Chapter21
... so it isn’t reasonable to treat single stars as if they were ordinary and binary stars as if they were unusual. Second, we now have a clear enough picture of the evolution of close binary systems that it seemed important to present an organized discussion of the evolution of close binary systems, wh ...
... so it isn’t reasonable to treat single stars as if they were ordinary and binary stars as if they were unusual. Second, we now have a clear enough picture of the evolution of close binary systems that it seemed important to present an organized discussion of the evolution of close binary systems, wh ...
galctr
... M. Reid: Is Sgr A* a SMBH at the dynamic center of the Milky Way? Is Sgr A* at the center of the stellar cluster? -- yes, within 10 mas (orbit of S-2 has pericenter only 15 mas from Sgr A*) Is Sgr A* tied to the stellar cluster? -- yes; comparing proper motions from IR, radio; velocity with 70 ...
... M. Reid: Is Sgr A* a SMBH at the dynamic center of the Milky Way? Is Sgr A* at the center of the stellar cluster? -- yes, within 10 mas (orbit of S-2 has pericenter only 15 mas from Sgr A*) Is Sgr A* tied to the stellar cluster? -- yes; comparing proper motions from IR, radio; velocity with 70 ...
Lecture18
... • The closest stars are three stars the make up a multiple system in the constellation of Centaurus ...
... • The closest stars are three stars the make up a multiple system in the constellation of Centaurus ...
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
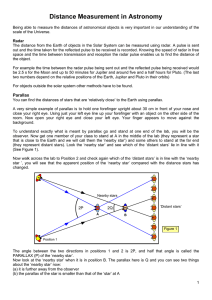
TAP 704- 8: The ladder of astronomical distances
... Brighter galaxies spin faster Beyond the distance where individual stars could be seen in galaxies, the only hope was to make further dangerous assumptions, for example that galaxies of the same type are equally bright, or equal in size. Neither method is helped by the fact that galaxies are seen at ...
... Brighter galaxies spin faster Beyond the distance where individual stars could be seen in galaxies, the only hope was to make further dangerous assumptions, for example that galaxies of the same type are equally bright, or equal in size. Neither method is helped by the fact that galaxies are seen at ...
The Relationship Between a Star`s Brightness and its Distance
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
Stars - gilbertmath.com
... The ______ ___________________ is actually just part of a larger star pattern known as ____________ ___________________, which is itself a _________________________. ...
... The ______ ___________________ is actually just part of a larger star pattern known as ____________ ___________________, which is itself a _________________________. ...
The double-degenerate, super-Chandrasekhar nucleus of the
... (M⊙ ). The origin of their complex morphologies is poorly understood1 , although several mechanisms involving binary interaction have been proposed2,3 . In close binary systems, the orbital separation is short enough for the primary star to overfill its Roche lobe as it expands during the Asymptotic ...
... (M⊙ ). The origin of their complex morphologies is poorly understood1 , although several mechanisms involving binary interaction have been proposed2,3 . In close binary systems, the orbital separation is short enough for the primary star to overfill its Roche lobe as it expands during the Asymptotic ...
Chapter 13
... • Aristotle wrote more than 2000 years ago that stars are heated by their passage through the heavens, but never considered that they evolved • In the 18th century, Immanuel Kant described the Sun as a fiery sphere, formed from the gases gravitated to the center of a solar nebula • In the 1850s and ...
... • Aristotle wrote more than 2000 years ago that stars are heated by their passage through the heavens, but never considered that they evolved • In the 18th century, Immanuel Kant described the Sun as a fiery sphere, formed from the gases gravitated to the center of a solar nebula • In the 1850s and ...
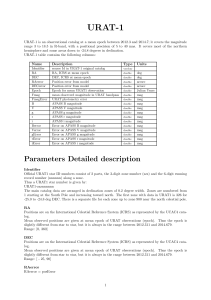
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 starting at the South Pole and increasing toward north. The first zone with data in URAT1 is 326 for -25.0 to -24.8 deg DEC. There is a separate file for each zone up to zone 900 ne ...
... URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 starting at the South Pole and increasing toward north. The first zone with data in URAT1 is 326 for -25.0 to -24.8 deg DEC. There is a separate file for each zone up to zone 900 ne ...
July 2014 BRAS Newsletter - The Baton Rouge Astronomical Society
... the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transi ...
... the constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transi ...
Heavy Metal from Ancient Superstars
... star formation histories of stellar populations The complexity of the Milky Way’s history is reflected in the compositions of its stars ...
... star formation histories of stellar populations The complexity of the Milky Way’s history is reflected in the compositions of its stars ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... This coordinate system is used to identify the position of an astronomical object as measured from the viewer’s location. Altitude – measures the vertical position of the object in degrees above (+ve) or below (-ve) the observer’s horizon. Azimuth – measures the horizontal position of the object ...
... This coordinate system is used to identify the position of an astronomical object as measured from the viewer’s location. Altitude – measures the vertical position of the object in degrees above (+ve) or below (-ve) the observer’s horizon. Azimuth – measures the horizontal position of the object ...
che
... due to a very wide X-ray eclipse In the hard X-ray range (18-60 keV) the eclipse form and width are very variable. ...
... due to a very wide X-ray eclipse In the hard X-ray range (18-60 keV) the eclipse form and width are very variable. ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
... Once the core hydrogen is exhausted, the star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that init ...
Telescopes: More Than Meets the Eye
... 1. What are the three main functions of a telescope? (the three main functions listed in order of importance are 1. light gathering 2. resolution 3. magnification) 2. What are some uses for a telescope? 3. Why does a stick appear to bend when it is placed partially in water? (refraction) Does it rea ...
... 1. What are the three main functions of a telescope? (the three main functions listed in order of importance are 1. light gathering 2. resolution 3. magnification) 2. What are some uses for a telescope? 3. Why does a stick appear to bend when it is placed partially in water? (refraction) Does it rea ...
Here
... • Using a good high resolution spectrum, you can get a much better measurement of the spectral energy distribution. • The disadvantage is that the efficiency is lower (more photons are lost in the complex optics). Also, it is difficult to measure more than one star at a time (in contrast to the dire ...
... • Using a good high resolution spectrum, you can get a much better measurement of the spectral energy distribution. • The disadvantage is that the efficiency is lower (more photons are lost in the complex optics). Also, it is difficult to measure more than one star at a time (in contrast to the dire ...
Magnitude of Stars - What`s Out Tonight?
... that passes through both the north and south to move and change in the sky because of the poles. Any spinning object has an axis that it Earth’s turning and circling. Think of the stars rotates about. Spin a small object and you will as the pictures and nicknacks on the walls of see that there is a ...
... that passes through both the north and south to move and change in the sky because of the poles. Any spinning object has an axis that it Earth’s turning and circling. Think of the stars rotates about. Spin a small object and you will as the pictures and nicknacks on the walls of see that there is a ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.