PRESS 2001 Project Report - Hong Kong University of Science and
... Half or more of all stars in the universe are in orbit around another star or stars. In most of these multiple-star systems, there is a type of system which consists of two stars only, known as a binary star system, whose components may be separated by a large fraction of a light year, or they may b ...
... Half or more of all stars in the universe are in orbit around another star or stars. In most of these multiple-star systems, there is a type of system which consists of two stars only, known as a binary star system, whose components may be separated by a large fraction of a light year, or they may b ...
Variable Stars – II. Pulsating stars
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
... In this case the star is unstable to pulsation and any small variation, will be reinforced – the pulsation will grow until the energy input by the κ-mechanism reaches a limit. The star will then be pulsating with a stable period and amplitude. Note that the partial ionization zones can be near the s ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
Searching for RR Lyrae Stars in M15
... RR Lyrae stars are special kinds of stars that undergo rapid changes in luminosity due to the regular, periodic pulsation of the star. The name comes from the fact that RR indicates that it is a variable star with variations in brightness and that the first of these stars were found in the constella ...
... RR Lyrae stars are special kinds of stars that undergo rapid changes in luminosity due to the regular, periodic pulsation of the star. The name comes from the fact that RR indicates that it is a variable star with variations in brightness and that the first of these stars were found in the constella ...
stars - acpsd
... Another fundamental property of a main sequence star evolution is hydrostatic equilibrium. Hydrostatic equilibrium reflects the required pressure in the core of a star to support the weight of the outer plasma layers. The heat produced from hydrogen in the core burning supports this outward pressure ...
... Another fundamental property of a main sequence star evolution is hydrostatic equilibrium. Hydrostatic equilibrium reflects the required pressure in the core of a star to support the weight of the outer plasma layers. The heat produced from hydrogen in the core burning supports this outward pressure ...
H-Band spectroscopic classification of OB stars
... using dome flats and then sky subtracted using another image from the grid with the star displaced by several positions along the slit (cross–dispersed mode) or with a median combination sky image (long slit mode). Individual spectra were extracted from each program star image and atmospheric standa ...
... using dome flats and then sky subtracted using another image from the grid with the star displaced by several positions along the slit (cross–dispersed mode) or with a median combination sky image (long slit mode). Individual spectra were extracted from each program star image and atmospheric standa ...
Supermassive Black Holes in Inactive Galaxies Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org
... holes (BHs) that accrete gas and stars and so transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Expected BH masses are M• ~ 106–109.5M⊙. A wide array of phenomena can be understood within this picture. However, the subject has had an outstanding problem: there was no dynamical evidence that B ...
... holes (BHs) that accrete gas and stars and so transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Expected BH masses are M• ~ 106–109.5M⊙. A wide array of phenomena can be understood within this picture. However, the subject has had an outstanding problem: there was no dynamical evidence that B ...
The Distances to the Stars
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
stellar spectra instructor notes
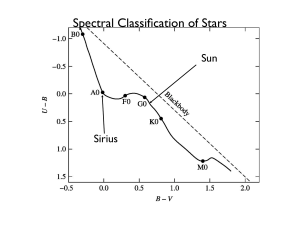
... elements, some method of classifying stellar spectra was desirable. The hydrogen Balmer line sequence was recognized from the earliest such studies, and so the earliest classification scheme of any duration was a Harvard scheme developed by Pickering and Fleming based upon photographically-recorded ...
... elements, some method of classifying stellar spectra was desirable. The hydrogen Balmer line sequence was recognized from the earliest such studies, and so the earliest classification scheme of any duration was a Harvard scheme developed by Pickering and Fleming based upon photographically-recorded ...
Science Grade 08 Unit 11 Exemplar Lesson 02: Classifying Stars
... Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continue to answer questions. Monitor students’ answers for accuracy as they compl ...
... Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continue to answer questions. Monitor students’ answers for accuracy as they compl ...
Chapter 15
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in ...
... Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in ...
Orion – The Hunter - Guild of Students
... The multiple star theta1 Ori, the northern star of the deggar of the Hunter is also called the Trapezium; it is located in the heart of the Orion nebula. This group of stars has been formed from the gas of the nebula, which now glows in their light. Zeta Ori (Alnitak), it is a tight double consistin ...
... The multiple star theta1 Ori, the northern star of the deggar of the Hunter is also called the Trapezium; it is located in the heart of the Orion nebula. This group of stars has been formed from the gas of the nebula, which now glows in their light. Zeta Ori (Alnitak), it is a tight double consistin ...
Solutions to the 1 st Astronomy Exam
... south and is called the Antarctic Pole.” Why did Aristotle not mention that Polaris is a fairly bright star located near the Arctic Pole? Answer in a couple of sentences. Aristotle did not mention that Polaris is a fairly bright star located near the Arctic Pole because at that time there was no bri ...
... south and is called the Antarctic Pole.” Why did Aristotle not mention that Polaris is a fairly bright star located near the Arctic Pole? Answer in a couple of sentences. Aristotle did not mention that Polaris is a fairly bright star located near the Arctic Pole because at that time there was no bri ...
Stellar Evolution – Cosmic Cycles of Formation and Destruction
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
LAB #5 - GEOCITIES.ws
... In the course of the Harvard classification study, some of the old spectral types were consolidated together, and the types were re-arranged to reflect a steady change in the strengths of representative spectral lines. The order of the spectral classes became O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, and though the ...
... In the course of the Harvard classification study, some of the old spectral types were consolidated together, and the types were re-arranged to reflect a steady change in the strengths of representative spectral lines. The order of the spectral classes became O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, and though the ...
Determination of kinetic energies of stars using Hipparcos data *
... has resulted in kind of a U-turn of the astronomical community towards stellar kinematics. This is not surprising, in view of the fact that the previous peak of the amount of works devoted to stellar kinematics was in 1930s when the General Catalogue by B. Boss became available (Boss, B. 1937). The ...
... has resulted in kind of a U-turn of the astronomical community towards stellar kinematics. This is not surprising, in view of the fact that the previous peak of the amount of works devoted to stellar kinematics was in 1930s when the General Catalogue by B. Boss became available (Boss, B. 1937). The ...
Asteroseismology of Solar-Like Stars
... With these scaling relations and an independent source of Tef f , the project can progress, and power spectra, along with stellar parameters can be determined. ...
... With these scaling relations and an independent source of Tef f , the project can progress, and power spectra, along with stellar parameters can be determined. ...
Dynamics of elliptical galaxies
... Dynamics of elliptical galaxies Galaxies that appear elliptical on the sky may be intrinsically oblate, prolate, or triaxial, depending upon their symmetries: ...
... Dynamics of elliptical galaxies Galaxies that appear elliptical on the sky may be intrinsically oblate, prolate, or triaxial, depending upon their symmetries: ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.