Where stars form: inside-out growth and coherent star formation from
... JF125W /HF140W /HF160W selected photometric catalogs (see Skelton et al. 2014). These photometric catalogs form the scaffolding of this project upon which all the remaining data products rest. For this study, we rely on the rest-frame colors, stellar masses, and star formation rates. All of these qu ...
... JF125W /HF140W /HF160W selected photometric catalogs (see Skelton et al. 2014). These photometric catalogs form the scaffolding of this project upon which all the remaining data products rest. For this study, we rely on the rest-frame colors, stellar masses, and star formation rates. All of these qu ...
sections 23-25 powerpoint
... Elliptical galaxy (E). A spheroidal galaxy containing millions to billions of old low-mass stars and no gas or dust. Spiral Galaxy (S). A galaxy with a spheroidal bulge of several million old low-mass stars and a flattened pancake-like disk of billions of old low-mass and young high-mass stars, alon ...
... Elliptical galaxy (E). A spheroidal galaxy containing millions to billions of old low-mass stars and no gas or dust. Spiral Galaxy (S). A galaxy with a spheroidal bulge of several million old low-mass stars and a flattened pancake-like disk of billions of old low-mass and young high-mass stars, alon ...
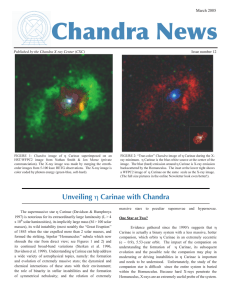
Chandra News March 2005 Published by the Chandra X-ray Center (CXC)
... on approach to the X-ray minimum, while the higher-temperature He-like Fe lines (which are unresolved in the HEG spectra) do not. The line shifts in all cases are much larger than the expected orbital velocities near periastron, and so do not appear to represent the bulk motion of the shock cone. Th ...
... on approach to the X-ray minimum, while the higher-temperature He-like Fe lines (which are unresolved in the HEG spectra) do not. The line shifts in all cases are much larger than the expected orbital velocities near periastron, and so do not appear to represent the bulk motion of the shock cone. Th ...
instructor notes: weeks 9/10
... Lenticular galaxies get their name because they are “lenslike,” but are more like spiral and barred spiral galaxies in possessing a flattened disk, rather than like elliptical galaxies which mostly possess an ellipsoidal symmetry. The distinguishing feature of lenticulars relative to spiral galaxie ...
... Lenticular galaxies get their name because they are “lenslike,” but are more like spiral and barred spiral galaxies in possessing a flattened disk, rather than like elliptical galaxies which mostly possess an ellipsoidal symmetry. The distinguishing feature of lenticulars relative to spiral galaxie ...
Here - NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database
... at which one is working). The effective temperatures T? of the ionizing stars lie in the range 35 000 – 50 000 K. The nebular geometries result from the structure of the parent molecular cloud. Stellar winds, at evolved stages, may produce ring-like structures, but the morphology of H ii regions is ...
... at which one is working). The effective temperatures T? of the ionizing stars lie in the range 35 000 – 50 000 K. The nebular geometries result from the structure of the parent molecular cloud. Stellar winds, at evolved stages, may produce ring-like structures, but the morphology of H ii regions is ...
Clusters: age scales for stellar physics
... were identified as the culprit (Bethe 1939). This is an important lesson: pieces which do not match in this enormous puzzle (our understanding of natural phenomena) do provide, eventually, very interesting hints for new avenues and discoveries. Age and related issues belong to this category. In the ...
... were identified as the culprit (Bethe 1939). This is an important lesson: pieces which do not match in this enormous puzzle (our understanding of natural phenomena) do provide, eventually, very interesting hints for new avenues and discoveries. Age and related issues belong to this category. In the ...
Stellar Intensity Interferometry: The Background John Davis Sydney Institute for Astronomy
... and Cassiopeia A, were unknown and some thought they were “radio stars”. Robert Hanbury Brown (RHB) was determined to measure them • If these sources were galaxies their angular sizes would be of the order of a minute of arc and easy to measure with a conventional interferometer but, if they were s ...
... and Cassiopeia A, were unknown and some thought they were “radio stars”. Robert Hanbury Brown (RHB) was determined to measure them • If these sources were galaxies their angular sizes would be of the order of a minute of arc and easy to measure with a conventional interferometer but, if they were s ...
Gaia 1 and 2. A pair of new satellites of the Galaxy
... Gaia-detected sources is indeed very prominent (top left and top middle panels). Note a white patch corresponding to a dearth of Gaia sources near the centre of the over-density. This is the location of Sirius, where Gaia struggles to detect genuine stars3 . The area affected by Sirius is much large ...
... Gaia-detected sources is indeed very prominent (top left and top middle panels). Note a white patch corresponding to a dearth of Gaia sources near the centre of the over-density. This is the location of Sirius, where Gaia struggles to detect genuine stars3 . The area affected by Sirius is much large ...
abstracts book - Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço
... the conference which is expected to set a critical milestone for the astero- and helioseismology community to prepare the future. The meeting will also cover major synergies with related fields, which benefit from a deeper understanding of the structure and evolution of the sun and stars across the ...
... the conference which is expected to set a critical milestone for the astero- and helioseismology community to prepare the future. The meeting will also cover major synergies with related fields, which benefit from a deeper understanding of the structure and evolution of the sun and stars across the ...
TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Short Answer
... First proposed by Georges Lemaitre, what is the name, most likely coined by Fred Hoyle, for the theory that the universe originated at a finite time many eons ago from an extremely compressed hot state? ANSWER: BIG BANG BONUS 14) ASTRONOMY Short Answer In what constellation is the star Polaris found ...
... First proposed by Georges Lemaitre, what is the name, most likely coined by Fred Hoyle, for the theory that the universe originated at a finite time many eons ago from an extremely compressed hot state? ANSWER: BIG BANG BONUS 14) ASTRONOMY Short Answer In what constellation is the star Polaris found ...
Luminosity profiles and sizes of massive star clusters in NGC 7252
... Observations of young cluster systems have shown that the clusters themselves are often grouped into larger structures, cluster complexes, with radii of tens to hundreds of parsecs (e.g. Zhang, Fall & Whitmore 2001; Larsen 2004). These complexes often appear to be centrally concentrated, hosting a d ...
... Observations of young cluster systems have shown that the clusters themselves are often grouped into larger structures, cluster complexes, with radii of tens to hundreds of parsecs (e.g. Zhang, Fall & Whitmore 2001; Larsen 2004). These complexes often appear to be centrally concentrated, hosting a d ...
Properties of White Dwarfs, Teacher Guide
... History: Freidrick Whilhelm Bessel Freidrick Bessel observed the motion of Sirius with respect to the background stars between 1831 and 1844. In that time, he saw part of this pattern in Sirius’s motion. The dark spots represent Sirius A, the brightest star in the sky. Sirius is bright not only beca ...
... History: Freidrick Whilhelm Bessel Freidrick Bessel observed the motion of Sirius with respect to the background stars between 1831 and 1844. In that time, he saw part of this pattern in Sirius’s motion. The dark spots represent Sirius A, the brightest star in the sky. Sirius is bright not only beca ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... identify with time-domain imaging surveys, even to large distances (5–120 kpc for surveys with a 14 < V < 21 magnitude range; e.g., Sesar et al. 2010). These properties, and the fact that almost every Milky Way dwarf satellite galaxy has at least one RR Lyrae star (including the faintest one, Segue ...
... identify with time-domain imaging surveys, even to large distances (5–120 kpc for surveys with a 14 < V < 21 magnitude range; e.g., Sesar et al. 2010). These properties, and the fact that almost every Milky Way dwarf satellite galaxy has at least one RR Lyrae star (including the faintest one, Segue ...
An X-Ray, Optical and Infra-red study of High-Mass X
... First and foremost I would like to thank my supervisor, Malcolm Coe, for his continued guidance and support. His drive to obtain and exploit all manner of data has given me a wealth of information on which to base my thesis and sent me to some of the world’s most incredible places in the process. I ...
... First and foremost I would like to thank my supervisor, Malcolm Coe, for his continued guidance and support. His drive to obtain and exploit all manner of data has given me a wealth of information on which to base my thesis and sent me to some of the world’s most incredible places in the process. I ...
Gamma Ray Bursts
... Inter-Planetary Network (IPN) 1978 – several spacecrafts far from the Earth ...
... Inter-Planetary Network (IPN) 1978 – several spacecrafts far from the Earth ...
Chemical Evolution of Galactic Systems
... to the issue of space-time variations in the fine-structure constant, as suggested by quasar absorption-line constraints. An excess abundance of heavy Mg isotopes in the absorbing clouds could partly account for the data, without needing to invoke variations in fundamental constants of nature. An en ...
... to the issue of space-time variations in the fine-structure constant, as suggested by quasar absorption-line constraints. An excess abundance of heavy Mg isotopes in the absorbing clouds could partly account for the data, without needing to invoke variations in fundamental constants of nature. An en ...
The Multitude of Molecular Hydrogen Knots in the Helix Nebula 1
... involved a 9 panel mosaic of the Helix using the ACS WFC instrument in the F658N filter (transmitting equally well both the Hα 6563 Å and [N II] 6584 Å lines) and the F502N filter (dominated by the [O III] 5007 Å line). In parallel with the ACS imaging, we used NICMOS (Thompson et al. 1998) to im ...
... involved a 9 panel mosaic of the Helix using the ACS WFC instrument in the F658N filter (transmitting equally well both the Hα 6563 Å and [N II] 6584 Å lines) and the F502N filter (dominated by the [O III] 5007 Å line). In parallel with the ACS imaging, we used NICMOS (Thompson et al. 1998) to im ...
act_science_bellringers
... 24. H—“ Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse and heat up”; gravitational force is the only one mentioned in the passage. 25. B—“ hydrogen to make helium in a shell surrounding its center.” This answer comes straight from the passage, and the question directs you to find the ans ...
... 24. H—“ Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse and heat up”; gravitational force is the only one mentioned in the passage. 25. B—“ hydrogen to make helium in a shell surrounding its center.” This answer comes straight from the passage, and the question directs you to find the ans ...
Starspots: A Key to the Stellar Dynamo | SpringerLink
... by cyclonic turbulence in the outer convection zone and penetrate the solar atmosphere forming sunspots, plages, network, etc. They further expand into the outer atmosphere and exhibit themselves as highly dynamic coronal loops. Thus, a detailed study of solar activity phenomena reveals the structur ...
... by cyclonic turbulence in the outer convection zone and penetrate the solar atmosphere forming sunspots, plages, network, etc. They further expand into the outer atmosphere and exhibit themselves as highly dynamic coronal loops. Thus, a detailed study of solar activity phenomena reveals the structur ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.