How do stars orbit in our galaxy?
... • Stars are born from the gravitational collapse of gas clumps in molecular clouds. Near the ends of their lives, stars more massive than our Sun create elements heavier than hydrogen and helium and expel them into space via supernovae and stellar winds. The supernovae and winds create hot bubbles i ...
... • Stars are born from the gravitational collapse of gas clumps in molecular clouds. Near the ends of their lives, stars more massive than our Sun create elements heavier than hydrogen and helium and expel them into space via supernovae and stellar winds. The supernovae and winds create hot bubbles i ...
classifying stars
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... age distribution of the LMC Cepheids is found to have a peak at log Age = 8.2 ± 0.1. This suggests that major star formation event took place at about 125–200 Myr ago which may have been triggered by a close encounter between the SMC and the LMC. Cepheids are found to be asymmetrically distributed t ...
... age distribution of the LMC Cepheids is found to have a peak at log Age = 8.2 ± 0.1. This suggests that major star formation event took place at about 125–200 Myr ago which may have been triggered by a close encounter between the SMC and the LMC. Cepheids are found to be asymmetrically distributed t ...
Application Exercise: Distances to Stars Using Measured Parallax
... Law being useful at the farthest distance (e.g., galaxies far, far away). In this exercise, we investigate the use of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still ...
... Law being useful at the farthest distance (e.g., galaxies far, far away). In this exercise, we investigate the use of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still ...
Star Formation in Our Galaxy - Wiley-VCH
... near the edge of the Orion A cloud, as depicted in Figure 1.6. While the ionization created by the OB association slowly eats its way into the cloud, hot matter on the other side streams out into the more rarefied gas adjacent to the cloud. As sketched in the figure, this streaming motion in the dir ...
... near the edge of the Orion A cloud, as depicted in Figure 1.6. While the ionization created by the OB association slowly eats its way into the cloud, hot matter on the other side streams out into the more rarefied gas adjacent to the cloud. As sketched in the figure, this streaming motion in the dir ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
Teacher`s Guide - Cornell Science Inquiry Partnerships
... Astronomy, Earth Science Audience This activity is aimed at a high school audience, but it could easily be modified for use with middle school students. Time Required The essential activities can be covered in 40 minutes, or the entire project can be stretched to 4 hours or even much longer. (In the ...
... Astronomy, Earth Science Audience This activity is aimed at a high school audience, but it could easily be modified for use with middle school students. Time Required The essential activities can be covered in 40 minutes, or the entire project can be stretched to 4 hours or even much longer. (In the ...
Stellar Physics 1
... 6. What is the constant ‘σ’ in the relation L= 4πR2σT4? A. Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Y B. Boltzmann constant. C. Wien constant. D. Planck constant. ...
... 6. What is the constant ‘σ’ in the relation L= 4πR2σT4? A. Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Y B. Boltzmann constant. C. Wien constant. D. Planck constant. ...
Apparent Motion of the Stars Worksheet
... [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equator, the slant angle relative to the vertical of lines of declination are equal to the observer’s latitude.] Draw the ...
... [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equator, the slant angle relative to the vertical of lines of declination are equal to the observer’s latitude.] Draw the ...
26.2 Stars - Clinton Public Schools
... the brightest stars in the sky. moving away from Earth. the most massive. ...
... the brightest stars in the sky. moving away from Earth. the most massive. ...
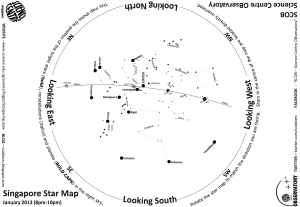
Setting Instruction
... • The constellation display includes the positions of 452 fixed stars with a brightness of the 4.0th magnitude or brighter, 119 major nebulae and star clusters, delimitation of constellations, and the ecliptic and the celestial equator based on their positions for the year 2000.0. (Maximum magnitude ...
... • The constellation display includes the positions of 452 fixed stars with a brightness of the 4.0th magnitude or brighter, 119 major nebulae and star clusters, delimitation of constellations, and the ecliptic and the celestial equator based on their positions for the year 2000.0. (Maximum magnitude ...
B LOG - Science Centre
... 1) M6 (Butterfly Cluster) – beautiful open star cluster arranged in curved chains like the wings of a butterfly. Visible in binoculars, best in telescope using low magnification. 2) M7 – large open cluster of about 70 stars. Triangular pattern. Close to M6 and other star clusters. ...
... 1) M6 (Butterfly Cluster) – beautiful open star cluster arranged in curved chains like the wings of a butterfly. Visible in binoculars, best in telescope using low magnification. 2) M7 – large open cluster of about 70 stars. Triangular pattern. Close to M6 and other star clusters. ...
PH607lec12-5gal3
... fainter lines in this region due to [NII]. HII regions appear reddish in this image because of the prominence of the H alpha line in the red region of the spectrum. The dark features running vertically trace emission in the hydrogen H-alpha line (left and stronger feature, rest wavelength 6563 Angst ...
... fainter lines in this region due to [NII]. HII regions appear reddish in this image because of the prominence of the H alpha line in the red region of the spectrum. The dark features running vertically trace emission in the hydrogen H-alpha line (left and stronger feature, rest wavelength 6563 Angst ...
July - Rose City Astronomers
... RCA July General Meeting “One Leg at a Time, How the Great Astronomers Put on Their Pants.” Presented By David Powell ...
... RCA July General Meeting “One Leg at a Time, How the Great Astronomers Put on Their Pants.” Presented By David Powell ...
JHK standard stars for large telescopes: the UKIRT Fundamental
... We present high-precision JHK photometry with the 3.8-m UK Infrared Telescope (UKIRT) of 82 standard stars, 28 from the widely used preliminary list known as the ‘UKIRT Faint Standards’, referred to here as the Fundamental List, and 54 additional stars referred to as the Extended List. The stars hav ...
... We present high-precision JHK photometry with the 3.8-m UK Infrared Telescope (UKIRT) of 82 standard stars, 28 from the widely used preliminary list known as the ‘UKIRT Faint Standards’, referred to here as the Fundamental List, and 54 additional stars referred to as the Extended List. The stars hav ...
Our Local Group of Galaxies
... • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be surveyed with SkyMapper. Likely to find ~20-30 new faint ...
... • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be surveyed with SkyMapper. Likely to find ~20-30 new faint ...
High Precision Parallax Collecting Satellite
... Many a night I saw the Pleiads, rising thro’ the mellow shade Glitter like a swarm of fireflies, tangled in a silver braid. ...
... Many a night I saw the Pleiads, rising thro’ the mellow shade Glitter like a swarm of fireflies, tangled in a silver braid. ...
the UKIRT Fundamental and Extended lists
... We present high-precision JHK photometry with the 3.8-m UK Infrared Telescope (UKIRT) of 82 standard stars, 28 from the widely used preliminary list known as the ‘UKIRT Faint Standards’, referred to here as the Fundamental List, and 54 additional stars referred to as the Extended List. The stars hav ...
... We present high-precision JHK photometry with the 3.8-m UK Infrared Telescope (UKIRT) of 82 standard stars, 28 from the widely used preliminary list known as the ‘UKIRT Faint Standards’, referred to here as the Fundamental List, and 54 additional stars referred to as the Extended List. The stars hav ...
PH607lec11-4gal2
... fainter lines in this region due to [NII]. HII regions appear reddish in this image because of the prominence of the H alpha line in the red region of the spectrum. The dark features running vertically trace emission in the hydrogen H-alpha line (left and stronger feature, rest wavelength 6563 Angst ...
... fainter lines in this region due to [NII]. HII regions appear reddish in this image because of the prominence of the H alpha line in the red region of the spectrum. The dark features running vertically trace emission in the hydrogen H-alpha line (left and stronger feature, rest wavelength 6563 Angst ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.