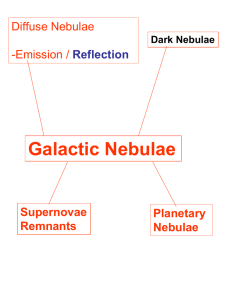
Practice Exam for 3 rd Astronomy Exam
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... young stars have been identified in each of these regions based on various techniques including objective prism surveys for chromospherically active Hα and CaII emission-line sources, the IRAS survey for objects with substantial mid-infrared excess due to circumstellar dust, and the ROSAT survey for ...
... young stars have been identified in each of these regions based on various techniques including objective prism surveys for chromospherically active Hα and CaII emission-line sources, the IRAS survey for objects with substantial mid-infrared excess due to circumstellar dust, and the ROSAT survey for ...
Notes 6 - University of Northern Iowa
... are particles that easily absorb energy, particularly large gas molecules and dust. Such large molecules can exist in the outer layers of these cool stars, and have been observed. The winds in these stars are actually best described as superwinds. These are the types of winds we see when we see larg ...
... are particles that easily absorb energy, particularly large gas molecules and dust. Such large molecules can exist in the outer layers of these cool stars, and have been observed. The winds in these stars are actually best described as superwinds. These are the types of winds we see when we see larg ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... travel between the two stars. Scientists say that Proxima Centauri is 4.2 light-years from the sun. One light-year, the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year, equals about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers). Stars are grouped in huge structures called galaxies. Telescopes hav ...
... travel between the two stars. Scientists say that Proxima Centauri is 4.2 light-years from the sun. One light-year, the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year, equals about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers). Stars are grouped in huge structures called galaxies. Telescopes hav ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 38-
... and look up at the stars. And after a little practice, they could pick a star and tell what its magnitude was. Because you only had six numbers to choose from and usually you could tell whether it was first, ‘cause they were very bright, or whether it was sixth, because you could hardly see them, an ...
... and look up at the stars. And after a little practice, they could pick a star and tell what its magnitude was. Because you only had six numbers to choose from and usually you could tell whether it was first, ‘cause they were very bright, or whether it was sixth, because you could hardly see them, an ...
Automated Detection and Analysis of Meteor Events Using Nightly
... sky and are more popularly known as “shooting stars”. I used an all-sky camera to observe these meteors. The all-sky camera is a low light sensitive camera with a fish-eye lens so it can observe the whole night sky. If a meteor occurs, the ASGARD motion detection program saves a video of the event a ...
... sky and are more popularly known as “shooting stars”. I used an all-sky camera to observe these meteors. The all-sky camera is a low light sensitive camera with a fish-eye lens so it can observe the whole night sky. If a meteor occurs, the ASGARD motion detection program saves a video of the event a ...
Pattern recognition of star constellations for spacecraft
... in attitude determination by the stars is as follows: some image forming device (e.g., a CCD-camera) is directed towards the stars. If the image can be matched to a reference, the direction of the imaging device is known, and thus the attitude of the spacecraft. One approach is to sweep the sky with ...
... in attitude determination by the stars is as follows: some image forming device (e.g., a CCD-camera) is directed towards the stars. If the image can be matched to a reference, the direction of the imaging device is known, and thus the attitude of the spacecraft. One approach is to sweep the sky with ...
Searching for stars in high-velocity clouds
... at similar distances to that of M31. In Fig. 1 we show the colour– magnitude plot for the three HVC fields and offsets. For a similar distance to M31 we would expect a cluster of stars (tip of red giant branch) around m I = 21–22 with colours of (V − I ) = 1.2–1.8 (box in Fig. 1). None of the colour ...
... at similar distances to that of M31. In Fig. 1 we show the colour– magnitude plot for the three HVC fields and offsets. For a similar distance to M31 we would expect a cluster of stars (tip of red giant branch) around m I = 21–22 with colours of (V − I ) = 1.2–1.8 (box in Fig. 1). None of the colour ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... based on how bright an object looks to us here on Earth, and intrinsic brightness (or luminosity), based on how bright an object actually is, independent of how far away it lies from a viewer. We have devised a scale of relative brightness called the “magnitude scale.” All objects of the same appare ...
... based on how bright an object looks to us here on Earth, and intrinsic brightness (or luminosity), based on how bright an object actually is, independent of how far away it lies from a viewer. We have devised a scale of relative brightness called the “magnitude scale.” All objects of the same appare ...
Project Descriptions - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... known as “blinking” in order to identify asteroids in the field. Even though asteroids are much smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be ...
... known as “blinking” in order to identify asteroids in the field. Even though asteroids are much smaller than stars, they are also much closer, which makes them appear as infinitely small, star-like objects when imaged with a telescope. This makes their identification confusing, as they can often be ...
The Great Debate - The Story Behind The Science
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
Navigating the Night Sky – Teacher Guide Argos Online Subject
... • Identify limitations of the map: o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, ...
... • Identify limitations of the map: o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, ...
Presentation - Relativity Group
... millions to billions of years? • By taking observations of many stars, we can study stars in many phases of life, just as we might study how humans age by observing the humans living in a village at one time. • What two basic physical properties do astronomers use to classify stars? • Stars are clas ...
... millions to billions of years? • By taking observations of many stars, we can study stars in many phases of life, just as we might study how humans age by observing the humans living in a village at one time. • What two basic physical properties do astronomers use to classify stars? • Stars are clas ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
The Sculptor dwarf irregular galaxy SDIG: present and past
... the distance modulus would be 27.85, based upon our measured apparent total magnitude and the calibration of absolute magnitudes by Richer & McCall (1995). The result is founded upon an LMC distance modulus of 18.37. It places SDIG near the far side of the Sculptor group, the members of which have d ...
... the distance modulus would be 27.85, based upon our measured apparent total magnitude and the calibration of absolute magnitudes by Richer & McCall (1995). The result is founded upon an LMC distance modulus of 18.37. It places SDIG near the far side of the Sculptor group, the members of which have d ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.