Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. ...
... that the axis of the Earth is pointing to for about the next 2,000 years. The Earth has a wobble, and the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be north. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. ...
The Cosmic Near-Infrared Background: Remnant light form
... IR background. CIBER-I consists of a wide-field two-color camera for fluctuation measurements, a low-resolution absolute spectrometer for absolute EBL measurements, and a narrow-band imaging spectrometer to measure and correct scattered emission from the foreground zodiacal cloud. CIBER-I was succes ...
... IR background. CIBER-I consists of a wide-field two-color camera for fluctuation measurements, a low-resolution absolute spectrometer for absolute EBL measurements, and a narrow-band imaging spectrometer to measure and correct scattered emission from the foreground zodiacal cloud. CIBER-I was succes ...
Document
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
Section 1 Notes on Stars
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
Document
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor; and if you could find the very first stars, they would have no metals at all • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of ...
Proper Motion of a Star
... measured in arc seconds per year, and symbolized with the Greek letter “mu” μ. Proper motion is generally measured by taking photographs several years apart and measuring the movement of the image of a star with respect to more distant background stars over that time period. Usually decades must ela ...
... measured in arc seconds per year, and symbolized with the Greek letter “mu” μ. Proper motion is generally measured by taking photographs several years apart and measuring the movement of the image of a star with respect to more distant background stars over that time period. Usually decades must ela ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... f) The faintest galaxies observed by the Hubble Space Telescope have apparent magnitudes around 30. Suppose these galaxies are ≈ 3 gigaparsecs away (3 × 109 parsecs). Assuming every star in these galaxies emits about the same amount of light as the Sun (a false assumption, but let’s make it just the ...
... f) The faintest galaxies observed by the Hubble Space Telescope have apparent magnitudes around 30. Suppose these galaxies are ≈ 3 gigaparsecs away (3 × 109 parsecs). Assuming every star in these galaxies emits about the same amount of light as the Sun (a false assumption, but let’s make it just the ...
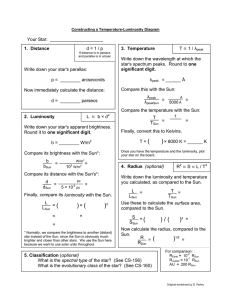
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... They include the closest star to us other than the Sun (Proxima Centauri, which is too faint to see with the unaided eye) as well as the Sun's "twin", Alpha Centauri, and the second brightest star in the night sky (Canopus). Name Sun Proxima Cen. Alpha Cen. A Alpha Cen. B Canopus Achernar Acrux B ...
... They include the closest star to us other than the Sun (Proxima Centauri, which is too faint to see with the unaided eye) as well as the Sun's "twin", Alpha Centauri, and the second brightest star in the night sky (Canopus). Name Sun Proxima Cen. Alpha Cen. A Alpha Cen. B Canopus Achernar Acrux B ...
TRANSIT
... Markarian’s Chain is a 1.5 degree long arc of galaxies that all belong to the Virgo Cluster, although some of the members are in fact in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was first described by the Armenian astronomer B E Markarian (1913-1985) in December 1961. A paper in 1983 by Litzroth support ...
... Markarian’s Chain is a 1.5 degree long arc of galaxies that all belong to the Virgo Cluster, although some of the members are in fact in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was first described by the Armenian astronomer B E Markarian (1913-1985) in December 1961. A paper in 1983 by Litzroth support ...
Can we detect asteroid impacts with rocky extrasolar planets?
... solar system, so we can expect one to be hit every 25 million years. However, half of these impacts will be on the side facing away from the Earth so a visible impact occurs, on average, once every 50 million years. During the first billion years of our solar system, though, the impact rate was at l ...
... solar system, so we can expect one to be hit every 25 million years. However, half of these impacts will be on the side facing away from the Earth so a visible impact occurs, on average, once every 50 million years. During the first billion years of our solar system, though, the impact rate was at l ...
1705 Star Charts
... Sirius is the brightest star, though star-like Venus and Jupiter, and sometimes Mars, are brighter. Sirius appears bright because it is both brighter than the sun -- 23 times brighter -- and relatively a close 8.6 light years* away. Sirius was often called 'the dog star' being the brightest star in ...
... Sirius is the brightest star, though star-like Venus and Jupiter, and sometimes Mars, are brighter. Sirius appears bright because it is both brighter than the sun -- 23 times brighter -- and relatively a close 8.6 light years* away. Sirius was often called 'the dog star' being the brightest star in ...
Masers and high mass star formation Claire Chandler
... that the radio source I (apparently a thermal jet), is also moving in the sky, receding from a point between it and the BN object. ...
... that the radio source I (apparently a thermal jet), is also moving in the sky, receding from a point between it and the BN object. ...
Surveying the Stars
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -- which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -- which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
L11
... The convective core becomes exhausted homogeneously, while it contracts to a smaller volume and becomes hotter. The star also develops a H-burning shell around the He dominated core. The temperature at the bottom of the hydrogen envelope is too high to sustain hydrostatic equilibrium. The envelope e ...
... The convective core becomes exhausted homogeneously, while it contracts to a smaller volume and becomes hotter. The star also develops a H-burning shell around the He dominated core. The temperature at the bottom of the hydrogen envelope is too high to sustain hydrostatic equilibrium. The envelope e ...
V Example: our SUN (G2V)
... star apart, usually leaving behind a neutron star. Supernovae can also be produced when enough material is deposited on a white dwarf so that is exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit and collapses to a neutron star. Both types of supernova drastically alter the stars and are the result of the collapse ste ...
... star apart, usually leaving behind a neutron star. Supernovae can also be produced when enough material is deposited on a white dwarf so that is exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit and collapses to a neutron star. Both types of supernova drastically alter the stars and are the result of the collapse ste ...
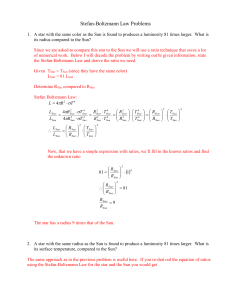
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
... 6. A star is five times as luminous as the Sun and has a surface temperature of 98,000 K. What is its radius, compared to that of the Sun? Again, this is a Stefan-Boltzmann problem (luminosity, radius and temperature) that will be most easily solved using a ratio approach. See the first problem to r ...
... 6. A star is five times as luminous as the Sun and has a surface temperature of 98,000 K. What is its radius, compared to that of the Sun? Again, this is a Stefan-Boltzmann problem (luminosity, radius and temperature) that will be most easily solved using a ratio approach. See the first problem to r ...
3.1 Introduction
... Although the broad spectral distribution of stars approximates that of a blackbody, on closer scrutiny there are deviations (see Figure 2.7). Thus a star colour is not a very precise measure of its temperature. Furthermore, the presence of interstellar dust grains between a star and our telescopes o ...
... Although the broad spectral distribution of stars approximates that of a blackbody, on closer scrutiny there are deviations (see Figure 2.7). Thus a star colour is not a very precise measure of its temperature. Furthermore, the presence of interstellar dust grains between a star and our telescopes o ...
H-R Diagram
... cores of giants and supergiants. 7. Classify: Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to the Sun. It has a luminosity of 0.0017 and a temperature of 3,000 K. A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ...
... cores of giants and supergiants. 7. Classify: Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to the Sun. It has a luminosity of 0.0017 and a temperature of 3,000 K. A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ...
After the ZAMS - Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School
... other If we didn’t make this assumption, we’d be unable to predict what will happen to one star in the cluster by looking at others in the same cluster that are further along in their development. ...
... other If we didn’t make this assumption, we’d be unable to predict what will happen to one star in the cluster by looking at others in the same cluster that are further along in their development. ...
July 2013 - Skyscrapers, Inc.
... towards the north is Perseus. Between the two patterns we can easily see the Double Cluster with the naked eye. While binoculars will enhance the view, a telescope under low magnification will reveal the magnificent beauty of this open cluster of stars. Our next stop “down” (south) the Milky Way is ...
... towards the north is Perseus. Between the two patterns we can easily see the Double Cluster with the naked eye. While binoculars will enhance the view, a telescope under low magnification will reveal the magnificent beauty of this open cluster of stars. Our next stop “down” (south) the Milky Way is ...
Luminosity - U of L Class Index
... If we measure a star’s apparent brightness and distance, we can compute its luminosity with the inverse square law for light How do we measure stellar temperatures? A star’s color and spectral type both reflect its temperature How do we measure stellar masses? Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law ...
... If we measure a star’s apparent brightness and distance, we can compute its luminosity with the inverse square law for light How do we measure stellar temperatures? A star’s color and spectral type both reflect its temperature How do we measure stellar masses? Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.