large enough sample of stars, and would as such be very v ...
... usually provides rather precise absolute ages (e.g. Vandenberg et al. 1996). However, for stellar clusters (especially globular clusters), radioactive dating could produce an age estimate of comparable or even higher precision if applied to a large enough sample of stars, and would as such be very v ...
Summer 2004 ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Professor: ER Capriotti Sample Questions
... 35. The astronomer Tycho Brahe was known for his, A. measurement of the Earth's rotation. B. use of the telescope. C. accurate observations of planet positions. D. observation of the Moon's features. E. theory of epicycles. 36. The discovery that planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at th ...
... 35. The astronomer Tycho Brahe was known for his, A. measurement of the Earth's rotation. B. use of the telescope. C. accurate observations of planet positions. D. observation of the Moon's features. E. theory of epicycles. 36. The discovery that planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at th ...
A STEP - Observatoire de la Côte d`Azur
... not undergo temporal correlation and detection limit with “red noise” (linked to systematic effects - green line) – The pink to red part of the diagram shows the density of Hot Jupiter planets at given transit depth and target star magnitude. These effects, combined with the unfavorable window funct ...
... not undergo temporal correlation and detection limit with “red noise” (linked to systematic effects - green line) – The pink to red part of the diagram shows the density of Hot Jupiter planets at given transit depth and target star magnitude. These effects, combined with the unfavorable window funct ...
Week 1
... One hour of right ascension is 15 degrees of celestial longitude (not 15 angular degrees, except at the equator) The sky rotates by at 15 arcseconds per second at the Equator Since lines of RA converge toward the pole – 1 minute of RA spans a different angle depending on Declination – a factor of co ...
... One hour of right ascension is 15 degrees of celestial longitude (not 15 angular degrees, except at the equator) The sky rotates by at 15 arcseconds per second at the Equator Since lines of RA converge toward the pole – 1 minute of RA spans a different angle depending on Declination – a factor of co ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.