Part 2 of Our Lecture
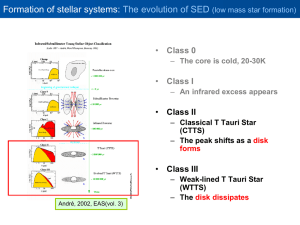
... Formation of stellar systems: Observations (4) • SEDs of low-mass stars in NGC 7160 (about 10 Myr) (according to the same procedures followed for Tr 37) only 1 sample shows indications of active accretion (CTTS). – black dotted line : similar spectral type derived from Kenyon & ...
... Formation of stellar systems: Observations (4) • SEDs of low-mass stars in NGC 7160 (about 10 Myr) (according to the same procedures followed for Tr 37) only 1 sample shows indications of active accretion (CTTS). – black dotted line : similar spectral type derived from Kenyon & ...
Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... and formaldehyde (H2CO). Clouds and Nebulae 1. Interstellar cirrus clouds contain less than 1,000 molecules per cubic centimeter. 2. A reflection nebula is an interstellar dust cloud that is visible due to reflected light from a nearby star. 3. Dust clouds can contain up to 1 million molecules per c ...
... and formaldehyde (H2CO). Clouds and Nebulae 1. Interstellar cirrus clouds contain less than 1,000 molecules per cubic centimeter. 2. A reflection nebula is an interstellar dust cloud that is visible due to reflected light from a nearby star. 3. Dust clouds can contain up to 1 million molecules per c ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 38-
... Then astronomers labeled a second group of stars as second magnitude. So you might think of those as second class stars, not quite as important but still quite bright. If you’re trying to think of how bright they would be, the Big Dipper stars are almost all second magnitude. So if you’re looking at ...
... Then astronomers labeled a second group of stars as second magnitude. So you might think of those as second class stars, not quite as important but still quite bright. If you’re trying to think of how bright they would be, the Big Dipper stars are almost all second magnitude. So if you’re looking at ...
My power point presentation on spectroscopy of stars (ppt file)
... about temperature, pressure, chemical composition, rotation velocity, magnetic fields, binary companions ...
... about temperature, pressure, chemical composition, rotation velocity, magnetic fields, binary companions ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
1.2.43The stellar populations of the Milky Way
... main sequence stars burning hydrogen in their cores. The more massive stars that formed at the same time as the surviving low-mass ones have already left the main sequence and are now red giants or white dwarfs. For a long time it was thought that all Pop. II stars had much lower metallicities than ...
... main sequence stars burning hydrogen in their cores. The more massive stars that formed at the same time as the surviving low-mass ones have already left the main sequence and are now red giants or white dwarfs. For a long time it was thought that all Pop. II stars had much lower metallicities than ...
Widener University
... Exercise #2 A star has mass 2.5 Msun = 5.0 x 1030 kg, radius 2.0 Rsun = 1.4 x 109 m, and luminosity 40 Lsun = 1.6 x 1028 W. The star is initially composed of 100% H and converts all of it to He, each chain of 4H He releasing an amount of energy E = 4.3 x 10-12 J. Calculate: a) the total number o ...
... Exercise #2 A star has mass 2.5 Msun = 5.0 x 1030 kg, radius 2.0 Rsun = 1.4 x 109 m, and luminosity 40 Lsun = 1.6 x 1028 W. The star is initially composed of 100% H and converts all of it to He, each chain of 4H He releasing an amount of energy E = 4.3 x 10-12 J. Calculate: a) the total number o ...
Lecture 10: Stellar Evolution
... The closest supernova in the last four centuries was seen in 1987 ...
... The closest supernova in the last four centuries was seen in 1987 ...
ph507rev1
... also\line along the same main-sequence strip. However they appear very dim,\of course due to their distance. On comparison of fluxes, we determine the distance. This works out to about 100,000 pc, beyond which main-sequence stars are too \dim. ...
... also\line along the same main-sequence strip. However they appear very dim,\of course due to their distance. On comparison of fluxes, we determine the distance. This works out to about 100,000 pc, beyond which main-sequence stars are too \dim. ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
August 2014 Saguaro Skies
... 20” f5 Dobsonian, 180X, Ken Reeves: Very large, pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnific ...
... 20” f5 Dobsonian, 180X, Ken Reeves: Very large, pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnific ...
Understanding Stars
... Try to distribute the work so each group member is responsible for one star – and if you have more stars than group members, feel free to leave off any extra stars. The values for the Sun are given in the first row for reference. ...
... Try to distribute the work so each group member is responsible for one star – and if you have more stars than group members, feel free to leave off any extra stars. The values for the Sun are given in the first row for reference. ...
Document
... Main Sequence Stars • For main sequence stars luminosity and colour are related • If you know the spectral type of a main sequence star, the HR diagram gives the luminosity • Use inverse square law to get distance • Good to 10s of kpc • Also known (confusingly) as spectroscopic parallax ...
... Main Sequence Stars • For main sequence stars luminosity and colour are related • If you know the spectral type of a main sequence star, the HR diagram gives the luminosity • Use inverse square law to get distance • Good to 10s of kpc • Also known (confusingly) as spectroscopic parallax ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in ...
... Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in ...
Lesson Plan G2 The Stars
... Stars are born, evolve and die. Stars have a life cycle that depends on the initial mass of the star. The composition and structure of stars changes at different stages in their life cycle. Stars in the Milky Way can be different from the Sun in size, temperature, age and brightness. The Sun is a ma ...
... Stars are born, evolve and die. Stars have a life cycle that depends on the initial mass of the star. The composition and structure of stars changes at different stages in their life cycle. Stars in the Milky Way can be different from the Sun in size, temperature, age and brightness. The Sun is a ma ...
Sky-High 2013 - Irish Astronomical Society
... as we see them for our immediate purpose. The fact that the Earth turns on its axis about every 24 hours causes the Sun to rise in the east and set in the west, and it is due south at noon. A similar situation applies to all the other heavenly bodies except that since they appear to move relative to ...
... as we see them for our immediate purpose. The fact that the Earth turns on its axis about every 24 hours causes the Sun to rise in the east and set in the west, and it is due south at noon. A similar situation applies to all the other heavenly bodies except that since they appear to move relative to ...
Powerpoint Review
... The size of the light source. The strength of the light source. Since not all stars are the same distance from your eye, size, or strength, every star will have a different brightness when you look up into the night sky. The brightness of a star as it appears from the earth, without the effect of th ...
... The size of the light source. The strength of the light source. Since not all stars are the same distance from your eye, size, or strength, every star will have a different brightness when you look up into the night sky. The brightness of a star as it appears from the earth, without the effect of th ...
preliminary version - University of Exeter
... The most efficient method of determining large numbers of periods for young stars is via photometric monitoring. Unfortunately, this method has proved insensitive to periods amongst CTTs in the past, largely due to the irregular variability shown by CTTs[2,3]. This bias against CTTs is a major probl ...
... The most efficient method of determining large numbers of periods for young stars is via photometric monitoring. Unfortunately, this method has proved insensitive to periods amongst CTTs in the past, largely due to the irregular variability shown by CTTs[2,3]. This bias against CTTs is a major probl ...
16. Magnitude Systems
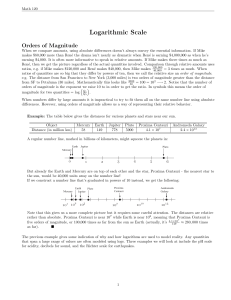
... (RI by Cousins) – and extended to a system of cheaper glass filters by Bessell • In this system (calibrated by flux measurements of many stars) Vega’s magnitude is close to 0 in every passband: – UVega = 0; BVega = 0; VVega = 0; RVega = 0; IVega = 0 ...
... (RI by Cousins) – and extended to a system of cheaper glass filters by Bessell • In this system (calibrated by flux measurements of many stars) Vega’s magnitude is close to 0 in every passband: – UVega = 0; BVega = 0; VVega = 0; RVega = 0; IVega = 0 ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.