Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
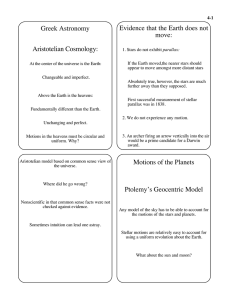
... 14. Why would using a cluster of stars in which all the stars are the same distance to plot on an HR diagram be very useful? a) The stars would then all be the same brightness b) The stars would then all be the same color c) Stars with different apparent magnitudes have different absolute magnitudes ...
... 14. Why would using a cluster of stars in which all the stars are the same distance to plot on an HR diagram be very useful? a) The stars would then all be the same brightness b) The stars would then all be the same color c) Stars with different apparent magnitudes have different absolute magnitudes ...
Detectability of Earth-like Planets by Direct Imaging - RIT
... • By calculating the integration time to reach SNR = 5, we find that the total integration time to image each HZ once is ~200 days. • In less than 5 years each HZ could be searched 5 times to SNR = 5. ...
... • By calculating the integration time to reach SNR = 5, we find that the total integration time to image each HZ once is ~200 days. • In less than 5 years each HZ could be searched 5 times to SNR = 5. ...
Section 1
... nuclear fuel powering the star is consumed. Hence the studies of stellar structure and of stellar evolution are inextricably linked. ...
... nuclear fuel powering the star is consumed. Hence the studies of stellar structure and of stellar evolution are inextricably linked. ...
PHYS 390 Lectures 1/2 - The Big Picture 1/2
... Knowing the radius of the Earth’s orbit Res, distances to nearby stars can be found through parallax, the apparent motion of nearby stars caused by the motion of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extr ...
... Knowing the radius of the Earth’s orbit Res, distances to nearby stars can be found through parallax, the apparent motion of nearby stars caused by the motion of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extr ...
Powerpoint for today
... stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. Why "H II Region? H I: Hydrogen atom H II: Ionized Hyd ...
... stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV photons. Why "H II Region? H I: Hydrogen atom H II: Ionized Hyd ...
Picture: Alnitak is the left-hand star in Orion`s Belt. Image: NASA
... carbon/oxygen ratios that are typically four to five times higher than those of normal red giants and show little trace of the light metal oxide bands that are the usual red giant hallmark. They resemble S stars in their relative proportion of heavy and light metals, but contain far more carbon in t ...
... carbon/oxygen ratios that are typically four to five times higher than those of normal red giants and show little trace of the light metal oxide bands that are the usual red giant hallmark. They resemble S stars in their relative proportion of heavy and light metals, but contain far more carbon in t ...
Physical Science Laboratory: Skyglobe
... The plane of the Earth’s orbit about the Sun, which is approximately the plane of the solar system as a whole. The apparent path of the Sun throughout a year. ...
... The plane of the Earth’s orbit about the Sun, which is approximately the plane of the solar system as a whole. The apparent path of the Sun throughout a year. ...
Consulting the Planetary Expert: You
... change their position quite quickly relative to stars. Outer planets (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) also display retrograde motion. Planets move eastward in the night sky but once a year for a month or two they move westward. This “reversal” is called retrograde motion. Try the Retrograde ...
... change their position quite quickly relative to stars. Outer planets (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) also display retrograde motion. Planets move eastward in the night sky but once a year for a month or two they move westward. This “reversal” is called retrograde motion. Try the Retrograde ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by their D ...
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by their D ...
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
Progress of LiJET and Transit Search with Lijiang 2.4m Telescope
... To determine planet parameters for planet candidates being ‘significantly’ detected in the MARVELS but not well determined orbit parameter ...
... To determine planet parameters for planet candidates being ‘significantly’ detected in the MARVELS but not well determined orbit parameter ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • She proposed that most stars were made up of Hydrogen and Helium • Her 1925 PhD Harvard thesis on these topics was voted best Astronomy thesis of the 20th century ...
... • She proposed that most stars were made up of Hydrogen and Helium • Her 1925 PhD Harvard thesis on these topics was voted best Astronomy thesis of the 20th century ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
Galactic Structure
... either managed to retain significant gas after onset of star formation, or the gas went out, but came back in. Gas-free now – why? Ram pressure stripping? Low mean stellar metallicity, typically less than a tenth solar, combined with invariant IMF, means gas removal from star formation, not by s ...
... either managed to retain significant gas after onset of star formation, or the gas went out, but came back in. Gas-free now – why? Ram pressure stripping? Low mean stellar metallicity, typically less than a tenth solar, combined with invariant IMF, means gas removal from star formation, not by s ...
Space Exploration Review Notes
... period (year), etc. Generally, data tables compare other planets to Earth so Earth is often given the value of “1” for such things as distance from the sun (1 AU), period of rotation (1 day), mass (1) and gravity (1). For example, if a planet’s mass is “4”, it is 4 times greater than Earth whose mas ...
... period (year), etc. Generally, data tables compare other planets to Earth so Earth is often given the value of “1” for such things as distance from the sun (1 AU), period of rotation (1 day), mass (1) and gravity (1). For example, if a planet’s mass is “4”, it is 4 times greater than Earth whose mas ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.