Stars PowerPoint
... • Parallax is the apparent shift in position of an object caused by the motion of the observer. ...
... • Parallax is the apparent shift in position of an object caused by the motion of the observer. ...
English Summary
... is called radiation and gives the star a colour. The colour of a star is related to its temperature. For instance, Rigel in the constellation Orion is very blue (and hot) while Betelgeuse is red (and cool). This concept is easier if we think of a wire that is being heated up. As it gets hotter (radi ...
... is called radiation and gives the star a colour. The colour of a star is related to its temperature. For instance, Rigel in the constellation Orion is very blue (and hot) while Betelgeuse is red (and cool). This concept is easier if we think of a wire that is being heated up. As it gets hotter (radi ...
APOD Wall Calendar 2015 General: All Topics
... Explanation: The well known Pleiades star cluster is slowly destroying part of a passing cloud of gas and dust. The Pleiades is the brightest open cluster of stars on Earth's sky and can be seen from almost any northerly location with the unaided eye. The passing young dust cloud is thought to be pa ...
... Explanation: The well known Pleiades star cluster is slowly destroying part of a passing cloud of gas and dust. The Pleiades is the brightest open cluster of stars on Earth's sky and can be seen from almost any northerly location with the unaided eye. The passing young dust cloud is thought to be pa ...
LIFEPAC® 7th Grade Science Unit 3 Worktext - HomeSchool
... cloud of stars stretching across the sky. You can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is ...
... cloud of stars stretching across the sky. You can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is ...
The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
galaxy.
... April 1920: the Curtis-Shapely debate Shapely (Harvard): Argued that spiral nebulae were inside our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, ...
... April 1920: the Curtis-Shapely debate Shapely (Harvard): Argued that spiral nebulae were inside our galaxy for several reasons • Galaxy was huge (he didn’t know about dust). • van Maanen’s observations showed that one spiral nebula, M 101, could be observed to rotate. It it were outside our galaxy, ...
H-RDiagramSE
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
Animals in Estonian Folk Astronomy
... The Classic System of Constellations was finished by Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy), who listed 48 constellations in his Almagest (2d cent. a.d.). The Mainz Globe is one of only three surviving celestial globes that have survived from the Classical world. It shows 48 Classical constellations and the ...
... The Classic System of Constellations was finished by Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy), who listed 48 constellations in his Almagest (2d cent. a.d.). The Mainz Globe is one of only three surviving celestial globes that have survived from the Classical world. It shows 48 Classical constellations and the ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... b. Where on the main sequence (ie., what color) are the most massive stars found? ...
... b. Where on the main sequence (ie., what color) are the most massive stars found? ...
question - UW Canvas
... 23. How is it that the core of a massive star is able to fuse heavier and heavier elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that ...
... 23. How is it that the core of a massive star is able to fuse heavier and heavier elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that ...
Notes
... Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking and heating up, until nuclear burning ceases Masses between 0.55 and 1+ solar masses (more massive are brighter) Outflowing winds seen in “P Cygni” profiles Hydrogen abundance l ...
... Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking and heating up, until nuclear burning ceases Masses between 0.55 and 1+ solar masses (more massive are brighter) Outflowing winds seen in “P Cygni” profiles Hydrogen abundance l ...
Document
... The new stars continue to contract because of gravity. The increasing pressure heats the nucleus of the star and makes it shine. If gravity was the only source of energy our Sun would shine for less than 18,000,000 years. There must be another source of energy. ...
... The new stars continue to contract because of gravity. The increasing pressure heats the nucleus of the star and makes it shine. If gravity was the only source of energy our Sun would shine for less than 18,000,000 years. There must be another source of energy. ...
Lecture 8: The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Globular cluster: Up to a million or more stars in a dense ball bound together by gravity ...
... Globular cluster: Up to a million or more stars in a dense ball bound together by gravity ...
How many stars are in the Milky Way Galaxy?
... 1: Draw and label diagrams of the Milky Way from top and side views, showing the major components. Indicate the approximate dimensions of the components and note the location of the Sun in each diagram. 2: Describe the galactic distribution of general interstellar material, nebulae, and open and glo ...
... 1: Draw and label diagrams of the Milky Way from top and side views, showing the major components. Indicate the approximate dimensions of the components and note the location of the Sun in each diagram. 2: Describe the galactic distribution of general interstellar material, nebulae, and open and glo ...
what are stars made of?
... Stars begin their lives as main sequence stars. They burn hydrogen in their cores, creating nuclear fusion. Some of these stars are average in size and some are huge. Main sequence stars are grouped by astronomers according to the colours they give out. Stars that look blue and white are the hottest ...
... Stars begin their lives as main sequence stars. They burn hydrogen in their cores, creating nuclear fusion. Some of these stars are average in size and some are huge. Main sequence stars are grouped by astronomers according to the colours they give out. Stars that look blue and white are the hottest ...
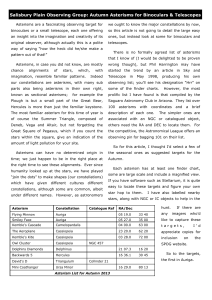
Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
... angles to your first line and have sweep round with your binoculars and you should find the Cascade. Cassiopeia: The Aeroplane The Aeroplane actually looks like its intended name, and appears to be dive-bombing M52! It’s alternative name is the Arrow, but I think the former is better. Images reveal ...
... angles to your first line and have sweep round with your binoculars and you should find the Cascade. Cassiopeia: The Aeroplane The Aeroplane actually looks like its intended name, and appears to be dive-bombing M52! It’s alternative name is the Arrow, but I think the former is better. Images reveal ...
On the nature of early-type emission line objects in NGC6611
... NGC6611 is a young open cluster with log(Age) = 6.2 or 6.8, depending on the authors. According to Hillenbrand et al. (1993) and to de Winter et al. (1997) it contains a great number of emission line stars (ELS), whereas Herbig & Dahm (2001) only found a small number of these. It is however worth no ...
... NGC6611 is a young open cluster with log(Age) = 6.2 or 6.8, depending on the authors. According to Hillenbrand et al. (1993) and to de Winter et al. (1997) it contains a great number of emission line stars (ELS), whereas Herbig & Dahm (2001) only found a small number of these. It is however worth no ...
Slide 1
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
The Significance of Mega Stars
... Even though the Sun and Deneb were 60° apart in terms of latitude, there was still a conjunction in longitude, with the Sun crossing the Deneb meridian at the time of the miracle. Just as there are meridians—lines of energy flow—in the human being, these meridians exist also in the greater cosmos of ...
... Even though the Sun and Deneb were 60° apart in terms of latitude, there was still a conjunction in longitude, with the Sun crossing the Deneb meridian at the time of the miracle. Just as there are meridians—lines of energy flow—in the human being, these meridians exist also in the greater cosmos of ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.