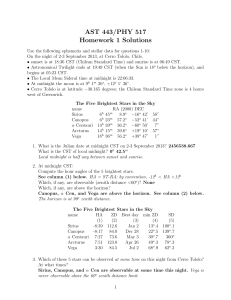
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Evolution of low
... Evolution of 4Mo Stars • For stars less than 6Mo these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. • For stars that start with 4Mo, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to ...
... Evolution of 4Mo Stars • For stars less than 6Mo these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. • For stars that start with 4Mo, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to ...
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect—28 Oct Outline • Announcements
... – Separation of two wavelengths grows larger, then smaller. ...
... – Separation of two wavelengths grows larger, then smaller. ...
Luminosity
... It would be only 1/3 as bright. It would be only 1/6 as bright. It would be only 1/9 as bright. It would be three times as bright. ...
... It would be only 1/3 as bright. It would be only 1/6 as bright. It would be only 1/9 as bright. It would be three times as bright. ...
cocoon - Adams State University
... Radio image of CO emission – it is too cold for molecular H to emit ...
... Radio image of CO emission – it is too cold for molecular H to emit ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... the associated luminosity is determined. The luminosity is then either used directly or converted to absolute magnitude and used with the apparent magnitude in the distance modulus equation to calculate cosmological distances within the Milky Way Galaxy and to other galaxies. Long Period Variables ( ...
... the associated luminosity is determined. The luminosity is then either used directly or converted to absolute magnitude and used with the apparent magnitude in the distance modulus equation to calculate cosmological distances within the Milky Way Galaxy and to other galaxies. Long Period Variables ( ...
Star Formation
... Open Clusters & Associations Open Cluster: Group of ~hundreds youngish stars formed at same time from same molecular cloud - Association-tens of young stars not gravitationally bound together ...
... Open Clusters & Associations Open Cluster: Group of ~hundreds youngish stars formed at same time from same molecular cloud - Association-tens of young stars not gravitationally bound together ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to
... which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the size of a black hole in the core of the star might als ...
... which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the size of a black hole in the core of the star might als ...
Light-years
... Remain in position over one spot Are farther away from Earth’s surface Do not revolve around the Earth Are only a few hundred kilometers high ...
... Remain in position over one spot Are farther away from Earth’s surface Do not revolve around the Earth Are only a few hundred kilometers high ...
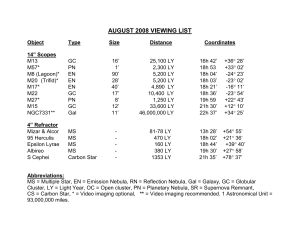
August
... reveals the outer gaseous regions that complete the spherical structure of the ejected gas bubble. The age is uncertain, with estimates ranging from 3,000 to 48,000 years. (Use an Olll filter for optimum eyepiece viewing) M15 in the constellation Pegasus (PEG-uh-sus) is among the more conspicuous of ...
... reveals the outer gaseous regions that complete the spherical structure of the ejected gas bubble. The age is uncertain, with estimates ranging from 3,000 to 48,000 years. (Use an Olll filter for optimum eyepiece viewing) M15 in the constellation Pegasus (PEG-uh-sus) is among the more conspicuous of ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to various
... which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the size of a black hole in the core of the star might als ...
... which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the size of a black hole in the core of the star might als ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... Orbital paths of inner planets and sun. Time Animation. Black, white, and red star chart colors for normal, bright, and night viewing conditions, respectively. Chart can be rotated to any of the 16 compass points and also flipped along the North - South axis. Chart can be "live, realtime", or static ...
... Orbital paths of inner planets and sun. Time Animation. Black, white, and red star chart colors for normal, bright, and night viewing conditions, respectively. Chart can be rotated to any of the 16 compass points and also flipped along the North - South axis. Chart can be "live, realtime", or static ...
Early Spring Observing – Millstone News Night Sky
... Note: Globular clusters are distributed in a halo around our galaxy: Globular clusters are normally associated with a host galaxy and most galaxies, including the Milky Way, are surrounded and penetrated by a globular cluster system - courtesy http://relativity. livingreviews.org/Articles/lrr-2013-4 ...
... Note: Globular clusters are distributed in a halo around our galaxy: Globular clusters are normally associated with a host galaxy and most galaxies, including the Milky Way, are surrounded and penetrated by a globular cluster system - courtesy http://relativity. livingreviews.org/Articles/lrr-2013-4 ...
New light on our Sun`s fate - Space Telescope Science Institute
... that a star’s mass controls its life; along the way, that property also determines its brightness and temperature. We now summarize all stages of stellar evolution on this important diagram. Today, astronomers use powerful telescopes, on the ground and in space, to measure stars’ brightnesses, color ...
... that a star’s mass controls its life; along the way, that property also determines its brightness and temperature. We now summarize all stages of stellar evolution on this important diagram. Today, astronomers use powerful telescopes, on the ground and in space, to measure stars’ brightnesses, color ...
Activity 1 - Mathematical and Scientific Methods
... causes their evolution to be so different from the Sun. Masses have more mass and therefore more gravity pushing down on the core. Luminosity is greater, lifetime is shorter. Core doesn’t go degenerate because next fusion cycle sets in when pressures and temperatures reach high ...
... causes their evolution to be so different from the Sun. Masses have more mass and therefore more gravity pushing down on the core. Luminosity is greater, lifetime is shorter. Core doesn’t go degenerate because next fusion cycle sets in when pressures and temperatures reach high ...
Stellar and Gas Kinematics in the Core and Bar Regions of M100
... The stellar and gas kinematics of the bar and starbursting circumnuclear region in the barred spiral galaxy M100 have been measured and are presented here as two-dimensional maps. The data have been obtained using the SAURON integral field spectrograph on the William Herschel Telescope. In this prog ...
... The stellar and gas kinematics of the bar and starbursting circumnuclear region in the barred spiral galaxy M100 have been measured and are presented here as two-dimensional maps. The data have been obtained using the SAURON integral field spectrograph on the William Herschel Telescope. In this prog ...
Extreme Tidal Waves in Binary Star Systems
... compact binary systems. The first is through the force of friction created as the stars are stretched back and forth, as described above. The second way that tides can affect stars is by exciting large scale waves that move within the stars. These waves are periodic global deformations of the star, ...
... compact binary systems. The first is through the force of friction created as the stars are stretched back and forth, as described above. The second way that tides can affect stars is by exciting large scale waves that move within the stars. These waves are periodic global deformations of the star, ...
ParalStellarDist.V2doc
... where the units of r and s are in meters and is in degrees. 2. Using a distant reference point such as a feature on the McDowell Mountains, measure the angle between your partner and the reference point from two different positions as shown below: angle a ...
... where the units of r and s are in meters and is in degrees. 2. Using a distant reference point such as a feature on the McDowell Mountains, measure the angle between your partner and the reference point from two different positions as shown below: angle a ...
$doc.title
... Use Star Walk or your team’s own naked-‐eye observations to check the accuracy of your finding chart. If your chart does not correctly show the position of the planet, explain what went wrong: ...
... Use Star Walk or your team’s own naked-‐eye observations to check the accuracy of your finding chart. If your chart does not correctly show the position of the planet, explain what went wrong: ...
Sample Answer Sheet for The 10 Tourist Wonders of the
... up into a huge star, cooler than it used to be, called a red giant. Our own Sun is expected to become such a red giant in about 5 to 6 billion years. Betelgeuse is a well-known and much studied example of a red giant and the first star beyond the Sun for which astronomers actually got an image which ...
... up into a huge star, cooler than it used to be, called a red giant. Our own Sun is expected to become such a red giant in about 5 to 6 billion years. Betelgeuse is a well-known and much studied example of a red giant and the first star beyond the Sun for which astronomers actually got an image which ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.