Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
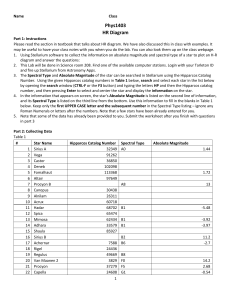
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
... 3) Choose one of the White Dwarf Stars. Calculate its radius in terms of the Sun’s radius. Hint we have done an example in class, see the PowerPoint notes on class webpage. Show your work in detail. ...
... 3) Choose one of the White Dwarf Stars. Calculate its radius in terms of the Sun’s radius. Hint we have done an example in class, see the PowerPoint notes on class webpage. Show your work in detail. ...
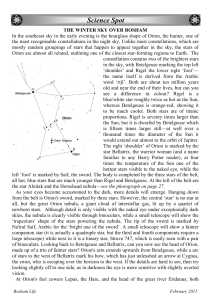
The winter sky over Bosham
... constellation contains two of the brightest stars in the sky, with Betelgeuse marking the top left ‘shoulder’ and Rigel the lower right ‘foot’— the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference i ...
... constellation contains two of the brightest stars in the sky, with Betelgeuse marking the top left ‘shoulder’ and Rigel the lower right ‘foot’— the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference i ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's Belt. The Belt line points left and down to orange Aldebaran, the eye of Taurus the Bull. Continuing the s ...
... the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's Belt. The Belt line points left and down to orange Aldebaran, the eye of Taurus the Bull. Continuing the s ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
... *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
Name: Notes – #45 The Diverse Sizes of Stars 1. A Hertzsprung
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
Sirius - Springer
... astrophysics in a way which provides a realistic view of how science progresses over time ▶ Explains how studies of the star Sirius have played a pivotal role in achieving our current understanding of the nature and fate of stars ▶ Demonstrates the importance of Sirius to many civilisations and cult ...
... astrophysics in a way which provides a realistic view of how science progresses over time ▶ Explains how studies of the star Sirius have played a pivotal role in achieving our current understanding of the nature and fate of stars ▶ Demonstrates the importance of Sirius to many civilisations and cult ...
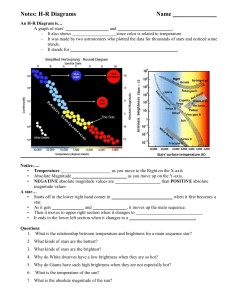
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Starts off in the lower right hand corner in ___________________________ when it first becomes a star. • As it gets ______________ and _______________, it moves up the main sequence. • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to _____________________________. • It ends in the lower lef ...
... • Starts off in the lower right hand corner in ___________________________ when it first becomes a star. • As it gets ______________ and _______________, it moves up the main sequence. • Then it moves to upper right section when it changes to _____________________________. • It ends in the lower lef ...
Star
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
The hierarchical structure of the Universe (go from little to large)
... D 50% inside the Galaxy, 50% outside. E nowhere close to the Galaxy, which is much farther away from us than the individual stars in the sky are. ...
... D 50% inside the Galaxy, 50% outside. E nowhere close to the Galaxy, which is much farther away from us than the individual stars in the sky are. ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
Chapter 30.1
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...