Properties of Galactic early-type O
... space (hereafter called velocity porosity). This arises because the dense absorbing clumps along a given line of sight, only occur at discrete velocities, and leads to a reduction in the strength of P Cygni absorption components (Owocki 2008). This velocity porosity has been implemented in 2D/3D sto ...
... space (hereafter called velocity porosity). This arises because the dense absorbing clumps along a given line of sight, only occur at discrete velocities, and leads to a reduction in the strength of P Cygni absorption components (Owocki 2008). This velocity porosity has been implemented in 2D/3D sto ...
Stellar Populations of Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies: UBVRI Photometry
... UBVRI images of 16 dwarf elliptical galaxies in the Virgo Cluster were obtained with the VATT 1.8m on 2003 March 29-31. The telescope was equipped with CCD26, a thinned Loral 3 2048 × 2048 CCD with 15µm pixels. CCD26 has a read noise of 5.7 e− and a gain of 1.9 e− per ADU was used. On-chip binning o ...
... UBVRI images of 16 dwarf elliptical galaxies in the Virgo Cluster were obtained with the VATT 1.8m on 2003 March 29-31. The telescope was equipped with CCD26, a thinned Loral 3 2048 × 2048 CCD with 15µm pixels. CCD26 has a read noise of 5.7 e− and a gain of 1.9 e− per ADU was used. On-chip binning o ...
How We See The Sky
... Diffraction places a limit on the resolution of an optical system. As detail becomes smaller, diffraction has a proportionally stronger “smearing” effect (failure to fully “transfer” scene contrast), diminishing the ability of the optical system to resolve fine detail. High MTF at low contrast level ...
... Diffraction places a limit on the resolution of an optical system. As detail becomes smaller, diffraction has a proportionally stronger “smearing” effect (failure to fully “transfer” scene contrast), diminishing the ability of the optical system to resolve fine detail. High MTF at low contrast level ...
Galaxy formation in the Planck cosmology - II. Star
... VESPA recovers the SFH of a galaxy in 3 to 16 age bins (depending on the quality of the spectra), logarithmically spaced between 0.002 Gyr and the age of the Universe. For each age bin, VESPA returns the total mass formed within the bin and a mass-weighted metallicity of the bin, together with an es ...
... VESPA recovers the SFH of a galaxy in 3 to 16 age bins (depending on the quality of the spectra), logarithmically spaced between 0.002 Gyr and the age of the Universe. For each age bin, VESPA returns the total mass formed within the bin and a mass-weighted metallicity of the bin, together with an es ...
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... sophisticated and easy to use telescopes available on the market today. Take time to read through this manual before embarking on your journey through the Universe. It may take a few observing sessions to become familiar with your NexStar, so you should keep this manual handy until you have fully ma ...
... sophisticated and easy to use telescopes available on the market today. Take time to read through this manual before embarking on your journey through the Universe. It may take a few observing sessions to become familiar with your NexStar, so you should keep this manual handy until you have fully ma ...
MPhil Thesis - Final - Suzanne Knight
... While post main sequence evolution pose barriers to close planetary companions for white dwarfs, giant planets have nevertheless been detected, such as the confirmed ~ 2.5 MJup planetary companion at a distance ~ 43 AU from its primary located in the 2M1207 system (Sigurdsson et al. 2003; Chauvin et ...
... While post main sequence evolution pose barriers to close planetary companions for white dwarfs, giant planets have nevertheless been detected, such as the confirmed ~ 2.5 MJup planetary companion at a distance ~ 43 AU from its primary located in the 2M1207 system (Sigurdsson et al. 2003; Chauvin et ...
The Life and Work of Edward Emerson Barnard
... his sick bed long enough to note that the ring was still visible in the 40-inch telescope, though 'very thin' and with a satellite at each end. 'Without occultation it was almost impossible to see any trace of the ring on the sky,' he noted 'The condensations were feebly seen as slightly brighter pa ...
... his sick bed long enough to note that the ring was still visible in the 40-inch telescope, though 'very thin' and with a satellite at each end. 'Without occultation it was almost impossible to see any trace of the ring on the sky,' he noted 'The condensations were feebly seen as slightly brighter pa ...
Altas Farnese
... differences are universal, they cannot be used to point towards or away from any one source. Instead, these differences indicate changes made after the information had left the astronomer, likely by the sculptor. Similarly, the universal similarities between the globe and all ancient sources (e.g., ...
... differences are universal, they cannot be used to point towards or away from any one source. Instead, these differences indicate changes made after the information had left the astronomer, likely by the sculptor. Similarly, the universal similarities between the globe and all ancient sources (e.g., ...
Comets, historical records and vedic literature
... Ketus (in plural), meaning rays of light or fire-smoke combine, have also been discussed in Atharvaveda, and it is very likely that they represented comets or meteors (Kochhar, 2010). Book one of Rigveda has two hymns (1,24,7) and (1,24,8) which have been translated by Griffith (1896) as follows: 7. ...
... Ketus (in plural), meaning rays of light or fire-smoke combine, have also been discussed in Atharvaveda, and it is very likely that they represented comets or meteors (Kochhar, 2010). Book one of Rigveda has two hymns (1,24,7) and (1,24,8) which have been translated by Griffith (1896) as follows: 7. ...
2 Statistical properties of a sample of periodically variable B-type supergiants
... oscillations rather than mass loss. Lovy et al. (1984) indeed managed to come up with a theoretical PLC relation in agreement with the observed one for this type of stars. However, only 40% of the variable supergiants have periods compatible with the radial fundamental mode, while the majority must ...
... oscillations rather than mass loss. Lovy et al. (1984) indeed managed to come up with a theoretical PLC relation in agreement with the observed one for this type of stars. However, only 40% of the variable supergiants have periods compatible with the radial fundamental mode, while the majority must ...
The physics of star formation
... recent decades that we have begun to gain some physical understanding of how this happens. Observations at many wavelengths, especially radio and infrared, have led to great advances in our knowledge of the subject, and the observational study of star formation is now a large and active field of res ...
... recent decades that we have begun to gain some physical understanding of how this happens. Observations at many wavelengths, especially radio and infrared, have led to great advances in our knowledge of the subject, and the observational study of star formation is now a large and active field of res ...
The physics of star formation - Yale Astronomy
... recent decades that we have begun to gain some physical understanding of how this happens. Observations at many wavelengths, especially radio and infrared, have led to great advances in our knowledge of the subject, and the observational study of star formation is now a large and active field of res ...
... recent decades that we have begun to gain some physical understanding of how this happens. Observations at many wavelengths, especially radio and infrared, have led to great advances in our knowledge of the subject, and the observational study of star formation is now a large and active field of res ...
Binarity in carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars
... elements (e.g. Suda et al. 2004). Mass transfer mechanisms that would transfer carbon – but no or few s-process elements – are theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some r ...
... elements (e.g. Suda et al. 2004). Mass transfer mechanisms that would transfer carbon – but no or few s-process elements – are theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some r ...
Annual Report 2006/2007
... supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A). This object is the brightest radio source in the sky, and has been created by a supernova explosion about 330 year ago. The star itself had a mass of around 20 times the mass of the sun, but by the time it exploded it must have lost most of the outer layers. T ...
... supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A). This object is the brightest radio source in the sky, and has been created by a supernova explosion about 330 year ago. The star itself had a mass of around 20 times the mass of the sun, but by the time it exploded it must have lost most of the outer layers. T ...
13.1 Galaxy Evolution: Introduction
... You take a quantity of gas and turn it all into stars instantaneously – a delta function starformation rate – distributed according to your initial mass function, and then follow its evolution in time. This is what's known as a simple stellar population. There is no such thing in real ...
... You take a quantity of gas and turn it all into stars instantaneously – a delta function starformation rate – distributed according to your initial mass function, and then follow its evolution in time. This is what's known as a simple stellar population. There is no such thing in real ...
A Search for Extrasolar Planets Using Echoes Produced in Flare
... noticeable amount of energy that disturbs the steady state of the star on the whole or a part of it.’” The first noted occurrence of a flare from a star other than the Sun was in 1924 by Hertzsprung. At the time of the observation, Ejnar Hertzsprung attributed the brightening of the star to an in fa ...
... noticeable amount of energy that disturbs the steady state of the star on the whole or a part of it.’” The first noted occurrence of a flare from a star other than the Sun was in 1924 by Hertzsprung. At the time of the observation, Ejnar Hertzsprung attributed the brightening of the star to an in fa ...
Hunting for Substructure in the Milky Way
... has evolved over time with ongoing research in the area. At its most basic level, the Milky Way is a barred disk galaxy with spiral arms. Its main components are the central bulge, the disk and the surrounding halo. When analysed in further detail, the disk can be divided into two components; a thin ...
... has evolved over time with ongoing research in the area. At its most basic level, the Milky Way is a barred disk galaxy with spiral arms. Its main components are the central bulge, the disk and the surrounding halo. When analysed in further detail, the disk can be divided into two components; a thin ...
Carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars in dwarf galaxies
... [Fe/H]≤ −4.5 are CEMP-no stars. These objects have peculiar chemical abundance patterns consistent with the yields predicted for primordial faint SN (e.g. Iwamoto et al. 2005). However, we also note that these extreme stars are part of a common, global trend, which involves stars in both the Galacti ...
... [Fe/H]≤ −4.5 are CEMP-no stars. These objects have peculiar chemical abundance patterns consistent with the yields predicted for primordial faint SN (e.g. Iwamoto et al. 2005). However, we also note that these extreme stars are part of a common, global trend, which involves stars in both the Galacti ...
Long-term monitoring of the short period SU UMa
... 4.1. superhump period change Her simply lies in the majority of SU UMa-type dwarf Historically, the superhump period had been known to novae. decrease during the course of the superoutburst before In order to examine whether V844 Her shows other the tidal instability was discovered (Haefner et al. 1 ...
... 4.1. superhump period change Her simply lies in the majority of SU UMa-type dwarf Historically, the superhump period had been known to novae. decrease during the course of the superoutburst before In order to examine whether V844 Her shows other the tidal instability was discovered (Haefner et al. 1 ...
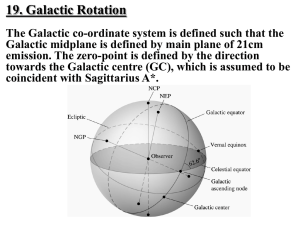
sections 19-22 instructor notes
... The maximum and/or minimum observed radial velocities of hydrogen clouds along such lines of sight in the 1st and 4th quadrants, respectively, must originate from gas located at the tangent points, if there is any. In general terms there will always be some hydrogen gas at the tangent points, but t ...
... The maximum and/or minimum observed radial velocities of hydrogen clouds along such lines of sight in the 1st and 4th quadrants, respectively, must originate from gas located at the tangent points, if there is any. In general terms there will always be some hydrogen gas at the tangent points, but t ...
Multiwavelength observations of XTE J1118+480`s outburst
... up to 0.1 mJy associated with low/hard X-ray emission => compact object is a neutron star But correlation not always verified… S. Chaty - ESO - 28/11/2006 ...
... up to 0.1 mJy associated with low/hard X-ray emission => compact object is a neutron star But correlation not always verified… S. Chaty - ESO - 28/11/2006 ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.