ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
... • So, a large cloud (1000s to ~million solar masses) gets cold enough that many cores collapse into stars, giving a cluster • Each star clears gas disk away, but the cluster as a whole also blows out all the remaining interstellar gas, shutting down star formation • The stars settle onto the main se ...
Name - MIT
... A) It is the world's largest operating telescope. B) It refers to any kind of instrument that can be hooked up to a telescope. C) It is an electronic detector that can be used in place of photographic film for taking images of the sky. D) It is a unit used by astronomers to measure angular resolutio ...
... A) It is the world's largest operating telescope. B) It refers to any kind of instrument that can be hooked up to a telescope. C) It is an electronic detector that can be used in place of photographic film for taking images of the sky. D) It is a unit used by astronomers to measure angular resolutio ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... other spiral galaxies to help us predict its structure. 2 million light yrs. away ...
... other spiral galaxies to help us predict its structure. 2 million light yrs. away ...
Announcements Evolution of High-Mass Stars: Red Supergiants
... Period-Luminosity Relation • The connection between a Cepheid’s pulse period and its luminosity. ...
... Period-Luminosity Relation • The connection between a Cepheid’s pulse period and its luminosity. ...
Lecture16
... distance, we could find their luminosity. We can measure the distance to stars with parallax (our old friend). ...
... distance, we could find their luminosity. We can measure the distance to stars with parallax (our old friend). ...
Exam 03
... D) Red. The reflection nebula is hot and glows red because of the strong H-α emission line. E) Blue. A cool reflection nebula reflects and scatters the blue light that strikes it. 53. An emission nebula will typically appear A) White. A nebula is a cloud of water vapor, so it appears white or maybe ...
... D) Red. The reflection nebula is hot and glows red because of the strong H-α emission line. E) Blue. A cool reflection nebula reflects and scatters the blue light that strikes it. 53. An emission nebula will typically appear A) White. A nebula is a cloud of water vapor, so it appears white or maybe ...
Hubble`s Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a
... for the density wave theory, not the other way around. Similarly, the fact that we see star formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Also, while population I stars are younger than population II stars, not all (or even most) populati ...
... for the density wave theory, not the other way around. Similarly, the fact that we see star formation implies that elliptical galaxies were once more efficient then spirals, not the other way around. Also, while population I stars are younger than population II stars, not all (or even most) populati ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
... locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not interact then we call this an optical double. It is possible, but rarer for 4 or 6 stars to be grouped into Computer simulati ...
Chapter 12
... 5. Only stars within about 120 parsecs (400 light-years) have parallax angles great enough to allow accurate calculations of their distances from Earth. 6. The satellite Hipparchos measured positions and parallaxes to an accuracy of 0.001 arcsecond. Its successor, Gaia (to be launched in 2011), will ...
... 5. Only stars within about 120 parsecs (400 light-years) have parallax angles great enough to allow accurate calculations of their distances from Earth. 6. The satellite Hipparchos measured positions and parallaxes to an accuracy of 0.001 arcsecond. Its successor, Gaia (to be launched in 2011), will ...
proper motion
... parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as good as +/- 1 arc minute, but he could measure no parallaxes. This implied either that the stars were more than 3000 Astronomical Units away, or that the Earth was ...
... parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as good as +/- 1 arc minute, but he could measure no parallaxes. This implied either that the stars were more than 3000 Astronomical Units away, or that the Earth was ...
Document
... http://www.fedtrek.com/staff/omega13a/celestia/omega_galaxy/index.php?mode=view&type=moon&num=8&parent_id=83249&star=1125858 ...
... http://www.fedtrek.com/staff/omega13a/celestia/omega_galaxy/index.php?mode=view&type=moon&num=8&parent_id=83249&star=1125858 ...
Double Stars in Scorpio`s Claws
... stars that are a rewarding challenge to any astronomer. Some of these are actual double stars (pairs of stars that orbit about each other), others are ‘apparent doubles’ – stars that simply lie along the same line of sight, but are very distant from each other in space. The map below indicates the l ...
... stars that are a rewarding challenge to any astronomer. Some of these are actual double stars (pairs of stars that orbit about each other), others are ‘apparent doubles’ – stars that simply lie along the same line of sight, but are very distant from each other in space. The map below indicates the l ...
How Far is far ?
... easier to spot in distant galaxies • Some types of Supernova have an intrinsic brightness which can be compared to their actual brightness observed on Earth to judge distance. • But Supernova are not all the same... ...
... easier to spot in distant galaxies • Some types of Supernova have an intrinsic brightness which can be compared to their actual brightness observed on Earth to judge distance. • But Supernova are not all the same... ...
Reading the Stars
... 1. Examine color-magnitude diagrams of clusters of stars. Since a cluster of stars is a group of stars that were formed at the same time from the same cloud of gas and dust, we can learn a lot about the stars within that cluster. A color-magnitude diagram is a kind of H-R Diagram. The horizontal axi ...
... 1. Examine color-magnitude diagrams of clusters of stars. Since a cluster of stars is a group of stars that were formed at the same time from the same cloud of gas and dust, we can learn a lot about the stars within that cluster. A color-magnitude diagram is a kind of H-R Diagram. The horizontal axi ...
The Sun Compared to Other Stars
... The Sun Compared to Other Stars • Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram: A graph plot indicating individual stars as points, with stellar luminosity on the vertical axis & surface temperature (spectral type) on the horizontal axis • We can use spectroscopy to determine the spectral type & luminosity of a ...
... The Sun Compared to Other Stars • Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram: A graph plot indicating individual stars as points, with stellar luminosity on the vertical axis & surface temperature (spectral type) on the horizontal axis • We can use spectroscopy to determine the spectral type & luminosity of a ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... Identify the temperature associated with each color, and include an example of a star that would appear each color. ...
... Identify the temperature associated with each color, and include an example of a star that would appear each color. ...
The Night Sky
... Every August, the night sky produces its own version of fireworks, the Perseid meteor shower. This meteor shower is a summertime classic and among the oldest and most publicized of all such showers. Astronomers have determined that comet Swift-Tuttle is the source of the Perseid shower as once every ...
... Every August, the night sky produces its own version of fireworks, the Perseid meteor shower. This meteor shower is a summertime classic and among the oldest and most publicized of all such showers. Astronomers have determined that comet Swift-Tuttle is the source of the Perseid shower as once every ...
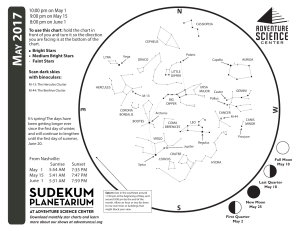
1705 chart front
... them orbit around their parent planet. If you have trouble steadying your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Mo ...
... them orbit around their parent planet. If you have trouble steadying your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Mo ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.