The Year and The Seasons
... were tipped at 35 degrees, instead of 23.5 degrees? • How about if it were not tipped? ...
... were tipped at 35 degrees, instead of 23.5 degrees? • How about if it were not tipped? ...
Game Guide / Chronopticon
... • Like the sun, any given star or constellation seems to move in an arc across the sky over the course of hours • Different constellations are visible during different times of year (or different seasons) • You can calculate elapsed time (hours) based on the apparent motion of constellations during ...
... • Like the sun, any given star or constellation seems to move in an arc across the sky over the course of hours • Different constellations are visible during different times of year (or different seasons) • You can calculate elapsed time (hours) based on the apparent motion of constellations during ...
Answers - Physics@Brock
... 12. The universe is believed to have an age of about (a) 14 thousand years. (b) 14 million years. (c) * 14 billion years. (d) 14 trillion years. 13. The planets change their positions relative to the stars because (a) of the rotation of the Earth. (b) of the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. (c) of t ...
... 12. The universe is believed to have an age of about (a) 14 thousand years. (b) 14 million years. (c) * 14 billion years. (d) 14 trillion years. 13. The planets change their positions relative to the stars because (a) of the rotation of the Earth. (b) of the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. (c) of t ...
Answer - Physics@Brock
... 12. The universe is believed to have an age of about (a) 14 thousand years. (b) 14 million years. (c) 14 billion years. (d) 14 trillion years. 13. The planets change their positions relative to the stars because (a) of the rotation of the Earth. (b) of the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. (c) of the ...
... 12. The universe is believed to have an age of about (a) 14 thousand years. (b) 14 million years. (c) 14 billion years. (d) 14 trillion years. 13. The planets change their positions relative to the stars because (a) of the rotation of the Earth. (b) of the Sun’s motion along the ecliptic. (c) of the ...
May 8, 2012 - Plummer Pumas Science
... The Sun’s temperature was much cooler and it was much smaller. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
... The Sun’s temperature was much cooler and it was much smaller. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
Solar system topics
... direction (counterclockwise as you view the solar system from the direction that allows you to see the Earth's north pole). The orbital inclinations of the other planets are very small compared to the plane of the Earth's orbit. This is why the planets are found at most a couple degrees north or sou ...
... direction (counterclockwise as you view the solar system from the direction that allows you to see the Earth's north pole). The orbital inclinations of the other planets are very small compared to the plane of the Earth's orbit. This is why the planets are found at most a couple degrees north or sou ...
Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects
... make across the sky. The “actual motion” may be different. ...
... make across the sky. The “actual motion” may be different. ...
The Inner Planets
... and 8 months to rotate once on its axis, a day on Venus is longer than its year. Venus also rotates east to west, the only planet to do so. This retrograde rotation (backward) was probably caused by Venus being struck by a large object early in its history. ...
... and 8 months to rotate once on its axis, a day on Venus is longer than its year. Venus also rotates east to west, the only planet to do so. This retrograde rotation (backward) was probably caused by Venus being struck by a large object early in its history. ...
IMPORTANT HISTORICAL DATES AND EVENTS
... Closest to the sun are the four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The inner planets are compact and rocky with just three moons between them. They are called terrestrial planets because they are more or less earth-like. All of them have secondary atmospheres (produced after their format ...
... Closest to the sun are the four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The inner planets are compact and rocky with just three moons between them. They are called terrestrial planets because they are more or less earth-like. All of them have secondary atmospheres (produced after their format ...
DaysSeasnsYears
... • “The time it takes for the Earth (or any planet/moon) to make one complete rotation.” • 24 hours • Part of each 24-hour day is lighted (daytime), part is dark (night). • The length of daytime and nighttime varies depending on how the Earth is tilted. ...
... • “The time it takes for the Earth (or any planet/moon) to make one complete rotation.” • 24 hours • Part of each 24-hour day is lighted (daytime), part is dark (night). • The length of daytime and nighttime varies depending on how the Earth is tilted. ...
venus_transit - University of Glasgow
... “Happy is our Century, to which has been reserved the glory of being witness to an event which will render it memorable in the annals of the Sciences!” ...
... “Happy is our Century, to which has been reserved the glory of being witness to an event which will render it memorable in the annals of the Sciences!” ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The Earth experiences seasons because it is tilted on its axis. At summer solstice, the Earth is tilted towards the Sun, causing solar rays to fall on the Earth’s atmosphere more directly. At this time of year, the Sun remains longer in the sky. These two factors cause the temperature of the atmosph ...
... The Earth experiences seasons because it is tilted on its axis. At summer solstice, the Earth is tilted towards the Sun, causing solar rays to fall on the Earth’s atmosphere more directly. At this time of year, the Sun remains longer in the sky. These two factors cause the temperature of the atmosph ...
ch16 b - Manasquan Public Schools
... give Earth perfect conditions to support life as we know it. ...
... give Earth perfect conditions to support life as we know it. ...
SCI 103
... B) Only the planets whose orbits are larger in size than that of the Earth exhibit retrograde motion C) The planets orbit roughly in the ecliptic plane. D) Only planets whose orbits are smaller in size than that of the Earth exhibit a new phase for observers on or near the Earth. E) The planets rise ...
... B) Only the planets whose orbits are larger in size than that of the Earth exhibit retrograde motion C) The planets orbit roughly in the ecliptic plane. D) Only planets whose orbits are smaller in size than that of the Earth exhibit a new phase for observers on or near the Earth. E) The planets rise ...
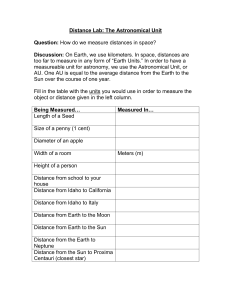
Galaxy and Beyond
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
Key 3 - UNLV Physics
... (c) looking at the change in velocity of a star from its spectra (d) looking at locations near stars for planets 36. Which of the following describes the Transit Method of detecting planets? (a) looking for reduced light as a planet passes between us and the star. (b) looking for the change in posit ...
... (c) looking at the change in velocity of a star from its spectra (d) looking at locations near stars for planets 36. Which of the following describes the Transit Method of detecting planets? (a) looking for reduced light as a planet passes between us and the star. (b) looking for the change in posit ...
Physics Problems
... 2. The crankshaft in an idling automobile engine turns at 1500 revolutions per minute. What is the frequency in hertz and the period in seconds? 3. What is the tangential speed (in km/s) of the earth as it orbits the sun? The earth is 151 million kilometers from the sun. Hint: how much time does it ...
... 2. The crankshaft in an idling automobile engine turns at 1500 revolutions per minute. What is the frequency in hertz and the period in seconds? 3. What is the tangential speed (in km/s) of the earth as it orbits the sun? The earth is 151 million kilometers from the sun. Hint: how much time does it ...
lecture 2
... Lunar eclipses occur at FULL Moon PHASE Lunar eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon’s orbital plane is tilted with respect to the ecliptic – a total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon crosses the ecliptic at full Moon – since the Earth’s shadow is much bigger than the Moon, total lunar ...
... Lunar eclipses occur at FULL Moon PHASE Lunar eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon’s orbital plane is tilted with respect to the ecliptic – a total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon crosses the ecliptic at full Moon – since the Earth’s shadow is much bigger than the Moon, total lunar ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... opposition on August 27th when it will be closer to the Earth than it has been in 50,000 years. Such a close approach will make for great viewing if the weather cooperates. Tonight it rises around 10:00pm and will appear as a magnitude -2.5 object in the constellation of Aquarius. If you’ve never se ...
... opposition on August 27th when it will be closer to the Earth than it has been in 50,000 years. Such a close approach will make for great viewing if the weather cooperates. Tonight it rises around 10:00pm and will appear as a magnitude -2.5 object in the constellation of Aquarius. If you’ve never se ...
Star - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... Celestial bodies- All objects seen in the sky (the sun, Moon, stars and planets) Constellations- Groupings of stars that form patterns, which appear like objects and are given names (such as Orion, the hunter)there are 88 constellations and many are explained in Greek Mythology. (ex. Ursa Major) Ast ...
... Celestial bodies- All objects seen in the sky (the sun, Moon, stars and planets) Constellations- Groupings of stars that form patterns, which appear like objects and are given names (such as Orion, the hunter)there are 88 constellations and many are explained in Greek Mythology. (ex. Ursa Major) Ast ...
Seasons and the Tilted Earth Name TEK 8.7A Date Period _____
... This is how it works. Remember that the Earth is tilted all the time that it is moving around the Sun. The Earth moves around the Sun once every year. It follows an elliptical orbit. This means that it goes almost in a circle around the sun, but gets a little further away at some times. The path it ...
... This is how it works. Remember that the Earth is tilted all the time that it is moving around the Sun. The Earth moves around the Sun once every year. It follows an elliptical orbit. This means that it goes almost in a circle around the sun, but gets a little further away at some times. The path it ...
43 Astronomy 43.1 Recall that Earth is one of the many planets in
... o Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, (Pluto ...
... o Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, (Pluto ...
The Sky and its Motions
... Venus appears at most ~ 460 from the sun. It can occasionally be seen for at most a few hours after sunset in the west or before sunrise in the east. ...
... Venus appears at most ~ 460 from the sun. It can occasionally be seen for at most a few hours after sunset in the west or before sunrise in the east. ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.