File
... star’s properties? • Star radii differ greatly – Most are roughly the size of our Sun – Some, like Betelgeuse, are hundreds of times larger. These are Giants – Smaller stars, including our Sun, are Dwarfs, or ...
... star’s properties? • Star radii differ greatly – Most are roughly the size of our Sun – Some, like Betelgeuse, are hundreds of times larger. These are Giants – Smaller stars, including our Sun, are Dwarfs, or ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... Size- Giant, main sequence, and dwarf Temperature- blue=hot; red=cooler Brightness- apparent brightness and absolute magnitude HR diagram shows temperature, brightness, color of stars and where the star is in its life cycle. Used to graph the surface temperature (x-axis) vs. brightness (yaxis) Hotte ...
... Size- Giant, main sequence, and dwarf Temperature- blue=hot; red=cooler Brightness- apparent brightness and absolute magnitude HR diagram shows temperature, brightness, color of stars and where the star is in its life cycle. Used to graph the surface temperature (x-axis) vs. brightness (yaxis) Hotte ...
M13 – The Great Hercules Cluster
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
Document
... Microwave: The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Shortly after the Big Bang, the Universe cooled enough to allow atoms to form. After this point in time, radiation was able to travel freely through the Universe. Initially, the radiation (known as the CMB) from this epoch had a short wavelength, how ...
... Microwave: The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Shortly after the Big Bang, the Universe cooled enough to allow atoms to form. After this point in time, radiation was able to travel freely through the Universe. Initially, the radiation (known as the CMB) from this epoch had a short wavelength, how ...
Star Formation
... Massive newborn stars are indicated by the arrows. Note that some (2, 3, & 4) are hidden to visible light. Arrows 1 and 5 indicate a compact cluster of bright young stars. Sources 6 & 7 may be due to outflow jets from the cluster 5. ...
... Massive newborn stars are indicated by the arrows. Note that some (2, 3, & 4) are hidden to visible light. Arrows 1 and 5 indicate a compact cluster of bright young stars. Sources 6 & 7 may be due to outflow jets from the cluster 5. ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
Death of High Mass Stars
... protons to create neutrons. • Core collapses until pressure from physical force of neutrons bouncing against each other stops it. • Core rebounds and runs into outer material that is still falling inward. ...
... protons to create neutrons. • Core collapses until pressure from physical force of neutrons bouncing against each other stops it. • Core rebounds and runs into outer material that is still falling inward. ...
RTFS Test - 2017 BCS Cobra
... parallax of 1.03 arcseconds, while the Star B has a parallax of 1.70 arcseconds. Which star is closer to earth? 76. What process is the main energy source of the star Aldebaran, a red ...
... parallax of 1.03 arcseconds, while the Star B has a parallax of 1.70 arcseconds. Which star is closer to earth? 76. What process is the main energy source of the star Aldebaran, a red ...
Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness
... Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness 1 The magnitude system 1.1 Apparent magnitude Astronomers are stuck with the antiquated old system of magnitudes and so a clear explanation of what this system is and how it relates to more sensible units is important. The magnitude scale is a logarit ...
... Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness 1 The magnitude system 1.1 Apparent magnitude Astronomers are stuck with the antiquated old system of magnitudes and so a clear explanation of what this system is and how it relates to more sensible units is important. The magnitude scale is a logarit ...
Document
... apparent Magnitude is a measure of intensity, which is determined by both distance and intrinsic brightness. Intensity can be the same for a flashlight close up, or a car headlight far away. If all objects were at same distance,however, magnitude would measure Luminosity (intrinsic brightness) Lumin ...
... apparent Magnitude is a measure of intensity, which is determined by both distance and intrinsic brightness. Intensity can be the same for a flashlight close up, or a car headlight far away. If all objects were at same distance,however, magnitude would measure Luminosity (intrinsic brightness) Lumin ...
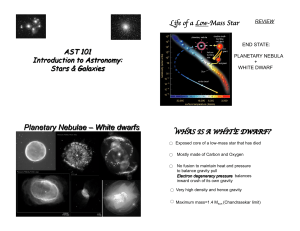
Planetary Nebulae – White dwarfs
... more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
... more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
Study Guide
... Post-Main Sequence Evolution of a High Mass Star • End of the Life of a Massive Star: – Burn H through Si in successive cores – Finally build a massive Iron core ...
... Post-Main Sequence Evolution of a High Mass Star • End of the Life of a Massive Star: – Burn H through Si in successive cores – Finally build a massive Iron core ...
astro2_lec1 - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... Apparent brightness, or flux, falls off with the square of the distance, because the surface area of a sphere increases with the square of its radius ...
... Apparent brightness, or flux, falls off with the square of the distance, because the surface area of a sphere increases with the square of its radius ...
Solution Sheet Lab 1
... Purpose. To determine the length of the sidereal day (the “star” day) from an image of the circumpolar region of the sky. The length of the sidereal day is defined as the time interval between two successive transits of the vernal equinox across the meridian. It is time based upon the Earth’s rotati ...
... Purpose. To determine the length of the sidereal day (the “star” day) from an image of the circumpolar region of the sky. The length of the sidereal day is defined as the time interval between two successive transits of the vernal equinox across the meridian. It is time based upon the Earth’s rotati ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
Hinsdale Astro TEST
... 14. Is this a young star or an old star? Image H 15. Give the proper name of this substellar brown dwarf. 16. What type of radiation does this type of object mainly emit? ...
... 14. Is this a young star or an old star? Image H 15. Give the proper name of this substellar brown dwarf. 16. What type of radiation does this type of object mainly emit? ...
Searching for planets around evolved stars with COROT
... of our precise radial velocity (RV) measurements of G and K giants (ref a). A number of stars from our list of 80 targets have been observed for 14 months, using the fibre-fed echelle spectrograph FEROS at the 1.52 m ESO telescope in La Silla, Chile. Long-term accuracy better than 10 m/s is required ...
... of our precise radial velocity (RV) measurements of G and K giants (ref a). A number of stars from our list of 80 targets have been observed for 14 months, using the fibre-fed echelle spectrograph FEROS at the 1.52 m ESO telescope in La Silla, Chile. Long-term accuracy better than 10 m/s is required ...
PHYS3380_102615_bw
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
January 2006
... may look strange, e.g. K5III for Aldebaran. Ignore the roman numbers ( III means a giant star, V means dwarf star, etc). First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
... may look strange, e.g. K5III for Aldebaran. Ignore the roman numbers ( III means a giant star, V means dwarf star, etc). First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.