Interpolation of Magnitude.
... You were looking at a computer, not the sky. You are still learning! ...
... You were looking at a computer, not the sky. You are still learning! ...
Planetary Nebula
... What resemble dainty butterfly wings are actually roiling cauldrons of gas heated to more than 36,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The gas is tearing across space at more than 600,000 miles an hour -- fast enough to travel from Earth to the moon in 24 minutes! A dying star that was once about five times the ...
... What resemble dainty butterfly wings are actually roiling cauldrons of gas heated to more than 36,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The gas is tearing across space at more than 600,000 miles an hour -- fast enough to travel from Earth to the moon in 24 minutes! A dying star that was once about five times the ...
Microsoft Word 97
... 4) Clouds of dust surrounding hot stars, like some of the stars in the star cluster known as the Pleiades, are examples of reflection nebulae. a) They merely reflect the starlight toward us without emitting visible radiation of their own. b) Reflection nebulae usually look bluish for two reasons: 1) ...
... 4) Clouds of dust surrounding hot stars, like some of the stars in the star cluster known as the Pleiades, are examples of reflection nebulae. a) They merely reflect the starlight toward us without emitting visible radiation of their own. b) Reflection nebulae usually look bluish for two reasons: 1) ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... recurring questions. We especially appreciate questions and comments of former students after they navigate their first ocean crossing. Comments from new navigators are invaluable to the development of teaching methods and course materials. This booklet is one example. Most discoveries of new naviga ...
... recurring questions. We especially appreciate questions and comments of former students after they navigate their first ocean crossing. Comments from new navigators are invaluable to the development of teaching methods and course materials. This booklet is one example. Most discoveries of new naviga ...
Galaxies - WordPress.com
... moving toward us, its wavelength shortens, and the light shifts towards the blue end of the color spectrum. If an object is moving away fom us, its wavelength gets longer, and the light shifts towards the red end of the ...
... moving toward us, its wavelength shortens, and the light shifts towards the blue end of the color spectrum. If an object is moving away fom us, its wavelength gets longer, and the light shifts towards the red end of the ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... • Historically specific stellar absorption features over narrow wavelength intervals were used when analyzing galaxy spectra to obtain the ages and metallicities of the stellar populations • For galaxies with old stellar populations, the Lick/IDS system of ~25 narrow-band indices is often used (Wor ...
... • Historically specific stellar absorption features over narrow wavelength intervals were used when analyzing galaxy spectra to obtain the ages and metallicities of the stellar populations • For galaxies with old stellar populations, the Lick/IDS system of ~25 narrow-band indices is often used (Wor ...
StellarManual
... implicit measure of intrinsic brightness and how much energy a star is releasing per second (luminosity). Thus: Avior (m = 1.9) and Alkaid (m = 1.9) appear to be the same brightness, but Avior (M = -4.8) emits more energy than Alkaid (M = -1.8). Barnard’s Star (m = 9.5) appears brighter than Wolf 35 ...
... implicit measure of intrinsic brightness and how much energy a star is releasing per second (luminosity). Thus: Avior (m = 1.9) and Alkaid (m = 1.9) appear to be the same brightness, but Avior (M = -4.8) emits more energy than Alkaid (M = -1.8). Barnard’s Star (m = 9.5) appears brighter than Wolf 35 ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... Check show isoradius lines. Note that at each point on a green line, stars have the same value of radius. Use these isoradius lines to check your answers in the table above. ...
... Check show isoradius lines. Note that at each point on a green line, stars have the same value of radius. Use these isoradius lines to check your answers in the table above. ...
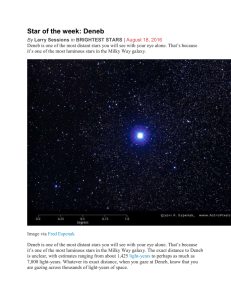
in BRIGHTEST STARS
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
A near IR adaptive optics search for faint companions to early
... population was studied by Graham & Hege (1989). The visual components C, D, E at separations 6300 – 9300 from A are probably physical (Abt et al. 1976). No close visual components to A or B were discovered by speckle-interferometry (Mason et al. 1998). The new component P is likely to be physical. I ...
... population was studied by Graham & Hege (1989). The visual components C, D, E at separations 6300 – 9300 from A are probably physical (Abt et al. 1976). No close visual components to A or B were discovered by speckle-interferometry (Mason et al. 1998). The new component P is likely to be physical. I ...
Surveying the Stars
... • How do we measure stellar masses? —Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law tells us the total mass of a binary system, if we can measure the orbital period (p) and average orbital separation of the system ...
... • How do we measure stellar masses? —Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law tells us the total mass of a binary system, if we can measure the orbital period (p) and average orbital separation of the system ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... i in infrared. The TullyFisher relation states that the bigger the galaxy is, the faster it rotates. The faster the galaxy rotates, the wider is the emission line in velocity. Also, the bigger the galaxy, the more is its luminosity. TullyFisher relation shows that for normal galaxies, the velocity w ...
... i in infrared. The TullyFisher relation states that the bigger the galaxy is, the faster it rotates. The faster the galaxy rotates, the wider is the emission line in velocity. Also, the bigger the galaxy, the more is its luminosity. TullyFisher relation shows that for normal galaxies, the velocity w ...
Galaxies - SD43 Teacher Sites
... 2218 shines brightly in this image, with many other galaxies visible farther behind it. ...
... 2218 shines brightly in this image, with many other galaxies visible farther behind it. ...
Our Local Group of Galaxies
... How complete is the list of Milky Way dSph companions? • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be s ...
... How complete is the list of Milky Way dSph companions? • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be s ...
sections 12-15 instructor notes
... J. C. Kapteyn, the first director of the famous Laboratory of Statistical Astronomy in Gröningen, Holland, and his successor, P. J. van Rhijn, gave us through their work in the first third of the twentieth century the basic GLF that still serves us at the present time. For the range of observable ab ...
... J. C. Kapteyn, the first director of the famous Laboratory of Statistical Astronomy in Gröningen, Holland, and his successor, P. J. van Rhijn, gave us through their work in the first third of the twentieth century the basic GLF that still serves us at the present time. For the range of observable ab ...
Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false
... ____ 21. HS-ESS1-1 Which of the following stages is the earliest in the development of a star? a. Nebula c. Neutron star b. Protostar d. Giant ____ 22. HS-ESS1-1 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: a. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen b. ...
... ____ 21. HS-ESS1-1 Which of the following stages is the earliest in the development of a star? a. Nebula c. Neutron star b. Protostar d. Giant ____ 22. HS-ESS1-1 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: a. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen b. ...
As far as - Sangeeta Malhotra
... performed spectroscopy on the HUDF target region between October 2002 and January 2003, using about 10 percent of the time that went into imaging. We quickly discovered that GRAPES is not just an extragalactic survey, for the HUDF distance scale starts within our own galaxy. The closest object we ha ...
... performed spectroscopy on the HUDF target region between October 2002 and January 2003, using about 10 percent of the time that went into imaging. We quickly discovered that GRAPES is not just an extragalactic survey, for the HUDF distance scale starts within our own galaxy. The closest object we ha ...
EvoluGon of high mass stars Solar-‐type stars end their lives by
... type Ib (there are no hydrogen lines in the spectrum, indica=ng that the hydrogen envelope was lost before the explosion) type Ic (no hydrogen or helium lines, so all the hydrogen and ...
... type Ib (there are no hydrogen lines in the spectrum, indica=ng that the hydrogen envelope was lost before the explosion) type Ic (no hydrogen or helium lines, so all the hydrogen and ...
Elliptical galaxies
... About 10 to 20% of the elliptical galaxies contain sharp steps in their luminosity profiles. These features are known as ripples and shells. Ripples and shells have also been detected in S0 and Sa galaxies. It is not clear whether this is present in later-type galaxies because it is difficult to ...
... About 10 to 20% of the elliptical galaxies contain sharp steps in their luminosity profiles. These features are known as ripples and shells. Ripples and shells have also been detected in S0 and Sa galaxies. It is not clear whether this is present in later-type galaxies because it is difficult to ...
THE ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE OF RR LYRAE - Cosmos
... when the true parallax is small, compared with error of parallax. Similarly the distant stars have too faint luminosities, i.e., have too large parallaxes, mainly because the true parallax is much smaller than error of parallax. Only one RR Lyrae star (HIC95497:[Fe/H]={1.37) is measured with a high ...
... when the true parallax is small, compared with error of parallax. Similarly the distant stars have too faint luminosities, i.e., have too large parallaxes, mainly because the true parallax is much smaller than error of parallax. Only one RR Lyrae star (HIC95497:[Fe/H]={1.37) is measured with a high ...
Big Bang Theory
... other galaxies and eventually helped to support the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang Theory – Hubble’s Law Gizmo™, select Region A. Look at the image of the Andromeda Galaxy, a galaxy relatively close to our own Milky Way galaxy. 1. Locate the two Cepheid variables, the ...
... other galaxies and eventually helped to support the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang Theory – Hubble’s Law Gizmo™, select Region A. Look at the image of the Andromeda Galaxy, a galaxy relatively close to our own Milky Way galaxy. 1. Locate the two Cepheid variables, the ...
Stories in the Stars
... Cluster. A group of objects close to each other; clusters of stars or galaxies. Star clusters are open or globular. Constellation. A pattern of stars that suggests the shape of some god, person, animal or object. Eclipse. Blocking of light from one body by another that passes in front of it. Eclipsi ...
... Cluster. A group of objects close to each other; clusters of stars or galaxies. Star clusters are open or globular. Constellation. A pattern of stars that suggests the shape of some god, person, animal or object. Eclipse. Blocking of light from one body by another that passes in front of it. Eclipsi ...
Interacting Galaxies
... While galaxies collide, with very rare exceptions, the stars within them do not. This is because so much of a galaxy is simply empty space, with distances between stars about 100 million times larger than their stellar diameters. What collides is the gas and dust between the stars, which produces a ...
... While galaxies collide, with very rare exceptions, the stars within them do not. This is because so much of a galaxy is simply empty space, with distances between stars about 100 million times larger than their stellar diameters. What collides is the gas and dust between the stars, which produces a ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.