Masses are much harder than distance, luminosity, or temperature
... Lifetimes on Main Sequence (MS) • Stars spend 90% of their lives on MS • Lifetime on MS = amount of time star fuses hydrogen (gradually) in its core • For Sun (G), this is about 10 billion years • For more massive stars (OBAF), lifetime is (much) shorter • For less massive stars (KM), lifetime ...
... Lifetimes on Main Sequence (MS) • Stars spend 90% of their lives on MS • Lifetime on MS = amount of time star fuses hydrogen (gradually) in its core • For Sun (G), this is about 10 billion years • For more massive stars (OBAF), lifetime is (much) shorter • For less massive stars (KM), lifetime ...
Stellarium01 Starter Part A B Doc - ASTR101
... galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, and much more! The last three objects are called Deep Sky Objects. Each of these is a distant object much bigger than a single star and (almost) permanently located at a certain spot in the sky, in a particular constellation. There are many catalogs of Deep Sky Obje ...
... galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, and much more! The last three objects are called Deep Sky Objects. Each of these is a distant object much bigger than a single star and (almost) permanently located at a certain spot in the sky, in a particular constellation. There are many catalogs of Deep Sky Obje ...
Triangulation Trigonometric Parallax
... stars differ enormously in radius – Some stars are hundreds of times larger than the Sun and are referred to as giants – Stars smaller than the giants are called dwarfs ...
... stars differ enormously in radius – Some stars are hundreds of times larger than the Sun and are referred to as giants – Stars smaller than the giants are called dwarfs ...
Problems_blackbody_spectra_hr
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
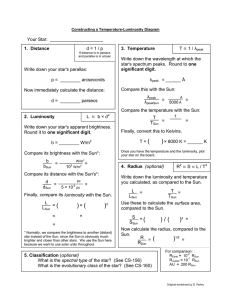
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 2. Why do massive stars last for a short time as main sequence stars but low-mass stars last a long time in the main sequence stage? Massive stars last for such a short time as main sequence stars because the higher central pressures in those stars drive faster fusion rates and created higher lumino ...
... 2. Why do massive stars last for a short time as main sequence stars but low-mass stars last a long time in the main sequence stage? Massive stars last for such a short time as main sequence stars because the higher central pressures in those stars drive faster fusion rates and created higher lumino ...
lecture19 - Stony Brook University
... that are moving away from us with huge speeds, using the observed Doppler shifts of known spectral lines. This indicates that they are very very far away (we will make this connection between recessional velocity and distance clear later – it’s called the Hubble expansion of the universe). From the ...
... that are moving away from us with huge speeds, using the observed Doppler shifts of known spectral lines. This indicates that they are very very far away (we will make this connection between recessional velocity and distance clear later – it’s called the Hubble expansion of the universe). From the ...
Sun`s Exterior
... The photosphere is also the bottom layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. The layers above are hotter than the photosphere. The layer above is called the chromosphere. This is the layer that contains the bright red storms visible during a solar eclipse. The temperature in the chromosphere ranges from 6,000 ...
... The photosphere is also the bottom layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. The layers above are hotter than the photosphere. The layer above is called the chromosphere. This is the layer that contains the bright red storms visible during a solar eclipse. The temperature in the chromosphere ranges from 6,000 ...
1. - TeacherWeb
... • Some supernovas form neutron stars and black holes. – If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black hole. • black hol ...
... • Some supernovas form neutron stars and black holes. – If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black hole. • black hol ...
Star Light, Star Bright
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Ask, Why does a streetlight just 10 meters away from us appear brighter to us than the full Moon or any stars in the night sky? (Even though the streetlight is less intense in brightness than the full Moon or stars, it is closer to us, so it ...
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Ask, Why does a streetlight just 10 meters away from us appear brighter to us than the full Moon or any stars in the night sky? (Even though the streetlight is less intense in brightness than the full Moon or stars, it is closer to us, so it ...
PEGASUS, THE FLYING HORSE Pegasus is a constellation in the
... depicted Pegasus as half of a horse, rising out of the ocean. CHARACTERISTICS The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the IAU in 1922, is 'Peg'. The official constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equato ...
... depicted Pegasus as half of a horse, rising out of the ocean. CHARACTERISTICS The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the IAU in 1922, is 'Peg'. The official constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equato ...
How far away are the Stars?
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age ...
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age ...
The Great Nebula in Orion
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
Part 1: If a 10000 K blackbody has a wavelength of peak emission at
... and review the material in Module 1 Lecture F. Also, as I said in class, if this inverse relation did not hold then cooler objects would be emitting short wavelength high energy photons which doesn’t make any physical sense because then a source at absolute zero would be emitting photons of infinite ...
... and review the material in Module 1 Lecture F. Also, as I said in class, if this inverse relation did not hold then cooler objects would be emitting short wavelength high energy photons which doesn’t make any physical sense because then a source at absolute zero would be emitting photons of infinite ...
Virtual HR Diagram Lab
... diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius. Fill in the table below: Size of Star Description ...
... diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius. Fill in the table below: Size of Star Description ...
File
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
Stellar Characteristics and Evolution
... Flash. The spectral type and luminosity is not constant however, and some stars can evolve though a large spread of spectral types while in the Horizontal Branch. Eventually, the Helium in the core is exhausted and converted to carbon. The core becomes degenerate and collapses, and the star expands ...
... Flash. The spectral type and luminosity is not constant however, and some stars can evolve though a large spread of spectral types while in the Horizontal Branch. Eventually, the Helium in the core is exhausted and converted to carbon. The core becomes degenerate and collapses, and the star expands ...
Surveying the Stars
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -- which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -- which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
G W ORIONIS, A 20000 YEARS OLD T TAURI STAR? 1\/"", _ 0.14
... Our knowledge 01' the actual ages 01' very young stars is very meager; the first indication Lhat we may be observing stars with ages 01' the onler 01' 10 000 years came indirectly from the analysis 01' the density distribution in the Orion nebula (Kahn am! Menon ]9(1) which showed that the latter co ...
... Our knowledge 01' the actual ages 01' very young stars is very meager; the first indication Lhat we may be observing stars with ages 01' the onler 01' 10 000 years came indirectly from the analysis 01' the density distribution in the Orion nebula (Kahn am! Menon ]9(1) which showed that the latter co ...
at A-stars?
... • Stars spend 90% of their lives on MS • Lifetime on MS = amount of time star fuses hydrogen (gradually) in its core • For Sun (G), this is about 10 billion years • For more massive stars (OBAF), lifetime is (much) shorter • For less massive stars (KM), lifetime is ...
... • Stars spend 90% of their lives on MS • Lifetime on MS = amount of time star fuses hydrogen (gradually) in its core • For Sun (G), this is about 10 billion years • For more massive stars (OBAF), lifetime is (much) shorter • For less massive stars (KM), lifetime is ...
Altair - the hottest `cool` star in X-rays
... 2.4 MK and its emission measure distribution (EMD) is dominated by rather cool plasma at temperatures in the range of 1 – 4 MK, additionally a weak hotter component seems to contribute at a few percent level. These properties are quite typical for weakly active stars and similar to those of the quie ...
... 2.4 MK and its emission measure distribution (EMD) is dominated by rather cool plasma at temperatures in the range of 1 – 4 MK, additionally a weak hotter component seems to contribute at a few percent level. These properties are quite typical for weakly active stars and similar to those of the quie ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.