The Milky Way Galaxy
... Shapley’s model Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the cen ...
... Shapley’s model Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the cen ...
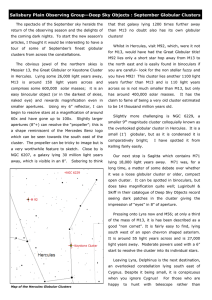
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
... this autumn, and get out under the night sky. ...
... this autumn, and get out under the night sky. ...
the life cycle of stars
... BLACK HOLE • A volume of space in which gravity is SO GREAT that nothing can escape, not even light, although objects can fall in • If the core of a supernova has a mass of more than about two Suns, its own gravity will squash it further, into a black hole. ...
... BLACK HOLE • A volume of space in which gravity is SO GREAT that nothing can escape, not even light, although objects can fall in • If the core of a supernova has a mass of more than about two Suns, its own gravity will squash it further, into a black hole. ...
The Life of a Star
... 2. Describe the differences between the life of a low-mass star and that of a star 10 times the Sun’s mass. Low-mass stars cool down and swell up into a red giant. Outer layers drift away and the star shrinks to become a white dwarf which will cool and fade away. High-mass stars swells into a red su ...
... 2. Describe the differences between the life of a low-mass star and that of a star 10 times the Sun’s mass. Low-mass stars cool down and swell up into a red giant. Outer layers drift away and the star shrinks to become a white dwarf which will cool and fade away. High-mass stars swells into a red su ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
Sammy Nagel · Annie Jump Cannon
... stars are.13. Look at what color stars are.14. She also determined what kind of gas they were.15. Won many other awards. Select one contribution and explain why this contribution was important. She discovered a system for describing how hot stars are. She used a mnemonic device to remember the lette ...
... stars are.13. Look at what color stars are.14. She also determined what kind of gas they were.15. Won many other awards. Select one contribution and explain why this contribution was important. She discovered a system for describing how hot stars are. She used a mnemonic device to remember the lette ...
May 2017 - Museums Wellington
... Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured A ...
... Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured A ...
Introduction to Stars ppt
... M-Sun star has 30 times more H than the Sun, but burns it with a luminosity that is 30,000 times greater. It’s lifetime is 30/30,000 = 1/10,000 as long as the Sun – corresponding to a lifetime of only a few million years. This is a very short time, cosmically speaking. This is one reason why massive ...
... M-Sun star has 30 times more H than the Sun, but burns it with a luminosity that is 30,000 times greater. It’s lifetime is 30/30,000 = 1/10,000 as long as the Sun – corresponding to a lifetime of only a few million years. This is a very short time, cosmically speaking. This is one reason why massive ...
review_one - MSU Solar Physics
... The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refracting telescopes Why the largest telescopes are reflecting ...
... The three components to measuring radiation The difference between light gathering power and resolving power The ways in which the atmosphere is not helpful to astronomy, and ways around it Compare and contrast reflecting and refracting telescopes Why the largest telescopes are reflecting ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
... Big Bang created hydrogen and some helium, along with a slew of other subatomic particles and electromagnetic radiation, but all the heavier elements were created inside stars. When the early massive stars “died” (their lifetimes were very short due to their enormous mass) the resulting explosions ( ...
Reading Preview
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
PHY2083
... The magnitudes of standard stars are corrected for absorption by the Earth’s atmosphere. The magnitude of any object determined by comparison is therefore a measure of its flux at Earth. This is called the APPARENT MAGNITUDE (m) In order to make comparisons more meaningful, define a measure of intri ...
... The magnitudes of standard stars are corrected for absorption by the Earth’s atmosphere. The magnitude of any object determined by comparison is therefore a measure of its flux at Earth. This is called the APPARENT MAGNITUDE (m) In order to make comparisons more meaningful, define a measure of intri ...
The Life Cycle of the Stars
... different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans, the typical star may last for millions or billions of years. While we cannot witness the complete life cycle of any one star, the night sky does reveal stars in various stages of stellar de ...
... different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans, the typical star may last for millions or billions of years. While we cannot witness the complete life cycle of any one star, the night sky does reveal stars in various stages of stellar de ...
Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... should make this a target for a night-time stellar-evolution lesson any time it is visible. The top part of the п-shaped constellation, centered on its brightest star, α, is in fact an OB association, a group of hot, young stars traveling in space together but not gravitationally bound enough to mai ...
... should make this a target for a night-time stellar-evolution lesson any time it is visible. The top part of the п-shaped constellation, centered on its brightest star, α, is in fact an OB association, a group of hot, young stars traveling in space together but not gravitationally bound enough to mai ...
and Concept Self-test (1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9)
... 5. What makes an ordinary star become a red giant is when the mass of helium outweighs the mass of hydrogen “burning” in the inner core, causing the helium to collapse inward, which forces the hydrogen to the outer core, where it continues fusion. Since the H is now in the outer core, the diameter ...
... 5. What makes an ordinary star become a red giant is when the mass of helium outweighs the mass of hydrogen “burning” in the inner core, causing the helium to collapse inward, which forces the hydrogen to the outer core, where it continues fusion. Since the H is now in the outer core, the diameter ...
Chapter 30 Section 2 Handout
... Gravitational energy is converted into heat energy, and the temperature of the protostar ...
... Gravitational energy is converted into heat energy, and the temperature of the protostar ...
Constellation ProjectConstellation Project(es)
... 7. What is the name of your Northern Hemisphere constellation? 8. What is your constellations coordinates? 9. What is the story of how your constellation got its name? (use the pdf “Stories of the con ...
... 7. What is the name of your Northern Hemisphere constellation? 8. What is your constellations coordinates? 9. What is the story of how your constellation got its name? (use the pdf “Stories of the con ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
stars
... • Are a group of stars that are connected together to make a picture (like connect the dots) • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
... • Are a group of stars that are connected together to make a picture (like connect the dots) • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
Problem set 2
... The star Proxima Centauri, probably bound gravitationally to α Centauri (α Cen), is a small main-sequence star of mass 0.123 solar. Using the empirical scaling between the mass and luminosity from the textbook, and between mass and radius (you can assume it’s linear, R ∼ M), compute Proxima’s effect ...
... The star Proxima Centauri, probably bound gravitationally to α Centauri (α Cen), is a small main-sequence star of mass 0.123 solar. Using the empirical scaling between the mass and luminosity from the textbook, and between mass and radius (you can assume it’s linear, R ∼ M), compute Proxima’s effect ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.