Stars - cayugascience
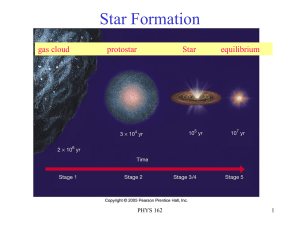
... the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount of matter will start to draw material towards it through gravity. This is where the star will form (Figure 8.4a). Material falling inward to the core has excess energy. This energy causes the centra ...
... the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount of matter will start to draw material towards it through gravity. This is where the star will form (Figure 8.4a). Material falling inward to the core has excess energy. This energy causes the centra ...
ASTRONOMY 301 EXAMPLES OF TEST
... (A) We would see completely different kinds of objects when we look at the night sky. (B) We would see only the most energetic objects – for example, supernovae – in the night sky. (C) We would see more or less the same objects that we see now, but hotter objects would be easier to see and colder ob ...
... (A) We would see completely different kinds of objects when we look at the night sky. (B) We would see only the most energetic objects – for example, supernovae – in the night sky. (C) We would see more or less the same objects that we see now, but hotter objects would be easier to see and colder ob ...
Descriptions For Posters
... Spiral Galaxy M81 2 M81 or Bode's galaxy is a large bright spiral galaxy located 11.8 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent magnitude of +6.9 it's easily visible with binoculars, a fine target for small telescope owners and a wonderful sight in larger sc ...
... Spiral Galaxy M81 2 M81 or Bode's galaxy is a large bright spiral galaxy located 11.8 million light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent magnitude of +6.9 it's easily visible with binoculars, a fine target for small telescope owners and a wonderful sight in larger sc ...
Research Papers-Cosmology/Download/5936
... it assumed that star is rotating with a large number of revolutions n = 645 r/s. In this case, there is a danger that it will be broken by centrifugal forces. The force of gravity is opposes to the centrifugal forces. In order to prevent the destruction of stars, we have to assume that a radius of ...
... it assumed that star is rotating with a large number of revolutions n = 645 r/s. In this case, there is a danger that it will be broken by centrifugal forces. The force of gravity is opposes to the centrifugal forces. In order to prevent the destruction of stars, we have to assume that a radius of ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends on its composition and its surface temperature, similar to glowing iron. When iron is ...
... to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends on its composition and its surface temperature, similar to glowing iron. When iron is ...
D2 Stellar characteristics and stellar evolution
... dimming) which is caused by periodic expansion and contraction of outer surface (brighter as it expands). This is to do with the balance between the nuclear and gravitational forces within the star. In most stars these forces are balanced over long periods but in Cepheid variables they seem to take ...
... dimming) which is caused by periodic expansion and contraction of outer surface (brighter as it expands). This is to do with the balance between the nuclear and gravitational forces within the star. In most stars these forces are balanced over long periods but in Cepheid variables they seem to take ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...
Here - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... Using the Greek alphabet, starting with Alpha, stars are labelled mainly (with certain exceptions) according to how bright they are. Thus the brightest star in Ursa Minor is called “Alpha Ursae Minoris” and written α UMi. Here is a list of all the 24 Greek letters used in astronomy: α - Alpha β - Be ...
... Using the Greek alphabet, starting with Alpha, stars are labelled mainly (with certain exceptions) according to how bright they are. Thus the brightest star in Ursa Minor is called “Alpha Ursae Minoris” and written α UMi. Here is a list of all the 24 Greek letters used in astronomy: α - Alpha β - Be ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... tell you that the seasons are caused by the tilt in Earth's axis, but when asked what the axis of rotation is tilted with respect to, they have no idea. Others believe that summer occurs when Earth is closest to the sun. The tilt in Earth's rotation axis with respect to the axis of the orbit needs t ...
... tell you that the seasons are caused by the tilt in Earth's axis, but when asked what the axis of rotation is tilted with respect to, they have no idea. Others believe that summer occurs when Earth is closest to the sun. The tilt in Earth's rotation axis with respect to the axis of the orbit needs t ...
Star
... the constellations come from Latin. • Some constellations are named for real or imaginary animals, such as Ursa Major (the great bear) or ancient gods or legendary heroes, such as Hercules or Orion. ...
... the constellations come from Latin. • Some constellations are named for real or imaginary animals, such as Ursa Major (the great bear) or ancient gods or legendary heroes, such as Hercules or Orion. ...
The Argonauts, background to the constellation Carina Argo Navis
... Keyhole Nebula, imaged by Hubble Space meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year. Telescope. The small nebula to the upper left has Eta Carinae's effects on the nebula can be seen directly: been nicknamed "finger of God" or "God's birdie", The dark globules in the image and some other l ...
... Keyhole Nebula, imaged by Hubble Space meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year. Telescope. The small nebula to the upper left has Eta Carinae's effects on the nebula can be seen directly: been nicknamed "finger of God" or "God's birdie", The dark globules in the image and some other l ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... AGB stars as a function of postion in the galaxy is interpreted using stellar evolutionary models. The selection criteria is homogeneous. ...
... AGB stars as a function of postion in the galaxy is interpreted using stellar evolutionary models. The selection criteria is homogeneous. ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the night sky far from city lights, you can see only about 3,000 of them without using binoculars or a telescope. Stars, like people, have life cycles -- they are born, pass through several phases, and ...
... galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the night sky far from city lights, you can see only about 3,000 of them without using binoculars or a telescope. Stars, like people, have life cycles -- they are born, pass through several phases, and ...
Evolution of a Planetary System
... Investigating Types of Stars What do you think, now? After completing your investigation, please answer these questions: 1. From Earth, stars appear to be different colors: blue, white, yellow, orange, and red. What causes one star to be a different color than another star? ...
... Investigating Types of Stars What do you think, now? After completing your investigation, please answer these questions: 1. From Earth, stars appear to be different colors: blue, white, yellow, orange, and red. What causes one star to be a different color than another star? ...
9J Gravity and Space
... The constellations that we see in the sky are not physical groupings held together by gravity. In most cases the stars in constellations are each very different distances from us, and only appear to be grouped because they lie in approximately the same direction. ...
... The constellations that we see in the sky are not physical groupings held together by gravity. In most cases the stars in constellations are each very different distances from us, and only appear to be grouped because they lie in approximately the same direction. ...
Order-of-Magnitude Astrophysics
... 26. A globular cluster has 105 stars and a 1-d velocity dispersion of 5 km/s. What is the covering fraction of stars? 27. In the intergalactic medium of a group with line-of-sight velocity dispersion of 200 km/s, what are the lightest atoms that will not be fully ionized? 28. The Space Interferomet ...
... 26. A globular cluster has 105 stars and a 1-d velocity dispersion of 5 km/s. What is the covering fraction of stars? 27. In the intergalactic medium of a group with line-of-sight velocity dispersion of 200 km/s, what are the lightest atoms that will not be fully ionized? 28. The Space Interferomet ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
... Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... The aggregate appearance of the naked-eye stars would appear to Galileo to be direct observational support for his ideas about the stars, and indirect observational support for the Copernican theory over the rival Tychonic theory. ...
... The aggregate appearance of the naked-eye stars would appear to Galileo to be direct observational support for his ideas about the stars, and indirect observational support for the Copernican theory over the rival Tychonic theory. ...
r*=13.6 km MPA1 EOS
... "None of this was realized before simply because we couldn't get to the scene of the explosion fast enough." "Swift has the unique ability to detect bursts and turn its X-ray and ultravioletoptical telescopes to the explosion's embers within minutes. As such, Swift is detecting new burst details tha ...
... "None of this was realized before simply because we couldn't get to the scene of the explosion fast enough." "Swift has the unique ability to detect bursts and turn its X-ray and ultravioletoptical telescopes to the explosion's embers within minutes. As such, Swift is detecting new burst details tha ...
stars & galaxies
... All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our sun is located on one of the spiral arms. It is rotating around the nucleus at 250 km/s. ...
... All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our sun is located on one of the spiral arms. It is rotating around the nucleus at 250 km/s. ...
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
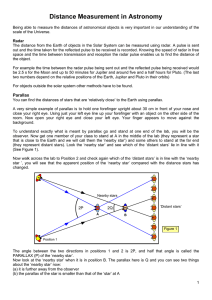
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.