Test 3, February 7, 2007 - Brock physics
... 42. In order to detect a black hole one looks for (a) a spot into which stars and their planets fall. (b) a binary system where a companion star is not visible but has a mass greater than 3 solar masses and is an intense X-ray source. (c) intense source of visible light. (d) the accompanying white h ...
... 42. In order to detect a black hole one looks for (a) a spot into which stars and their planets fall. (b) a binary system where a companion star is not visible but has a mass greater than 3 solar masses and is an intense X-ray source. (c) intense source of visible light. (d) the accompanying white h ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... outside layers also collapse layers closer to the center collapse faster than those near the surface. As the layers collapses, the gas compresses and ...
... outside layers also collapse layers closer to the center collapse faster than those near the surface. As the layers collapses, the gas compresses and ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... This question is about some of the properties of Barnard’s star. Barnard’s star, in the constellation Ophiuchus, has a parallax angle of 0.549 arc-second as measured from Earth. (a) ...
... This question is about some of the properties of Barnard’s star. Barnard’s star, in the constellation Ophiuchus, has a parallax angle of 0.549 arc-second as measured from Earth. (a) ...
Name - CLC Charter School
... exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. ...
... exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. ...
Constellation
... named after heroes and beasts from stories and after everyday objects. You probably know some constellations. The Big Dipper looks like a giant pot with a long handle. Orion is named after a hunter in Greek mythology. You can see his belt, marked by three bright stars, and his sword, which hangs fro ...
... named after heroes and beasts from stories and after everyday objects. You probably know some constellations. The Big Dipper looks like a giant pot with a long handle. Orion is named after a hunter in Greek mythology. You can see his belt, marked by three bright stars, and his sword, which hangs fro ...
Project 2. CCD Photometry
... Rather than just have one apparent magnitude, measured across the entire visible spectrum we can use a filter to restrict the incoming light to a narrow waveband. If, for instance, we use a filter that only allows light in the blue part of the spectrum, we can measure a star's blue ...
... Rather than just have one apparent magnitude, measured across the entire visible spectrum we can use a filter to restrict the incoming light to a narrow waveband. If, for instance, we use a filter that only allows light in the blue part of the spectrum, we can measure a star's blue ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... Auto reduces screen clutter by automatically adjusting the number of stars displayed appropriate to the zoom setting. Otherwise, the number of stars displayed depends on the magnitude selected: Magnitude Number of Stars ...
... Auto reduces screen clutter by automatically adjusting the number of stars displayed appropriate to the zoom setting. Otherwise, the number of stars displayed depends on the magnitude selected: Magnitude Number of Stars ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... On the display of the night sky, note that you can see the horizon and the cardinal (compass) directions. On the 2nd row of icons, the 4th icon from the left is “Horizon Grid”; click it and see the red grid lines of alt/azimuth. A nifty feature of The Sky is, unlike me, its encyclopedic knowledge of ...
... On the display of the night sky, note that you can see the horizon and the cardinal (compass) directions. On the 2nd row of icons, the 4th icon from the left is “Horizon Grid”; click it and see the red grid lines of alt/azimuth. A nifty feature of The Sky is, unlike me, its encyclopedic knowledge of ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Letter to the Editor Low
... our statistical subtraction is mainly limited by three factors: first, ...
... our statistical subtraction is mainly limited by three factors: first, ...
January 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... Betelgeuse appears to be edging towards the end of its life. In fact it is the closest star to us that might explode as a super nova at any time in the near future (astronomically speaking). It could explode and destroy itself sometime in the next million years (maybe as soon as tomorrow). For all w ...
... Betelgeuse appears to be edging towards the end of its life. In fact it is the closest star to us that might explode as a super nova at any time in the near future (astronomically speaking). It could explode and destroy itself sometime in the next million years (maybe as soon as tomorrow). For all w ...
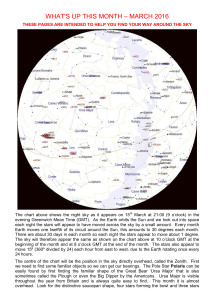
what`s up this month – march 2016
... This is due to the movement of Earth along its orbital path around the Sun. The Sun takes 1 year to complete its orbit around the Sun therefore it will move 1/12th of its orbit every month. Put another way it will have moved 360º 12 = 30º each month. This is to say, in another way, it moves about ...
... This is due to the movement of Earth along its orbital path around the Sun. The Sun takes 1 year to complete its orbit around the Sun therefore it will move 1/12th of its orbit every month. Put another way it will have moved 360º 12 = 30º each month. This is to say, in another way, it moves about ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
Astrophysics notes
... define the term ‘sensitivity’ of a telescope as the light-gathering power of the telescope (directly proportional to the square of the diameter of the objective) define the term parallax as the apparent shift in position of a close object against a distant background due to a change in position of t ...
... define the term ‘sensitivity’ of a telescope as the light-gathering power of the telescope (directly proportional to the square of the diameter of the objective) define the term parallax as the apparent shift in position of a close object against a distant background due to a change in position of t ...
Astronomy - Dalriada at dalriada.org.uk
... Moon, which were clearly not fixed to any celestial sphere - namely Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the planets, named from the Greek word for wanderer because they seem to wander among the stars. They are very difficult to explain on a geocentric basis, although Ptolemy tried ha ...
... Moon, which were clearly not fixed to any celestial sphere - namely Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the planets, named from the Greek word for wanderer because they seem to wander among the stars. They are very difficult to explain on a geocentric basis, although Ptolemy tried ha ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.