April 2011 - Skyscrapers, Inc.
... her and go to battle. She was so distraught at the possibility of losing him that she promised the gods she would donate her hair to them upon his safe return. He did; she did. The king then became so distraught that her waist-length hair had been shorn, until Berenice brought him outside and showed ...
... her and go to battle. She was so distraught at the possibility of losing him that she promised the gods she would donate her hair to them upon his safe return. He did; she did. The king then became so distraught that her waist-length hair had been shorn, until Berenice brought him outside and showed ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... The interior of a star produces a continuous spectrum of light, like a rainbow. Cooler gases in the outer layers of the star absorb certain wavelengths of light, causing dark lines to appear in the spectrum. The resulting absorption spectrum can tell astronomers a great deal about the star. 1. On th ...
... The interior of a star produces a continuous spectrum of light, like a rainbow. Cooler gases in the outer layers of the star absorb certain wavelengths of light, causing dark lines to appear in the spectrum. The resulting absorption spectrum can tell astronomers a great deal about the star. 1. On th ...
Stellarium Night Sky Search Key Commands Constellations buttons
... A. Zodiac constellations are those they lay along the ecliptic. What is the name of the zodiac constellation due south? [Hint: You will need to turn on the ecliptic.] ...
... A. Zodiac constellations are those they lay along the ecliptic. What is the name of the zodiac constellation due south? [Hint: You will need to turn on the ecliptic.] ...
Observations and Theoretical Models of Subdwarfs
... of the formation of the Milky Way. Due to their early formation, the gas clouds from which these stars formed had been only slightly enriched with heavy metals created in the cores of previous generations of stars, explaining the unusually faint metallic lines observed in their spectra. This also ex ...
... of the formation of the Milky Way. Due to their early formation, the gas clouds from which these stars formed had been only slightly enriched with heavy metals created in the cores of previous generations of stars, explaining the unusually faint metallic lines observed in their spectra. This also ex ...
4. Massive Stars and HII Regions
... much more compact H II regions observed (We cannot observe the high energy radiation directly, but H II regions emit a large amount of free-free – radio continuum radiation). These compact H II regions have size of 0.005 – 0.5 pc and electron densities of 2 · 103 – 3 · 105 cm−3 . Ultra compact H II ...
... much more compact H II regions observed (We cannot observe the high energy radiation directly, but H II regions emit a large amount of free-free – radio continuum radiation). These compact H II regions have size of 0.005 – 0.5 pc and electron densities of 2 · 103 – 3 · 105 cm−3 . Ultra compact H II ...
Lives of Stars - Amazon Web Services
... these stages, but you know the stages exist. Astronomers have a similar problem in trying to understand how stars age. They can't watch a single star for billions of years. Instead, they study many stars and other objects in space. Over time, astronomers have figured out that these objects represent ...
... these stages, but you know the stages exist. Astronomers have a similar problem in trying to understand how stars age. They can't watch a single star for billions of years. Instead, they study many stars and other objects in space. Over time, astronomers have figured out that these objects represent ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
Lecture 2
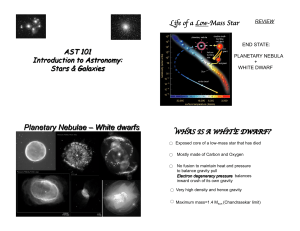
... Death of a Low-Mass Star • Low mass stars are not massive enough to turn carbon and oxygen cores into heavier elements (not hot enough) • These stars eject most of their outer layers • Only the core is left, which “lights-up” the gas that the star has been ejecting – causing a planetary nebula ...
... Death of a Low-Mass Star • Low mass stars are not massive enough to turn carbon and oxygen cores into heavier elements (not hot enough) • These stars eject most of their outer layers • Only the core is left, which “lights-up” the gas that the star has been ejecting – causing a planetary nebula ...
Full Press Release - The Open University
... This “mass loss” process is so important that it may well determine the final stage of the star’s life. Stars with masses close to that of our Sun will expand during the later stages of their life becoming so-called 'red-giant' stars. During this final phase of their life such stars often eject gas ...
... This “mass loss” process is so important that it may well determine the final stage of the star’s life. Stars with masses close to that of our Sun will expand during the later stages of their life becoming so-called 'red-giant' stars. During this final phase of their life such stars often eject gas ...
This Book of Hours calculation is a possible
... book of hours and is directly over the churches of Compagne les Bains and Les Sauzils. But more importantly it is over the snow capped Pic de Soularac in the Pyrenees, more about this mountain later. Porrima (due west) is the Goddess of childbirth and is represented by Chartres Cathedral in Carpenti ...
... book of hours and is directly over the churches of Compagne les Bains and Les Sauzils. But more importantly it is over the snow capped Pic de Soularac in the Pyrenees, more about this mountain later. Porrima (due west) is the Goddess of childbirth and is represented by Chartres Cathedral in Carpenti ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... neutron star stellar core. Rigel is a B8 spectral class star. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and left the main sequence. This is actually a triple star system – Rigel A and a binary pair referred to as Rigel B. The two stars composing Rigel B are B9V spectral class stars. Slide 28: M42, the Grea ...
... neutron star stellar core. Rigel is a B8 spectral class star. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and left the main sequence. This is actually a triple star system – Rigel A and a binary pair referred to as Rigel B. The two stars composing Rigel B are B9V spectral class stars. Slide 28: M42, the Grea ...
Lecture 10-11 - OSU Astronomy
... Which of the following spectral classifications represents the hottest stellar surface temperature? ...
... Which of the following spectral classifications represents the hottest stellar surface temperature? ...
Classifying the Spectra of Stars:
... M-stars are very cool and typically have broad features. They usually have strong sodium but it’s broader than it is in a K star. M-stars are a complicated mess that often has very large areas of absorption due to molecules in their atmospheres. We will not be dealing with this spectral type. ...
... M-stars are very cool and typically have broad features. They usually have strong sodium but it’s broader than it is in a K star. M-stars are a complicated mess that often has very large areas of absorption due to molecules in their atmospheres. We will not be dealing with this spectral type. ...
Compact stars
... are no longer sufficient to hold up the star. As the forces in dense hadronic matter are not well understood, this limit is not known exactly but is thought to be between 2 and 3 times the mass of the Sun. If more mass accretes onto a neutron star, eventually this mass limit will be reached. What ha ...
... are no longer sufficient to hold up the star. As the forces in dense hadronic matter are not well understood, this limit is not known exactly but is thought to be between 2 and 3 times the mass of the Sun. If more mass accretes onto a neutron star, eventually this mass limit will be reached. What ha ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.