Galaxies - cloudfront.net
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
An analogy
... – distant galaxies are younger than those used to define the Hubble Sequence – more peculiar galaxies are observed: could be due to patchy star formation (younger age) or to interactions being more frequent (denser Universe) – resolution is poor compared to local galaxies and usually limited to a fe ...
... – distant galaxies are younger than those used to define the Hubble Sequence – more peculiar galaxies are observed: could be due to patchy star formation (younger age) or to interactions being more frequent (denser Universe) – resolution is poor compared to local galaxies and usually limited to a fe ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
... • What is the significance of a rotation curve that is flat at large distances from the galactic center? • The Milky Way’s flat rotation curve implies that the matter associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or ga ...
Life Cycle of the Stars
... This H–R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun. The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the main sequence. ...
... This H–R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun. The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the main sequence. ...
- newmanlib.ibri.org
... Our galaxy has been called "the Milky Way" since ancient times, long before we knew what it was. It is shaped rather like two fried eggs laid back-to-back, or a pair of marching-band cymbals, that is, a rather flat disk of stars with a flattened-roundish bulge of stars in the center. It appears to b ...
... Our galaxy has been called "the Milky Way" since ancient times, long before we knew what it was. It is shaped rather like two fried eggs laid back-to-back, or a pair of marching-band cymbals, that is, a rather flat disk of stars with a flattened-roundish bulge of stars in the center. It appears to b ...
Chapter 12
... Thought Question What happens in a low-mass star when core temperature rises enough for helium fusion to begin? A. Helium fusion slowly starts up. B. Hydrogen fusion stops. C. Helium fusion rises very sharply. (Hint: Degeneracy pressure is the main form of pressure in the inert helium core.) ...
... Thought Question What happens in a low-mass star when core temperature rises enough for helium fusion to begin? A. Helium fusion slowly starts up. B. Hydrogen fusion stops. C. Helium fusion rises very sharply. (Hint: Degeneracy pressure is the main form of pressure in the inert helium core.) ...
CHP 11
... c. Hydrostatic equilibrium d. The neutrino process e. none of the above The Great Nebula in Orion a. is a Herbig-Haro object. b. is a reflection nebula. c. is an emission nebula. d. contains only young low mass stars. e. is believed to be about 5 billion years old. The capture of too few solar neutr ...
... c. Hydrostatic equilibrium d. The neutrino process e. none of the above The Great Nebula in Orion a. is a Herbig-Haro object. b. is a reflection nebula. c. is an emission nebula. d. contains only young low mass stars. e. is believed to be about 5 billion years old. The capture of too few solar neutr ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... cluster, the ‘jaw’ of the bull in the Taurus constellation. The data showed that some of the stars that were apparently part of this cluster were impostors: they are not in fact travelling with the cluster, and over time will part company with its true members. ...
... cluster, the ‘jaw’ of the bull in the Taurus constellation. The data showed that some of the stars that were apparently part of this cluster were impostors: they are not in fact travelling with the cluster, and over time will part company with its true members. ...
Science Grade 08 Unit 11 Exemplar Lesson 02: Classifying Stars
... 5. Ask students to open their notebooks to the Handout: Galaxies and Stars Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continu ...
... 5. Ask students to open their notebooks to the Handout: Galaxies and Stars Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continu ...
Supermassive black holes
... 1) They are generally very distant 2) They were more common early in time 3) Galaxy collisions might turn them on 4)Nearby galaxies might hold dead quasars ...
... 1) They are generally very distant 2) They were more common early in time 3) Galaxy collisions might turn them on 4)Nearby galaxies might hold dead quasars ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y- ...
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you to control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, BV, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y- ...
The evolution of stars - School of Physics
... Recall that the interstellar material from which the solar system formed consists mostly of hydrogen and helium, with other elements less than one-thousandth as abundant as hydrogen. ...
... Recall that the interstellar material from which the solar system formed consists mostly of hydrogen and helium, with other elements less than one-thousandth as abundant as hydrogen. ...
Astro 6590: Galaxies and the Universe Astro
... stars, plus an amount up to 1/2 of as much by mass of gas, and about 10X as much by mass of dark matter. The stars and gas are about 70% hydrogen by mass and 25% helium, the rest being heavier elements (called "metals"). • Typical scales are: masses between 106 to 1012 M (1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 k ...
... stars, plus an amount up to 1/2 of as much by mass of gas, and about 10X as much by mass of dark matter. The stars and gas are about 70% hydrogen by mass and 25% helium, the rest being heavier elements (called "metals"). • Typical scales are: masses between 106 to 1012 M (1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 k ...
It`s cosmic! - NSW Department of Education
... Photograph of a spiral galaxy courtesy NASA Extract from Science Syllabus Years 7-10 © Board of Studies, NSW 2003 Photograph of the crab nebula © Malin/Pasachoff/Caltech Photograph of a telescope, courtesy Ric Morante © Upgrade Business Systems Pty Ltd Photographs of Saturn and Pluto, courtesy of NA ...
... Photograph of a spiral galaxy courtesy NASA Extract from Science Syllabus Years 7-10 © Board of Studies, NSW 2003 Photograph of the crab nebula © Malin/Pasachoff/Caltech Photograph of a telescope, courtesy Ric Morante © Upgrade Business Systems Pty Ltd Photographs of Saturn and Pluto, courtesy of NA ...
Here - Astrophysics Research Institute
... (transit), and set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – beca ...
... (transit), and set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – beca ...
GoSkyWatch User`s Guide
... with how old you were for the star light seen. For star light older than you are, the date of the star light is shown. Tap the [Now] button to show the star light date of all stars. Comets. Can be sorted by name, distance or magnitude. * Only available with the universal iPhone/iPad version. ...
... with how old you were for the star light seen. For star light older than you are, the date of the star light is shown. Tap the [Now] button to show the star light date of all stars. Comets. Can be sorted by name, distance or magnitude. * Only available with the universal iPhone/iPad version. ...
Lecture Notes
... ‘Regular’ clusters appear to be populated mainly by elliptical galaxies, while ‘irregular’ clusters tend to include all galaxy types. Both often have a giant elliptical galaxy (a so-called cD galaxy), ∼200 kpc in diameter, at the centre of the gravitational well. It is thought that the large number ...
... ‘Regular’ clusters appear to be populated mainly by elliptical galaxies, while ‘irregular’ clusters tend to include all galaxy types. Both often have a giant elliptical galaxy (a so-called cD galaxy), ∼200 kpc in diameter, at the centre of the gravitational well. It is thought that the large number ...
Telescopes: More Than Meets the Eye
... Constellations: Imaginary, dot-to-dot pictures drawn using the stars as the dots. These are used to map the nighttime sky. There are 88 constellations all together. Deep Space Objects: These objects are very distant from Earth and can usually only be seen with a telescope. They include: galaxies, di ...
... Constellations: Imaginary, dot-to-dot pictures drawn using the stars as the dots. These are used to map the nighttime sky. There are 88 constellations all together. Deep Space Objects: These objects are very distant from Earth and can usually only be seen with a telescope. They include: galaxies, di ...
The star formation histories of two northern LMC fields
... and Fig. 6. Average star formation rates for each era are given assuming a Salpeter initial mass function (IMF) with cut-offs at 120 and 0.1 M(, which is consistent with the Holtzman et al. (1997) results. An IMF error would simply have the result of changing the ratio of old to young stars, but wou ...
... and Fig. 6. Average star formation rates for each era are given assuming a Salpeter initial mass function (IMF) with cut-offs at 120 and 0.1 M(, which is consistent with the Holtzman et al. (1997) results. An IMF error would simply have the result of changing the ratio of old to young stars, but wou ...
Chapter 20
... Though a given element always has the same number of protons in a nucleus, it can have several different numbers of neutrons. (The number of neutrons is usually somewhere between 1 and 2 times the number of protons. The most common form of hydrogen, just a single proton, is the main exception to thi ...
... Though a given element always has the same number of protons in a nucleus, it can have several different numbers of neutrons. (The number of neutrons is usually somewhere between 1 and 2 times the number of protons. The most common form of hydrogen, just a single proton, is the main exception to thi ...
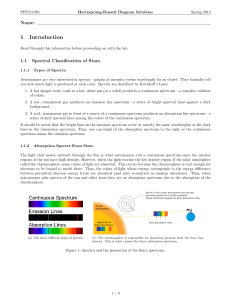
1 Introduction - High Point University
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
Dipper, Sword, Snake and Turtle
... such observations did not arise from academic or scientific interest in a modern sense, but were tightly linked to cosmological and religious concepts extant not only in prehistoric and early historic Mesopotamia and China (Kelley/Malone, 2005; Selin (Ed.), 2001; Hunger/Pingree 1999; Rogers, 1998; K ...
... such observations did not arise from academic or scientific interest in a modern sense, but were tightly linked to cosmological and religious concepts extant not only in prehistoric and early historic Mesopotamia and China (Kelley/Malone, 2005; Selin (Ed.), 2001; Hunger/Pingree 1999; Rogers, 1998; K ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.