15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... Large groups of stars, dust, and gas are called galaxies. Galaxies come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda ...
... Large groups of stars, dust, and gas are called galaxies. Galaxies come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... Astronomy is a Time Machine When we observe a star that is 100 light-years distant, then the light took 100 years to reach us. We are seeing it as it was 100 years ago. The nearest galaxy is about a million light-years from Earth. We see it as it was 1 million years ago. The most distant objects ob ...
... Astronomy is a Time Machine When we observe a star that is 100 light-years distant, then the light took 100 years to reach us. We are seeing it as it was 100 years ago. The nearest galaxy is about a million light-years from Earth. We see it as it was 1 million years ago. The most distant objects ob ...
A Hero`s Little Horse: Discovery of a Dissolving Star Cluster in
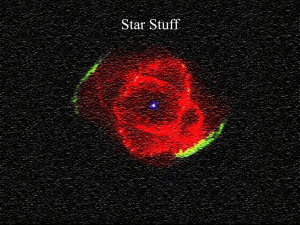
... the underlying stellar distribution. We obtain a half-light radius of 1.2 ± 0.1 arcmin or rh = 6.9 ± 0.6 pc, adopting the distance modulus of 16.48 mag. In analogy to Walsh et al. (2008) we estimate the total luminosity of Kim 1 by integrating the radial number density profile shown in Figure 6 to c ...
... the underlying stellar distribution. We obtain a half-light radius of 1.2 ± 0.1 arcmin or rh = 6.9 ± 0.6 pc, adopting the distance modulus of 16.48 mag. In analogy to Walsh et al. (2008) we estimate the total luminosity of Kim 1 by integrating the radial number density profile shown in Figure 6 to c ...
b. - UW Canvas
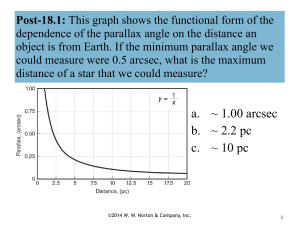
... dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
... dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
Entropy Production of Main-Sequence Stars
... relatively well-studied objects, such as, for instance, stars [11–15]. However, it is obvious that such calculations are extremely important for our understanding of the physics of the world around us. So, stars are the most common objects in the Universe, they contain more than 97% of the mass of a ...
... relatively well-studied objects, such as, for instance, stars [11–15]. However, it is obvious that such calculations are extremely important for our understanding of the physics of the world around us. So, stars are the most common objects in the Universe, they contain more than 97% of the mass of a ...
Procedurally Generating an Artificial Galaxy
... obviously want three dimensions. So we bring in (Z), an integer ranging from -50 to +49. This gives us a three-dimensional grid (X,Y,Z). With one cube at every combination of X, Y and Z, we have 10 000 × 10 000 × 100 = 1010 cubes. The density of stars in every cube is set by its position in the grid ...
... obviously want three dimensions. So we bring in (Z), an integer ranging from -50 to +49. This gives us a three-dimensional grid (X,Y,Z). With one cube at every combination of X, Y and Z, we have 10 000 × 10 000 × 100 = 1010 cubes. The density of stars in every cube is set by its position in the grid ...
10 - Keele Astrophysics Group
... designations no longer have specific meaning the names are still in use today. Each spectral class is divided into ten sub-classes, so that for instance a B0 star follows an O9 star. This classification scheme was based simply on the appearance of the spectra and the physical reason underlying these ...
... designations no longer have specific meaning the names are still in use today. Each spectral class is divided into ten sub-classes, so that for instance a B0 star follows an O9 star. This classification scheme was based simply on the appearance of the spectra and the physical reason underlying these ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.