Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
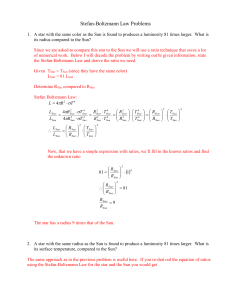
... This question is the most involved of th3ese practice problems because you are not given enough information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio o ...
... This question is the most involved of th3ese practice problems because you are not given enough information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio o ...
star
... The orbits are drawn to scale, but the sizes of the stars are exaggerated Sirius A is considerably larger than the Sun, while Sirius B is about the size of the Earth 28 July 2005 ...
... The orbits are drawn to scale, but the sizes of the stars are exaggerated Sirius A is considerably larger than the Sun, while Sirius B is about the size of the Earth 28 July 2005 ...
transparencies
... • The frequency of the bursts activity will decrease from a few emissions per 10 years to a few emissions per 100 years • The amplitude should decrease, because the angular velocity is reduced • Both feautures reflect the progressive draining of the energy source wich, in this model, is the Rotation ...
... • The frequency of the bursts activity will decrease from a few emissions per 10 years to a few emissions per 100 years • The amplitude should decrease, because the angular velocity is reduced • Both feautures reflect the progressive draining of the energy source wich, in this model, is the Rotation ...
Surveying the Stars
... stars are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
... stars are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... The flux of a star is the power in the light from that star that would hit a 1 m2 area facing the star. To measure a star’s flux, we use a telescope to collect light from the star, measure the power in the light we collect, and the divide the power by the collecting area of the telescope. (A bigger ...
... The flux of a star is the power in the light from that star that would hit a 1 m2 area facing the star. To measure a star’s flux, we use a telescope to collect light from the star, measure the power in the light we collect, and the divide the power by the collecting area of the telescope. (A bigger ...
Red Giants - Faculty Web Pages
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
Distances of the Stars
... Q. How can we tell that some stars are relatively close to us? A) They appear to move back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth’s motion around the Sun. B) They appear to be very bright, so must be close. C) They are occasionally eclipsed by our moon, so they must be close. D ...
... Q. How can we tell that some stars are relatively close to us? A) They appear to move back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth’s motion around the Sun. B) They appear to be very bright, so must be close. C) They are occasionally eclipsed by our moon, so they must be close. D ...
How Close is our Nearest Neighbor
... law so that their luminosities could be determined by measuring their periods of variation. These variable stars have been found in other galaxies, including our nearest neighbors. Introduction: Cepheid variable stars are simply stars whose brightness varies regularly. They are called Cepheids becau ...
... law so that their luminosities could be determined by measuring their periods of variation. These variable stars have been found in other galaxies, including our nearest neighbors. Introduction: Cepheid variable stars are simply stars whose brightness varies regularly. They are called Cepheids becau ...
Lab 1: The Celestial Sphere
... something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfills the opposite role: it tells us how to find something in the sky at a given time at a particular location. If somehow we could convert between these systems, we could look up the equat ...
... something in the sky when we go outside. The altitude-azimuth coordinate system, called the horizon system, fulfills the opposite role: it tells us how to find something in the sky at a given time at a particular location. If somehow we could convert between these systems, we could look up the equat ...
Section 4
... There are two major types of star clusters: open clusters and globular clusters. Open clusters have a loose, disorganized appearance and contain no more than a few thousand stars. They often contain many bright supergiants and much gas and dust. In contrast, globular clusters are large groupings of ...
... There are two major types of star clusters: open clusters and globular clusters. Open clusters have a loose, disorganized appearance and contain no more than a few thousand stars. They often contain many bright supergiants and much gas and dust. In contrast, globular clusters are large groupings of ...
Unit 1
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
Star Life Cycle Web Activity
... their life cycles of the Interactive Lab and try to answer the questions. Remember to notice the top of the animation to see if it reaches main sequence and notice for how long. ...
... their life cycles of the Interactive Lab and try to answer the questions. Remember to notice the top of the animation to see if it reaches main sequence and notice for how long. ...
Lecture 10-11 - OSU Astronomy
... interpretation of stellar spectra. • Based on the then new atomic physics. ...
... interpretation of stellar spectra. • Based on the then new atomic physics. ...
ph507lecnote06
... the most luminous stars--which appear toward the upper left--because we can see them more easily than we can the faintest stars. These are the GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS In contrast, the H-R diagram for the brightest stars includes a significant number of giants and supergiants as well as several early- ...
... the most luminous stars--which appear toward the upper left--because we can see them more easily than we can the faintest stars. These are the GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS In contrast, the H-R diagram for the brightest stars includes a significant number of giants and supergiants as well as several early- ...
17_LectureOutline
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
Slide 1
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.