Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z=8.6
... Although we cannot derive the characteristics of the stellar population in UDFy-38135539, similarly selected galaxies at lower redshifts, z < 5–7, seem to be young (ages between 10 and 100 million years, Myr) and have both low metallicity and low extinction15–17. Plausible characteristics for the st ...
... Although we cannot derive the characteristics of the stellar population in UDFy-38135539, similarly selected galaxies at lower redshifts, z < 5–7, seem to be young (ages between 10 and 100 million years, Myr) and have both low metallicity and low extinction15–17. Plausible characteristics for the st ...
ATLAS lifts the Cup: discovery of a new Milky Way satellite in Crater⋆†
... population implies that star formation occurred in Crater perhaps as recently as 400 Myr ago. No globular cluster has ever accomplished the feat of prolonging its star formation by several Gyr. Therefore, if our hypothesis that the blue bright stars in Crater are blue loop giants is correct, the new ...
... population implies that star formation occurred in Crater perhaps as recently as 400 Myr ago. No globular cluster has ever accomplished the feat of prolonging its star formation by several Gyr. Therefore, if our hypothesis that the blue bright stars in Crater are blue loop giants is correct, the new ...
The new X-ray universe
... of sources) and at the known distance of M82 this implied that it was “ultraluminous” (Lx >1039 erg s–1; the source in M82 varies up 1041 erg s–1). While the existence of such objects was hinted at by earlier missions, a substantial number have now been found in Chandra and XMM observations of nearb ...
... of sources) and at the known distance of M82 this implied that it was “ultraluminous” (Lx >1039 erg s–1; the source in M82 varies up 1041 erg s–1). While the existence of such objects was hinted at by earlier missions, a substantial number have now been found in Chandra and XMM observations of nearb ...
Rotation Periods of Wide Binaries in the Kepler Field
... Because most of the stars that satisfy the present criteria are relatively nearby, they should be expected to have low interstellar reddening. In any case, since the two components presumably lie at the same distance, the reddening would be expected to be the same, and so will not affect Figure 1. T ...
... Because most of the stars that satisfy the present criteria are relatively nearby, they should be expected to have low interstellar reddening. In any case, since the two components presumably lie at the same distance, the reddening would be expected to be the same, and so will not affect Figure 1. T ...
Navigating the Night Sky Checklist
... P# 5. Locating Objects With the Naked Eye 1. Reference a sky map, chart or other lists to identify the objects that are visible to the naked eye. A very good source is the monthly Sky Map available on the TAAS Fab 50 website. (www.TAAS.org) 2. Identify the constellation that the naked eye object is ...
... P# 5. Locating Objects With the Naked Eye 1. Reference a sky map, chart or other lists to identify the objects that are visible to the naked eye. A very good source is the monthly Sky Map available on the TAAS Fab 50 website. (www.TAAS.org) 2. Identify the constellation that the naked eye object is ...
Variations in Integrated Galactic Initial Mass Functions due to
... mass limit for clusters, if any, is unknown, this mass was taken because it is the lowest mass of groups of stars that is observed to be forming in the Taurus-Auriga region (Briceño et al., 2002). This lower limit is far below the range in which the power-law behaviour is observed. It is an extrapo ...
... mass limit for clusters, if any, is unknown, this mass was taken because it is the lowest mass of groups of stars that is observed to be forming in the Taurus-Auriga region (Briceño et al., 2002). This lower limit is far below the range in which the power-law behaviour is observed. It is an extrapo ...
Betelgeuse - TeacherWeb
... • In 1995 the Hubble’s telescope discovered Betelgeuse. It has been noticed before but never named. In 1836 Sir John Frederick William Hersche noticed that Betelgeuse had changed in brightness. ...
... • In 1995 the Hubble’s telescope discovered Betelgeuse. It has been noticed before but never named. In 1836 Sir John Frederick William Hersche noticed that Betelgeuse had changed in brightness. ...
ASTRONOMICAL BINOCULARS
... When you go out into the dark, your eyes need time to adjust. You will initially be able to see only a fraction of the stars and objects your eyes are capable of. Remain in the dark (don’t look at any lights or cell phones) for at least 30 minutes, and your eyes should be around 80% of their full da ...
... When you go out into the dark, your eyes need time to adjust. You will initially be able to see only a fraction of the stars and objects your eyes are capable of. Remain in the dark (don’t look at any lights or cell phones) for at least 30 minutes, and your eyes should be around 80% of their full da ...
Wolf-Rayet Stars
... tendency to refer to WN stars of classes 2 to 5 as early type (WNE) and classes 6 to 9 as late type (WNL). Similarly WC4-6 stars are designated as WCE, while WC7-9 stars are designated as WCL. Although there are important exceptions, WNE stars generally show no evidence for H emission while H emissi ...
... tendency to refer to WN stars of classes 2 to 5 as early type (WNE) and classes 6 to 9 as late type (WNL). Similarly WC4-6 stars are designated as WCE, while WC7-9 stars are designated as WCL. Although there are important exceptions, WNE stars generally show no evidence for H emission while H emissi ...
Neutron star masses: dwarfs, giants and neighbors
... magnetars an the fact that they are isolated • In a more conservative scenario we need large kicks to explain the fact that all known magnetars are isolated • Without detailed data about spatial velocities of magnetars it is difficult to make conclusions • Still, it is possible that the channel for ...
... magnetars an the fact that they are isolated • In a more conservative scenario we need large kicks to explain the fact that all known magnetars are isolated • Without detailed data about spatial velocities of magnetars it is difficult to make conclusions • Still, it is possible that the channel for ...
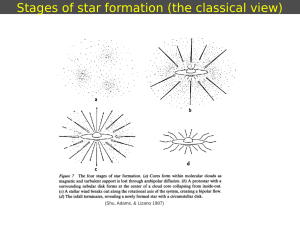
Stages of star formation (the classical view)
... High-mass star-forming regions are farther than low-mass. The closest is the Orion molecular cloud, at 500 pc (compared with Taurus at 140 pc) ...
... High-mass star-forming regions are farther than low-mass. The closest is the Orion molecular cloud, at 500 pc (compared with Taurus at 140 pc) ...
Neon abundances - UCL Astrophysics Group
... All observations were obtained with the Hamilton Echelle Spectrograph (HES; Vogt 1987) at the Lick Observatory, fed by the 0.6-m Coude Auxilliary Telescope (CAT), during four runs in 1994±1997. Further details of the instrument can be found in Misch (1997). Shortly before our observations in 1994, ...
... All observations were obtained with the Hamilton Echelle Spectrograph (HES; Vogt 1987) at the Lick Observatory, fed by the 0.6-m Coude Auxilliary Telescope (CAT), during four runs in 1994±1997. Further details of the instrument can be found in Misch (1997). Shortly before our observations in 1994, ...
offprint
... years. The two main reasons for this interest are the very strong, but rare outbursts, one of which started recently in 2001 (Štefl et al. 2001, 2003b, hereafter Paper I), and the well known short periodicity, analyzed by Štefl et al. (2003a, hereafter Paper II). The periodic line profile variabil ...
... years. The two main reasons for this interest are the very strong, but rare outbursts, one of which started recently in 2001 (Štefl et al. 2001, 2003b, hereafter Paper I), and the well known short periodicity, analyzed by Štefl et al. (2003a, hereafter Paper II). The periodic line profile variabil ...
The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027
... C HAPTER 2: The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 ...
... C HAPTER 2: The ISO–SWS Spectrum of Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 ...
CO OBSERVATIONS OF SPIRAL STRUCTURE AND THE LIFETIME
... Observations of CO emission at £=0 to 7 0 ° , |b| < 1 ° are analyzed to give a map of the molecular cloud distribution in the galaxy as viewed from the galactic pole. From the fact that this distribution shows no obvious spiral pattern we conclude that the giant molecular clouds sampled in the CO li ...
... Observations of CO emission at £=0 to 7 0 ° , |b| < 1 ° are analyzed to give a map of the molecular cloud distribution in the galaxy as viewed from the galactic pole. From the fact that this distribution shows no obvious spiral pattern we conclude that the giant molecular clouds sampled in the CO li ...
Protostellar/PMS Mass Infall Luminosity Problem
... However, this is still a rather poor indicator of age. ...
... However, this is still a rather poor indicator of age. ...
Part2
... Apologies in advance (but not really): I’m going to be very “CO-centric” (though not “COexclusive”). The reason, which I hope you’ll appreciate is that CO - by far the brightest mm line is already very sensitivity limited at extragalactic distances. ...
... Apologies in advance (but not really): I’m going to be very “CO-centric” (though not “COexclusive”). The reason, which I hope you’ll appreciate is that CO - by far the brightest mm line is already very sensitivity limited at extragalactic distances. ...
Galactic Parameters from Masers with Trigonometric Parallaxes
... But recently in the work by Schonrich et al. (2009), where gradient of metallicity of stars in the Galactic disk was taken into account, this velocity is different: (U,V,W)_LSR = (11.1,12.2,7.3)±(0.7,0.5,0.4) km/s. ...
... But recently in the work by Schonrich et al. (2009), where gradient of metallicity of stars in the Galactic disk was taken into account, this velocity is different: (U,V,W)_LSR = (11.1,12.2,7.3)±(0.7,0.5,0.4) km/s. ...
Fast Auto-Focus Method and Software for CCD
... 2. A full frame 3x3 binned image is taken with a minimal exposure time 3. The brightest star is found, the position determined and the HFD measured 4. The target star is sub-framed and a second exposure taken (download time is minimized due to the smaller frame size) 5. The focuser position is then ...
... 2. A full frame 3x3 binned image is taken with a minimal exposure time 3. The brightest star is found, the position determined and the HFD measured 4. The target star is sub-framed and a second exposure taken (download time is minimized due to the smaller frame size) 5. The focuser position is then ...
Fast Auto-Focus Method and Software for CCD-based
... 2. A full frame 3x3 binned image is taken with a minimal exposure time 3. The brightest star is found, the position determined and the HFD measured 4. The target star is sub-framed and a second exposure taken (download time is minimized due to the smaller frame size) 5. The focuser position is then ...
... 2. A full frame 3x3 binned image is taken with a minimal exposure time 3. The brightest star is found, the position determined and the HFD measured 4. The target star is sub-framed and a second exposure taken (download time is minimized due to the smaller frame size) 5. The focuser position is then ...
The Deaths of Very Massive Stars
... either to a wind or a binary companion, yet its remnant contains a neutron star. If the mass loss was to a companion, as is currently thought, then the progenitor mass was probably less than 20 M⊙ , but if a star of 30 M⊙ could explode after losing most of its envelope, this might provide an alterna ...
... either to a wind or a binary companion, yet its remnant contains a neutron star. If the mass loss was to a companion, as is currently thought, then the progenitor mass was probably less than 20 M⊙ , but if a star of 30 M⊙ could explode after losing most of its envelope, this might provide an alterna ...
X. Nuclear star clusters in low-mass early-type galaxies
... At faint magnitudes, the dominant noise is a combination of the readnoise and the sky background noise with a small contribution of Poisson noise from the host galaxy (see also Section 4.3 and Fig. 6). For a host galaxy absolute magnitude MF814W = −13 mag, the difference between the host galaxy magn ...
... At faint magnitudes, the dominant noise is a combination of the readnoise and the sky background noise with a small contribution of Poisson noise from the host galaxy (see also Section 4.3 and Fig. 6). For a host galaxy absolute magnitude MF814W = −13 mag, the difference between the host galaxy magn ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.