Progenitor and environment of the peculiar red nova V838 Mon
... We observed how emission spectrum of ionized gas increased its intensity. In 2009, neither the hot companion nor the emission spectrum are seen. The residual intensity at minimum of the TiO bands is zero. Thus, the hot companion plunged into the expanding ...
... We observed how emission spectrum of ionized gas increased its intensity. In 2009, neither the hot companion nor the emission spectrum are seen. The residual intensity at minimum of the TiO bands is zero. Thus, the hot companion plunged into the expanding ...
A near IR adaptive optics search for faint companions to early
... show a new bright component P (K = 11.2) and at least two additional fainter components Q and R. While little can be said about the fainter sources, the P component is very likely physical, judging by its proximity to C and its brightness. Its colour J − K = 1.24 is too red for a normal star, but no ...
... show a new bright component P (K = 11.2) and at least two additional fainter components Q and R. While little can be said about the fainter sources, the P component is very likely physical, judging by its proximity to C and its brightness. Its colour J − K = 1.24 is too red for a normal star, but no ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
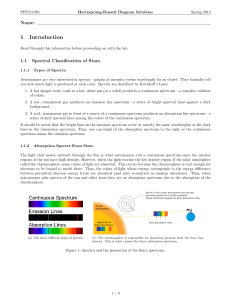
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of beta brings us to NGC 5915 and 5916. The western most galaxy NGC 5915 is the brighter, a face-on barred spiral that ...
... North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of beta brings us to NGC 5915 and 5916. The western most galaxy NGC 5915 is the brighter, a face-on barred spiral that ...
15_Testbank
... A) is decreased by a factor of four, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four. B) is decreased by a factor of two, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two. C) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two. D) remains the same, b ...
... A) is decreased by a factor of four, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four. B) is decreased by a factor of two, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two. C) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two. D) remains the same, b ...
Astronomy 114 - Department of Astronomy
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
13.1 Introduction 13.2 The Red Giant Branch
... Table 13.1 gives some representative values for the sizes and luminosities of red giant stars; a main sequence G V star may end up as a high-K or low-M luminosity class III giant. Note that the values in Table 13.1 depend largely on the spectral type, and not on the mass: stars of a wide range of ma ...
... Table 13.1 gives some representative values for the sizes and luminosities of red giant stars; a main sequence G V star may end up as a high-K or low-M luminosity class III giant. Note that the values in Table 13.1 depend largely on the spectral type, and not on the mass: stars of a wide range of ma ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... Parallaxes can be used to measure distances for stars within ~1000 light years from the Sun; parallaxes of more distant stars are too small to measure, even with modern telescopes. Most stars in the Milky are farther than 1000 light years, so we need another way to determine the diameter of the Milk ...
... Parallaxes can be used to measure distances for stars within ~1000 light years from the Sun; parallaxes of more distant stars are too small to measure, even with modern telescopes. Most stars in the Milky are farther than 1000 light years, so we need another way to determine the diameter of the Milk ...
Lec09_ch11_lifecycleofstars
... cluster stars reveals the age of the cluster – since the globular cluster stars are gravitationally bound close together, they are the same distance from us • use apparent magnitude ...
... cluster stars reveals the age of the cluster – since the globular cluster stars are gravitationally bound close together, they are the same distance from us • use apparent magnitude ...
Слайд 1 - Tuorla Observatory
... parallax technique enables – (a) To refine the accepted distance scale and absolute magnitude calibration used – (b) To take into account all observational errors – (c) To calculate full set of kinematical parameters of a given uniform stellar sample (space velocity of the Sun, rotation curve or oth ...
... parallax technique enables – (a) To refine the accepted distance scale and absolute magnitude calibration used – (b) To take into account all observational errors – (c) To calculate full set of kinematical parameters of a given uniform stellar sample (space velocity of the Sun, rotation curve or oth ...
Distance
... parallax technique enables – (a) To refine the accepted distance scale and absolute magnitude calibration used – (b) To take into account all observational errors – (c) To calculate full set of kinematical parameters of a given uniform stellar sample (space velocity of the Sun, rotation curve or oth ...
... parallax technique enables – (a) To refine the accepted distance scale and absolute magnitude calibration used – (b) To take into account all observational errors – (c) To calculate full set of kinematical parameters of a given uniform stellar sample (space velocity of the Sun, rotation curve or oth ...
Li-cai Deng
... Many surveys currently in progress will provide multi-color imaging of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scale structures of galaxies had just been discovered. But there was structure o ...
... Many surveys currently in progress will provide multi-color imaging of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scale structures of galaxies had just been discovered. But there was structure o ...
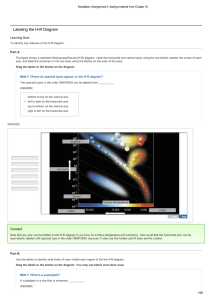
Labeling the HR Diagram - Mastering Physics Answers
... Spectral type is related to surface temperature, with stars of spectral type O having the highest surface temperature and stars of spectral type M having the lowest surface temperature. In other words, spectral type increases to the left on the HR diagram. Now proceed to Part E to determine how the ...
... Spectral type is related to surface temperature, with stars of spectral type O having the highest surface temperature and stars of spectral type M having the lowest surface temperature. In other words, spectral type increases to the left on the HR diagram. Now proceed to Part E to determine how the ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... RR Lyrae variables are periodic variable stars, commonly found in globular clusters, and often used as standard candles to measure galactic distances. • This type of variable is named after the prototype, the variable star RR Lyrae in the constellation Lyra. • RR Lyraes are pulsating horizontal bra ...
... RR Lyrae variables are periodic variable stars, commonly found in globular clusters, and often used as standard candles to measure galactic distances. • This type of variable is named after the prototype, the variable star RR Lyrae in the constellation Lyra. • RR Lyraes are pulsating horizontal bra ...
PHYS3380_102815_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... high mass stars are generally confined to a very small region, much smaller than the size of the convective core. - conditions under which a region of a star is unstable to convection is expresses by the Schwarzschild criterion: ...
... high mass stars are generally confined to a very small region, much smaller than the size of the convective core. - conditions under which a region of a star is unstable to convection is expresses by the Schwarzschild criterion: ...
A Stars
... stars of the same Temperature. – Means they must be smaller in radius. – L-R-T Relation predicts: R ~ 0.01 Rsun (~ size of Earth!) ...
... stars of the same Temperature. – Means they must be smaller in radius. – L-R-T Relation predicts: R ~ 0.01 Rsun (~ size of Earth!) ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
17_LectureOutline
... The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
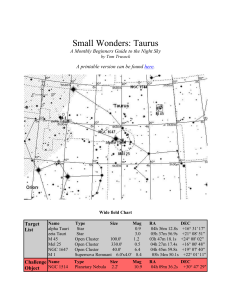
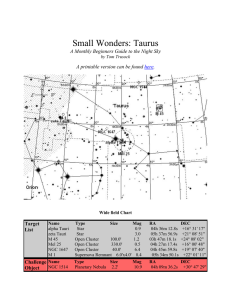
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... have that issue with 1514. The central star shines at a bright 9th magnitude while the nebula is listed at 11th. The nebula is fairly large at around 1.5'-3' in size, but dim. In smaller scopes, look for a circular haze surrounding a 9th magnitude star flanked by two other stars of similar brightnes ...
... have that issue with 1514. The central star shines at a bright 9th magnitude while the nebula is listed at 11th. The nebula is fairly large at around 1.5'-3' in size, but dim. In smaller scopes, look for a circular haze surrounding a 9th magnitude star flanked by two other stars of similar brightnes ...
Small Wonders: Taurus
... have that issue with 1514. The central star shines at a bright 9th magnitude while the nebula is listed at 11th. The nebula is fairly large at around 1.5'-3' in size, but dim. In smaller scopes, look for a circular haze surrounding a 9th magnitude star flanked by two other stars of similar brightnes ...
... have that issue with 1514. The central star shines at a bright 9th magnitude while the nebula is listed at 11th. The nebula is fairly large at around 1.5'-3' in size, but dim. In smaller scopes, look for a circular haze surrounding a 9th magnitude star flanked by two other stars of similar brightnes ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.