Stellar Evolution Notes
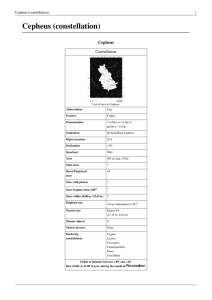
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Cepheus (constellation)
... Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern ...
... Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern ...
The Universe - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
The Universe
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
... • It provides us with many of the images we have of space. • It is an especially useful telescope because it does not have to view things through our atmosphere ...
Star Basics
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
Brichler-powerpoint
... • An object that orbits a star. • It must be large enough to have become rounded by it’s own gravity. • It must be the largest object in it’s orbit causing all particles to gravitate toward it. ...
... • An object that orbits a star. • It must be large enough to have become rounded by it’s own gravity. • It must be the largest object in it’s orbit causing all particles to gravitate toward it. ...
Nov13Guide - East-View
... Just below Andromeda lies the small constellation of Triangulum. Between the Andromeda Galaxy and Triangulum is another fairly large and local spiral galaxy, Messier 33 or the Pinwheel Galaxy. This galaxy is about three million light years distant but only contains about 40 billion stars. It is a di ...
... Just below Andromeda lies the small constellation of Triangulum. Between the Andromeda Galaxy and Triangulum is another fairly large and local spiral galaxy, Messier 33 or the Pinwheel Galaxy. This galaxy is about three million light years distant but only contains about 40 billion stars. It is a di ...
File
... from its visible light radiation? • We can use a star’s visible light spectrum to tell what that star is made of. • Prisms can be used to separate the colors of white light. The various wavelengths making up white light bend at different angles when they pass through the prism. They separate from ea ...
... from its visible light radiation? • We can use a star’s visible light spectrum to tell what that star is made of. • Prisms can be used to separate the colors of white light. The various wavelengths making up white light bend at different angles when they pass through the prism. They separate from ea ...
Document
... Only about half of this power reaches the earth's surface, meaning that a one square meter solar panel that is 15% efficient can generate about 100 watts while the sun is shining…that is enough to light six compact florescent bulbs ...
... Only about half of this power reaches the earth's surface, meaning that a one square meter solar panel that is 15% efficient can generate about 100 watts while the sun is shining…that is enough to light six compact florescent bulbs ...
Star Light, Star Bright: Exploring how stars are classified
... LP _________________________________________ Date ________ Objectives: • Students will work in small groups to organize stars into different categories based on observations of properties for a collection of stars. Materials: • One set of colored and laminated stars per 4 students: Star Set (pdf) Pr ...
... LP _________________________________________ Date ________ Objectives: • Students will work in small groups to organize stars into different categories based on observations of properties for a collection of stars. Materials: • One set of colored and laminated stars per 4 students: Star Set (pdf) Pr ...
Astronomy
... 18. What does apparent visual magnitude (mv) measure? What is the highest magnitude of stars that are still visible with the naked eye? How bright stars look from Earth. The dimmest we can see are about a magnitude of 6 ...
... 18. What does apparent visual magnitude (mv) measure? What is the highest magnitude of stars that are still visible with the naked eye? How bright stars look from Earth. The dimmest we can see are about a magnitude of 6 ...
docx - STAO
... When you gaze up in the night sky some stars will be very bright while other stars are barely visible to the unaided eye. With the aid of binoculars you may be able to observe different colours in the stars. The brightness and colour of a star depends on three factors: temperature, distance, and siz ...
... When you gaze up in the night sky some stars will be very bright while other stars are barely visible to the unaided eye. With the aid of binoculars you may be able to observe different colours in the stars. The brightness and colour of a star depends on three factors: temperature, distance, and siz ...
Teacher Demo: Bright Star or Close Star?
... When you gaze up in the night sky some stars will be very bright while other stars are barely visible to the unaided eye. With the aid of binoculars you may be able to observe different colours in the stars. The brightness and colour of a star depends on three factors: temperature, distance, and siz ...
... When you gaze up in the night sky some stars will be very bright while other stars are barely visible to the unaided eye. With the aid of binoculars you may be able to observe different colours in the stars. The brightness and colour of a star depends on three factors: temperature, distance, and siz ...
Birth and Death of Stars
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This depends on the amount of light emitted by the star and how close it is to the Earth. The lower the number the greater the apparent magnitude. • Absolute magnitude is how bright the star would be if all stars were the sam ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This depends on the amount of light emitted by the star and how close it is to the Earth. The lower the number the greater the apparent magnitude. • Absolute magnitude is how bright the star would be if all stars were the sam ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #20 Key
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... stars ? If an astronomer were observing from the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa, by how much would Vega shift during the Jovian year ? (Hint: Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the sun.) A parallax of 0.129 means that when the observer moves 1 AU, the star shifts 0.129 arcsec. Since the diameter of the Earth’ ...
... stars ? If an astronomer were observing from the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa, by how much would Vega shift during the Jovian year ? (Hint: Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the sun.) A parallax of 0.129 means that when the observer moves 1 AU, the star shifts 0.129 arcsec. Since the diameter of the Earth’ ...
Star Questions 2008 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... What does it mean for a star to have a life cycle? Explain what it means for a star to be on the main sequence. Which two pressures act upon any star on the main sequence? Why a star remains roughly the same diameter when on the main sequence. Explain the following relationships: a. Surface temperat ...
... What does it mean for a star to have a life cycle? Explain what it means for a star to be on the main sequence. Which two pressures act upon any star on the main sequence? Why a star remains roughly the same diameter when on the main sequence. Explain the following relationships: a. Surface temperat ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... Define brightness (see text), apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude. ...
... Define brightness (see text), apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude. ...
Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one other? 3. Are the same stars visible every night of the year? What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What cause ...
... 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one other? 3. Are the same stars visible every night of the year? What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What cause ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.