2.7 - 2.9a
... They are most common in spiral and irregular galaxies horse head nebula is one of the most widely known nebulae ...
... They are most common in spiral and irregular galaxies horse head nebula is one of the most widely known nebulae ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
ASTRONOMY
... 14. What unique features are found in Lacerta? 15. How can Capella be found in the night sky? 16. What is Mirphak and to what constellations does it belong? 17. What objects are visible in the sword of Perseus? 18. Why does Algol, a star in Perseus, seem to blink? ...
... 14. What unique features are found in Lacerta? 15. How can Capella be found in the night sky? 16. What is Mirphak and to what constellations does it belong? 17. What objects are visible in the sword of Perseus? 18. Why does Algol, a star in Perseus, seem to blink? ...
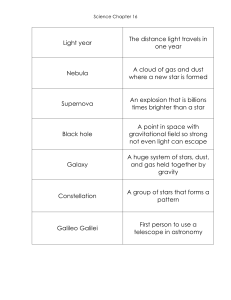
Light year The distance light travels in one year Nebula A cloud of
... The distance light travels in one year ...
... The distance light travels in one year ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
Stars
... The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the skies year after year. However, stars are actually in rapid motion, but their distances are so great that their relative changes in position become apparent only over the centuries. The nu ...
... The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the skies year after year. However, stars are actually in rapid motion, but their distances are so great that their relative changes in position become apparent only over the centuries. The nu ...
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
... Square is high in the south, Alpheratz is the upper left star. Its name comes from an Arabic phrase meaning “navel of the horse,” and reflects a time when Alpheratz was considered as part of Pegasus. Markab is the brightest star in Pegasus and the second brightest star of the Great Square. When the ...
One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
City Built Over Caves To be Explored in Mexico
... north of Andromeda, very appropriately, is her mother, Cassiopeia, a group shaped like the letter W. Between Cassiopeia, and the Pleiades, is Perseus, the hero who rescued Andromeda, according to the mythological story. Another planet decorates the eastern morning sky just before sunrise. This is Ve ...
... north of Andromeda, very appropriately, is her mother, Cassiopeia, a group shaped like the letter W. Between Cassiopeia, and the Pleiades, is Perseus, the hero who rescued Andromeda, according to the mythological story. Another planet decorates the eastern morning sky just before sunrise. This is Ve ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.