Quiz 2 Lecture 12
... important way. b. The Hubble constant would be one-half as great. c. The mv's of all the galaxies are one-half what we currently calculate them to be. d. The sizes of the galaxies are twice what we currently calculate them to be. answer: b ...
... important way. b. The Hubble constant would be one-half as great. c. The mv's of all the galaxies are one-half what we currently calculate them to be. d. The sizes of the galaxies are twice what we currently calculate them to be. answer: b ...
Astronomy Astrophysics − Astrophysical parameters of the peculiar X-ray transient
... with a circular rotation velocity at the position of the Sun (dGC = 8.5 kpc) of 220 km s−1 . Along this line of sight, LSR velocities start at small negative values and become more negative with distance until reaching a minimum at −18.5 km s−1 (at a Galactocentric distance of 7.9 kpc, 3.2 kpc away ...
... with a circular rotation velocity at the position of the Sun (dGC = 8.5 kpc) of 220 km s−1 . Along this line of sight, LSR velocities start at small negative values and become more negative with distance until reaching a minimum at −18.5 km s−1 (at a Galactocentric distance of 7.9 kpc, 3.2 kpc away ...
FIRST STELLAR ABUNDANCES IN THE DWARF IRREGULAR
... The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elements can be examined and quantified when using this approach. The chemi ...
... The analysis of bright nebular emission lines of H II regions has been the most frequent approach to modeling chemical evolution of more distant galaxies to date (Matteucci & Tosi 1985). So far, only a very limited number of elements can be examined and quantified when using this approach. The chemi ...
Mass loss of massive stars near the Eddington luminosity by core
... 2006). However, LBVs are not SN progenitors in standard stellar evolution theory (e.g., Langer 2012). Even if LBVs are actually SN progenitors, the unknown mechanism that induces the extreme mass loss observed in LBVs needs to be activated shortly before the core collapse by chance. However, we sugg ...
... 2006). However, LBVs are not SN progenitors in standard stellar evolution theory (e.g., Langer 2012). Even if LBVs are actually SN progenitors, the unknown mechanism that induces the extreme mass loss observed in LBVs needs to be activated shortly before the core collapse by chance. However, we sugg ...
on the pms star hbc 498 and its associated nebulous stars1
... out because of their associated reflection nebulosities (Dorchner & Gürtler 1963; van den Bergh 1966; Bernes 1977); Gyulbudaghian, Glushov, & Denisyuk 1978) and because they apparently constitute a tight trapezium of young stellar objects (Cohen 1980; Cohen & Kuhi 1979) associated with a small dark ...
... out because of their associated reflection nebulosities (Dorchner & Gürtler 1963; van den Bergh 1966; Bernes 1977); Gyulbudaghian, Glushov, & Denisyuk 1978) and because they apparently constitute a tight trapezium of young stellar objects (Cohen 1980; Cohen & Kuhi 1979) associated with a small dark ...
Principal Features of the Sky - Beck-Shop
... halves. The chart is a Mercator projection4 of a variant of the equatorial system, one way of viewing the celestial sphere independently of the observer. Figure B.2 provides views of the regions around the north and south celestial poles. Star charts, regardless of the superimposed constellation and ...
... halves. The chart is a Mercator projection4 of a variant of the equatorial system, one way of viewing the celestial sphere independently of the observer. Figure B.2 provides views of the regions around the north and south celestial poles. Star charts, regardless of the superimposed constellation and ...
Principal Features of the Sky
... halves. The chart is a Mercator projection4 of a variant of the equatorial system, one way of viewing the celestial sphere independently of the observer. Figure B.2 provides views of the regions around the north and south celestial poles. Star charts, regardless of the superimposed constellation and ...
... halves. The chart is a Mercator projection4 of a variant of the equatorial system, one way of viewing the celestial sphere independently of the observer. Figure B.2 provides views of the regions around the north and south celestial poles. Star charts, regardless of the superimposed constellation and ...
Is $^ 6$ Li in metal-poor halo stars produced in situ by solar
... It has been known for many years that the chromospheric and coronal activities of dwarf stars are closely related to their rotation (Kraft 1967). This relationship results from the generation and amplification of surface magnetic fields by a complex dynamo mechanism, whose efficiency depends on the in ...
... It has been known for many years that the chromospheric and coronal activities of dwarf stars are closely related to their rotation (Kraft 1967). This relationship results from the generation and amplification of surface magnetic fields by a complex dynamo mechanism, whose efficiency depends on the in ...
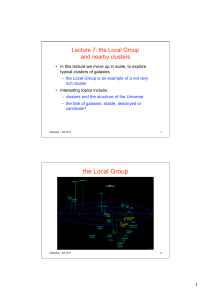
the Local Group - Simon P Driver
... – it’s mostly empty, i.e. galaxies are quite distant from each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is no ...
... – it’s mostly empty, i.e. galaxies are quite distant from each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is no ...
Lithium abundances along the red giant branch: FLAMES
... undergo a phase of Li production, which motivates the search for these stars. As it is unlikely that they skipped Li destruction at FDU, they must have somehow replenished it through Be decay (see the discussion in Palmerini et al. 2011). While the Li abundance has been measured already in an increa ...
... undergo a phase of Li production, which motivates the search for these stars. As it is unlikely that they skipped Li destruction at FDU, they must have somehow replenished it through Be decay (see the discussion in Palmerini et al. 2011). While the Li abundance has been measured already in an increa ...
Beyond simple depletion: phase behaviour of colloid–star polymer
... In this paper, we report experiments that go systematically beyond the idealized model: the nearly ideal linear polymer is replaced by star-branched polymers of increasing functionality (number of arms). To simplify the terminology, we will refer to the model system and the more complex systems just ...
... In this paper, we report experiments that go systematically beyond the idealized model: the nearly ideal linear polymer is replaced by star-branched polymers of increasing functionality (number of arms). To simplify the terminology, we will refer to the model system and the more complex systems just ...
Stars, Galaxies, Superuniverses and the Urantia Book, by Frederick
... stars in our Milky Way galaxy is estimated to be around 200 to 400 billion. This is pretty good agreement with our average number since our galaxy is the second largest in our local cluster of about 30 galaxies, and thus may be considered to be an exceptionally large galaxy. There are many more smal ...
... stars in our Milky Way galaxy is estimated to be around 200 to 400 billion. This is pretty good agreement with our average number since our galaxy is the second largest in our local cluster of about 30 galaxies, and thus may be considered to be an exceptionally large galaxy. There are many more smal ...
Notes on Stars
... fundamental diagram of stellar astrophysics: the color-magnitude diagram or Hertzsprung-Russel diagram. Already around 1910, Rosenberg, Hertzsprung and Russel discuss what is now called the Hertsprung-Russel Diagram. The name Hertzsprung-Russel diagram is reserved for a diagram which shows luminosit ...
... fundamental diagram of stellar astrophysics: the color-magnitude diagram or Hertzsprung-Russel diagram. Already around 1910, Rosenberg, Hertzsprung and Russel discuss what is now called the Hertsprung-Russel Diagram. The name Hertzsprung-Russel diagram is reserved for a diagram which shows luminosit ...
Galaxies
... • Astronomers now have decided that the morphology classification should consist of only two types of galaxies: the spiral and the elliptical. • Barred spirals are a subclass of spirals. Irregulars may be either spiral or barred spiral. ...
... • Astronomers now have decided that the morphology classification should consist of only two types of galaxies: the spiral and the elliptical. • Barred spirals are a subclass of spirals. Irregulars may be either spiral or barred spiral. ...
Abstracts - Physics of Evolved Stars 2015
... star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, these stars go through a phase of a lower mass-loss rate of at most a few times 10^-6 solar masses per year. Evolutionary models suggest that this phase does not last much longer than 10^5 years, ...
... star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, these stars go through a phase of a lower mass-loss rate of at most a few times 10^-6 solar masses per year. Evolutionary models suggest that this phase does not last much longer than 10^5 years, ...
Spectroscopic Variability of Supergiant Star HD14134, B3Ia
... In addition, some of the results of measurements in the spectra of HD14134 presented on a time scale in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582. ...
... In addition, some of the results of measurements in the spectra of HD14134 presented on a time scale in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582. ...
Spectroscopic Variability of Supergiant Star HD14134, B3Ia
... In addition, some of the results of measurements in the spectra of HD14134 presented on a time scale in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582. ...
... In addition, some of the results of measurements in the spectra of HD14134 presented on a time scale in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. It has been revealed that the variability of radial velocity, equivalent widths, depths and half-widths of Hβ line, as well as HeIλ5875.72Å and averaged CII (λ6578.05Å, λ6582. ...
Observational Data
... from R23 by using [O II], [O III] vs Hβ (or Hα by assuming intrinsic ratio of Hβ/Hα constant) as metallicity indicator. If these z~2 starbursts are progenitors of z~1 EROs and local ellipticals, their metallicity should be high, at least near-solar or more. Metallicity is a good indicator of stellar ...
... from R23 by using [O II], [O III] vs Hβ (or Hα by assuming intrinsic ratio of Hβ/Hα constant) as metallicity indicator. If these z~2 starbursts are progenitors of z~1 EROs and local ellipticals, their metallicity should be high, at least near-solar or more. Metallicity is a good indicator of stellar ...
white dwarfs and the age of the universe
... the interstellar medium [9], winds and so on. There is now a broad opinion that the distinction among the character DA and non–DA is inherited (i.e., it is linked to the origin of the white dwarf itself) although a fraction of them can change their external aspect during the evolution [10]. Standard ...
... the interstellar medium [9], winds and so on. There is now a broad opinion that the distinction among the character DA and non–DA is inherited (i.e., it is linked to the origin of the white dwarf itself) although a fraction of them can change their external aspect during the evolution [10]. Standard ...
Astronomy Astrophysics Detailed abundances of a large sample of giant stars in... and in the Sagittarius nucleus
... While some studies of the chemical composition of red giant branch (RGB) stars in this GC exist in the literature (Brown et al. 1999, hereinafter BWG99), they are limited to just a few stars, hence useful only to provide some interesting average values. What is still lacking is an extensive survey, ...
... While some studies of the chemical composition of red giant branch (RGB) stars in this GC exist in the literature (Brown et al. 1999, hereinafter BWG99), they are limited to just a few stars, hence useful only to provide some interesting average values. What is still lacking is an extensive survey, ...
What CAN You See With a Telescope?
... quite small, but that is not the whole story. An asteroid’s brightness varies according to several factors: how far away it is from the Sun, and how far it’s reflected light has to travel to reach the Earth. Furthermore, most asteroids have very irregular shapes. Their brightness also depends ...
... quite small, but that is not the whole story. An asteroid’s brightness varies according to several factors: how far away it is from the Sun, and how far it’s reflected light has to travel to reach the Earth. Furthermore, most asteroids have very irregular shapes. Their brightness also depends ...
Stellar evolution - Statistical Physics Group
... (vi) composition of surface layers. If a star is a partner in a binary system whose distance is known and whose apparent orbital elements can be observed, it is possible to find a value for (vii) stellar mass. If rather less information is available it may be possible to find one relation between th ...
... (vi) composition of surface layers. If a star is a partner in a binary system whose distance is known and whose apparent orbital elements can be observed, it is possible to find a value for (vii) stellar mass. If rather less information is available it may be possible to find one relation between th ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.