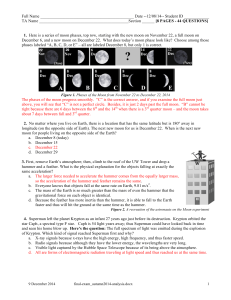
Unit 4: Astronomy
... of these in addition to an optical telescope. Assignment #2: Pages 568, 587-588 Topics: Distances to and motion of stars Objectives: 1) Describe how astronomers were first able to measure the distances to stars. 2) Describe the unit of the length developed by astronomers to measure and describe dist ...
... of these in addition to an optical telescope. Assignment #2: Pages 568, 587-588 Topics: Distances to and motion of stars Objectives: 1) Describe how astronomers were first able to measure the distances to stars. 2) Describe the unit of the length developed by astronomers to measure and describe dist ...
Characterizing Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, supergiant, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars? 9. Why are binary star systems important in astronomy? 10.How can a s ...
... 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, supergiant, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars? 9. Why are binary star systems important in astronomy? 10.How can a s ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... A: • Use the center of the vision to observe detail and color for bright object. • Use averted vision to detect/observe dim objects. More: • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and ...
... A: • Use the center of the vision to observe detail and color for bright object. • Use averted vision to detect/observe dim objects. More: • The color receptors, called cones, are distributed densely and mainly near the center of vision. • The more sensitive rods can only detect light intensity, and ...
Chapter 29 Review
... What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? 1. the emission of specific elements 2. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths 3. highly compressed, glowing gas 4. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum ...
... What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? 1. the emission of specific elements 2. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths 3. highly compressed, glowing gas 4. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
Lecture 5
... Binary Stars • Binary stars, in which two stars are held in orbit • around each other by their mutual gravitational attraction, are surprisingly common • Those that can be resolved into two distinct star images by an Earth-based telescope are called visual binaries • Each of the two stars in a bina ...
... Binary Stars • Binary stars, in which two stars are held in orbit • around each other by their mutual gravitational attraction, are surprisingly common • Those that can be resolved into two distinct star images by an Earth-based telescope are called visual binaries • Each of the two stars in a bina ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... with the naked eye simply as the twin stars Castor and Pollux, following Orion across the night sky. Appearing to the naked eye as a single white star at a distance of 46 light-years, Castor is actually a complex system. It was, in fact in the 18th century, the first binary system recognised. In 189 ...
... with the naked eye simply as the twin stars Castor and Pollux, following Orion across the night sky. Appearing to the naked eye as a single white star at a distance of 46 light-years, Castor is actually a complex system. It was, in fact in the 18th century, the first binary system recognised. In 189 ...
Infinity Express
... described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of the apparent motion of the sun, the moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, ...
... described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of the apparent motion of the sun, the moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, ...
bright - TutorPlus
... • The smaller the value, the brighter the star. • The Sun has a value of -27. A full moon has value -13. ...
... • The smaller the value, the brighter the star. • The Sun has a value of -27. A full moon has value -13. ...
chapter 7
... There are also trinary star systems (3 stars) and other multiple star systems in the galaxy. Single stars like the Sun are in the minority. For any two gravitationally interacting bodies, their barycenter is always closer to the more massive object. If the two stars have the same mass, their baryce ...
... There are also trinary star systems (3 stars) and other multiple star systems in the galaxy. Single stars like the Sun are in the minority. For any two gravitationally interacting bodies, their barycenter is always closer to the more massive object. If the two stars have the same mass, their baryce ...
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
(HR) Diagrams
... a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circle the hottest type. 7. Which is the coldest type of star ...
... a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circle the hottest type. 7. Which is the coldest type of star ...
Lecture 11
... Where Do Stars Form? • Stars don’t form uniformly in the galaxy • Stars like to form in the spiral arms of galaxies – We say that the arms appear “blue” while other parts appear “red” ...
... Where Do Stars Form? • Stars don’t form uniformly in the galaxy • Stars like to form in the spiral arms of galaxies – We say that the arms appear “blue” while other parts appear “red” ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • It is the total energy emitted by the star per second, measured in joules/second or watts. • It is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were at an infinite distance. • It is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were at a standard distance of 10 pc. 13. According to the inverse- ...
... • It is the total energy emitted by the star per second, measured in joules/second or watts. • It is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were at an infinite distance. • It is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were at a standard distance of 10 pc. 13. According to the inverse- ...
5. cosmic distance ladder ii: standard candles
... candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its lumino ...
... candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its lumino ...
Learning Objectives
... candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its lumino ...
... candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its lumino ...
Constants and Equations
... T☉ 5.8103 K M☉ 2.01030 kg G (Gravitational Constant) 6.6710-11m3kg-1s-2 (Stephan-Boltzmann Constant) 5.6710-8 Wm-2K-4 c (Speed of Light in Vacuum) 3108 ms-1 ...
... T☉ 5.8103 K M☉ 2.01030 kg G (Gravitational Constant) 6.6710-11m3kg-1s-2 (Stephan-Boltzmann Constant) 5.6710-8 Wm-2K-4 c (Speed of Light in Vacuum) 3108 ms-1 ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... • The Sun and our solar system is located in one of the outer arms (Orion’s Arm) of the galaxy. The distance from the Sun to the center of the galaxy is about 30,000 light years. • All objects in the galaxy revolve around ...
... • The Sun and our solar system is located in one of the outer arms (Orion’s Arm) of the galaxy. The distance from the Sun to the center of the galaxy is about 30,000 light years. • All objects in the galaxy revolve around ...
the May 2017 Newsletter!
... very close, the star could quite easily be seen as double in a 6 inch telescope. Other double stars were Castor and Alpha Centauri. Both of the latter have recently opened up from a close approach as viewed from Earth – Castor closed up for about 30 years. (See footnote 1); the Alpha Centauri pair a ...
... very close, the star could quite easily be seen as double in a 6 inch telescope. Other double stars were Castor and Alpha Centauri. Both of the latter have recently opened up from a close approach as viewed from Earth – Castor closed up for about 30 years. (See footnote 1); the Alpha Centauri pair a ...
Main Types of Galaxies
... • The Sun and our solar system is located in one of the outer arms (Orion’s Arm) of the galaxy. The distance from the Sun to the center of the galaxy is about 30,000 light years. • All objects in the galaxy revolve around ...
... • The Sun and our solar system is located in one of the outer arms (Orion’s Arm) of the galaxy. The distance from the Sun to the center of the galaxy is about 30,000 light years. • All objects in the galaxy revolve around ...
Stars
... usually done on spectral lines. • Essentially all of the mass measurements that we have for stars are for stars in binary systems – two stars orbiting each other. • The mass of the stars can be measured from their velocities and the distance between the stars. ...
... usually done on spectral lines. • Essentially all of the mass measurements that we have for stars are for stars in binary systems – two stars orbiting each other. • The mass of the stars can be measured from their velocities and the distance between the stars. ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... This guide is meant to assist with studying for Exam 3 on March 27, 2017. However, it is not comprehensive. This guide includes topic which might not be on this exam (but which might be on the final). It is also possible that something not specifically mentioned on the guide may be on the exam. Howe ...
... This guide is meant to assist with studying for Exam 3 on March 27, 2017. However, it is not comprehensive. This guide includes topic which might not be on this exam (but which might be on the final). It is also possible that something not specifically mentioned on the guide may be on the exam. Howe ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... If you measure a star's apparent magnitude and know its absolute magnitude, you can find the star's distance (using the inverse square law of light brightness). If you know a star's apparent magnitude and distance, you can find the star's luminosity A star can be luminous because it is hot or it is ...
... If you measure a star's apparent magnitude and know its absolute magnitude, you can find the star's distance (using the inverse square law of light brightness). If you know a star's apparent magnitude and distance, you can find the star's luminosity A star can be luminous because it is hot or it is ...
Summary: Stellar Distances
... Temperatures can also be inferred from the appearance of a star’s spectrum - the pattern of spectral lines. This spectral typing is not affected by interstellar dust. Surface temperatures of stars almost all lie between 40,000°K for the “bluest” stars to about 3,000°K for the “reddest” stars. Relati ...
... Temperatures can also be inferred from the appearance of a star’s spectrum - the pattern of spectral lines. This spectral typing is not affected by interstellar dust. Surface temperatures of stars almost all lie between 40,000°K for the “bluest” stars to about 3,000°K for the “reddest” stars. Relati ...
Chapter 8: Stars
... Types of Galaxies • There are many different types of galaxies. Edwin Hubble, the astronomer for whom The Hubble Space Telescope is named, began to classify galaxies, mostly by their shapes in the 1920s. • Here are a couple of galaxies, spiral galaxies, Milky Way, elliptical galaxies, and ...
... Types of Galaxies • There are many different types of galaxies. Edwin Hubble, the astronomer for whom The Hubble Space Telescope is named, began to classify galaxies, mostly by their shapes in the 1920s. • Here are a couple of galaxies, spiral galaxies, Milky Way, elliptical galaxies, and ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.