My Constellation
... water. In most cultures, it is drawn as a man pouring water from a bucket. This may arise from the fact that the Sun enters Aquarius in early winter when the rainy season begins in many parts of the world. Õ Alpha Aquarii ("Sadalmelik") and beta Aquarii ("Sadalsuud") are twin supergiants with nearly ...
... water. In most cultures, it is drawn as a man pouring water from a bucket. This may arise from the fact that the Sun enters Aquarius in early winter when the rainy season begins in many parts of the world. Õ Alpha Aquarii ("Sadalmelik") and beta Aquarii ("Sadalsuud") are twin supergiants with nearly ...
Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... and temperature change. 2. As the protostar shrinks, it gets hotter, emits more radiation, and gradually blows away the outer portions of its cocoon. 3. T Tauri stars are a certain class of young stars that show rapid and erratic changes in brightness in the form of enormous flares; these flares are ...
... and temperature change. 2. As the protostar shrinks, it gets hotter, emits more radiation, and gradually blows away the outer portions of its cocoon. 3. T Tauri stars are a certain class of young stars that show rapid and erratic changes in brightness in the form of enormous flares; these flares are ...
White Dwarfs
... 18. Which of the following statements accurately describe some observed properties of type Ia and type II supernovae? a. Type Ia supernovae have hydrogen lines in their spectra. b. Type II supernovae have hydrogen lines in their spectra. c. Type Ia supernovae are more luminous. d. Both a and c above ...
... 18. Which of the following statements accurately describe some observed properties of type Ia and type II supernovae? a. Type Ia supernovae have hydrogen lines in their spectra. b. Type II supernovae have hydrogen lines in their spectra. c. Type Ia supernovae are more luminous. d. Both a and c above ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
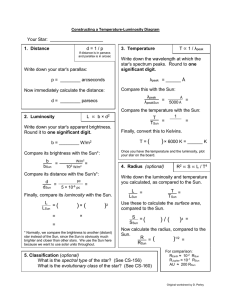
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
Chapter 6 Stars
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
... from the life cycle of a low-mass or medium-mass star. High-mass stars quickly evolve into brilliant supergiants. When a supergiant runs out of fuel, it can explode suddenly. Within hours, the star blazes millions of times brighter. The explosion is called a supernova. After a supernova, some of th ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... Globular clusters are dense compact spherical groups of stars which reside in the halos of galaxies, above and below the plane of the galaxy. They are very old Population II stars. Populations III is the first generation of stars and have not yet been detected. Population II stars have a little more ...
... Globular clusters are dense compact spherical groups of stars which reside in the halos of galaxies, above and below the plane of the galaxy. They are very old Population II stars. Populations III is the first generation of stars and have not yet been detected. Population II stars have a little more ...
Spectra PowerPoint
... Spectral Lines and Temperature • The strength of the hydrogen Balmer lines depends on the temperature of the star’s surface layers. – Both hot and cool stars have weak Balmer lines. – Medium-temperature stars have strong Balmer lines. ...
... Spectral Lines and Temperature • The strength of the hydrogen Balmer lines depends on the temperature of the star’s surface layers. – Both hot and cool stars have weak Balmer lines. – Medium-temperature stars have strong Balmer lines. ...
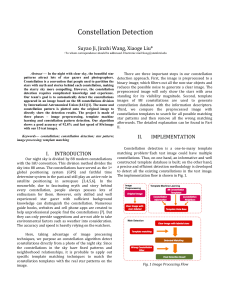
Constellation Detection
... Our algorithm successfully achieves accurate and relative fast constellation detection. Unlike regular template matching problems, constellations are scatter-based, so existing techniques such as SIFT detector or SURF detector cannot be applied. We build the database based on the information we need ...
... Our algorithm successfully achieves accurate and relative fast constellation detection. Unlike regular template matching problems, constellations are scatter-based, so existing techniques such as SIFT detector or SURF detector cannot be applied. We build the database based on the information we need ...
UniverseofGalaxies
... – No spiral structure – Blue, many young stars – Patchy light distribution ...
... – No spiral structure – Blue, many young stars – Patchy light distribution ...
The Bigger Picture
... Q. Two stars have the same Luminosity. Star A has a parallax angle of 1/3 arcsec, Star B has a parallax angle of 1/6 arcsec. c. Compare the apparent brightness of the two stars. Star B is twice as far away, same L, If there is no dust along the the line of sight to either star, B will be 1/4 as ...
... Q. Two stars have the same Luminosity. Star A has a parallax angle of 1/3 arcsec, Star B has a parallax angle of 1/6 arcsec. c. Compare the apparent brightness of the two stars. Star B is twice as far away, same L, If there is no dust along the the line of sight to either star, B will be 1/4 as ...
Distant Stars - How far away is it
... RR Lyrae is a variable star like Delta Cephei. As the brightest star in its class, it became the namesake for the RR Lyrae variable class of stars. The relationship between pulsation period and absolute magnitude of RR Lyraes makes them good standard candles. They are not as bright as Cepheid variab ...
... RR Lyrae is a variable star like Delta Cephei. As the brightest star in its class, it became the namesake for the RR Lyrae variable class of stars. The relationship between pulsation period and absolute magnitude of RR Lyraes makes them good standard candles. They are not as bright as Cepheid variab ...
Exam #2 Solutions
... The cooler giant stars are mostly K and M giants with temperatures around 5,000 K to 3,000K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities. The stars are all larger in radius than the Sun, being between 1 and 100 solar radii. All these stars will have very short lifetimes compared to ...
... The cooler giant stars are mostly K and M giants with temperatures around 5,000 K to 3,000K and luminosities between 50 and 5,000 solar luminosities. The stars are all larger in radius than the Sun, being between 1 and 100 solar radii. All these stars will have very short lifetimes compared to ...
constellation.
... galaxies and their evolution. (Your project should include information about the Big Bang Theory and how stars, planets and black holes are formed) a. Galaxies are clusters of billions of stars and may have different shapes. (Your project should include: the different types of galaxies, their shapes ...
... galaxies and their evolution. (Your project should include information about the Big Bang Theory and how stars, planets and black holes are formed) a. Galaxies are clusters of billions of stars and may have different shapes. (Your project should include: the different types of galaxies, their shapes ...
Descriptions For Posters
... M81 or Bode's galaxy is a large bright spiral galaxy located 11.8 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent magnitude of +6.9 it's easily visible with binoculars, a fine target for small telescope owners and a wonderful sight in larger scopes. The galaxy is ...
... M81 or Bode's galaxy is a large bright spiral galaxy located 11.8 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent magnitude of +6.9 it's easily visible with binoculars, a fine target for small telescope owners and a wonderful sight in larger scopes. The galaxy is ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... sufficient pressure to balance the gravity. As a consequence of this the surface layers are gradually expanding. In the case of the Sun the hydrogen in the core will be exhausted after some 10 billion years. At this time the hydrogen fusion will continue in a shell around the core. Since the shell i ...
... sufficient pressure to balance the gravity. As a consequence of this the surface layers are gradually expanding. In the case of the Sun the hydrogen in the core will be exhausted after some 10 billion years. At this time the hydrogen fusion will continue in a shell around the core. Since the shell i ...
Document
... • Measure the observed brightness • Compare the observed brightness with the luminosity to work out the distance ...
... • Measure the observed brightness • Compare the observed brightness with the luminosity to work out the distance ...
Observations and Theoretical Models of Subdwarfs
... spectra of these stars demonstrated abnormally faint metallic lines for their spectral class. Four years later, Gerard Kuiper renamed them “subdwarfs” after observing that these intermediate stars had less in common with the degenerate white dwarfs than they did with main sequence dwarf stars [1]. S ...
... spectra of these stars demonstrated abnormally faint metallic lines for their spectral class. Four years later, Gerard Kuiper renamed them “subdwarfs” after observing that these intermediate stars had less in common with the degenerate white dwarfs than they did with main sequence dwarf stars [1]. S ...
EarthComm_c1s9
... core temperature reaches 15 million K, hydrogen atoms combine or fuse to form heavier helium atoms. In the process, energy is emitted. In stars less massive than the Sun, this is the only reaction that takes place. In all other stars, fusion reactions involving elements heavier than hydrogen also oc ...
... core temperature reaches 15 million K, hydrogen atoms combine or fuse to form heavier helium atoms. In the process, energy is emitted. In stars less massive than the Sun, this is the only reaction that takes place. In all other stars, fusion reactions involving elements heavier than hydrogen also oc ...
Astro 3 Spring, 2004 (Prof
... -- Both white dwarfs and neutron stars are composed of degenerate matter. The two populations of stars are as follows (this is important and comes up over and over again in the chapters dealing with galaxies!): -- Population I stars are young stars that have a lot of elements beyond hydrogen and hel ...
... -- Both white dwarfs and neutron stars are composed of degenerate matter. The two populations of stars are as follows (this is important and comes up over and over again in the chapters dealing with galaxies!): -- Population I stars are young stars that have a lot of elements beyond hydrogen and hel ...
CloudsToSolarSystems_EXES
... Molecular gas (as mapped by CO emission) extends over even more of the space mapped out in previous image. ...
... Molecular gas (as mapped by CO emission) extends over even more of the space mapped out in previous image. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.