DSLR photometry - British Astronomical Association
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons that were captured is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons that were captured is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
File - greenscapes4you
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
astronomy - Scioly.org
... 46. How much brighter is a -2 magnitude star than a +2 magnitude star? 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits th ...
... 46. How much brighter is a -2 magnitude star than a +2 magnitude star? 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits th ...
galaxy
... of a single star. The galaxy can’t be any YOUNGER than its oldest stars, so this technique yields a MINIMUM age for the Milky Way. – Astronomers determined the star’s age by measuring its chemistry. They found that it contains only minute traces of anything heavier than hydrogen and helium, the two ...
... of a single star. The galaxy can’t be any YOUNGER than its oldest stars, so this technique yields a MINIMUM age for the Milky Way. – Astronomers determined the star’s age by measuring its chemistry. They found that it contains only minute traces of anything heavier than hydrogen and helium, the two ...
Test 2, Nov. 17, 2015 - Physics@Brock
... (a) star S has hotter surface than star U. (b) star S has colder surface than star U. (c) both stars have the same surface temperature. (d) [No comparison of their surface temperatures can be made.] 16. A photon can be absorbed by an atom only if the photon energy is equal to the energy difference o ...
... (a) star S has hotter surface than star U. (b) star S has colder surface than star U. (c) both stars have the same surface temperature. (d) [No comparison of their surface temperatures can be made.] 16. A photon can be absorbed by an atom only if the photon energy is equal to the energy difference o ...
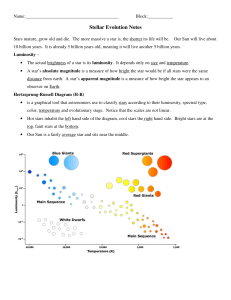
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... Section 2: Short Answer. 40 pts per question lowest score is dropped. 1) A) For a brief period after the Hydrogen in a core of a star is all fused to Helium where does the energy that a star needs to survive come from (before it starts to fuse Helium) and how does that affect the size and temperatur ...
... Section 2: Short Answer. 40 pts per question lowest score is dropped. 1) A) For a brief period after the Hydrogen in a core of a star is all fused to Helium where does the energy that a star needs to survive come from (before it starts to fuse Helium) and how does that affect the size and temperatur ...
Star Types
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
Review Packet
... 1. What is the proper name of the H-R Diagram A. Heat-Radiance Diagram B. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram C. That is the proper name D. Horizontal-Redshift Diagram My corrected answer is B, as the H-R Diagram is named for the two astronomers, Hertzsprung and Russell who were its main contributors. Revie ...
... 1. What is the proper name of the H-R Diagram A. Heat-Radiance Diagram B. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram C. That is the proper name D. Horizontal-Redshift Diagram My corrected answer is B, as the H-R Diagram is named for the two astronomers, Hertzsprung and Russell who were its main contributors. Revie ...
Phys133-Sample MT2
... A) They were produced in the Big Bang. B) They were produced inside stars. C) They evolved from hydrogen and helium shortly after the Big Bang. D) They were produced inside dense interstellar gas. E) all of the above ...
... A) They were produced in the Big Bang. B) They were produced inside stars. C) They evolved from hydrogen and helium shortly after the Big Bang. D) They were produced inside dense interstellar gas. E) all of the above ...
Lives of Stars - Madison County Schools
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.