ChAPTER 10 sTARS
... a. What images or pictures can you envision in these stars? Imagine a picture in the stars that is your own original constellation outline the picture on your handout b. Select a name for your constellation. In your science notebook, write why you chose that name and briefly describe your constellat ...
... a. What images or pictures can you envision in these stars? Imagine a picture in the stars that is your own original constellation outline the picture on your handout b. Select a name for your constellation. In your science notebook, write why you chose that name and briefly describe your constellat ...
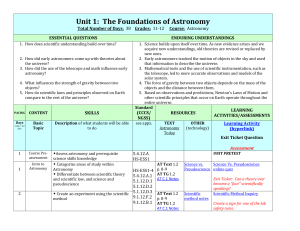
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
Electronic version of lab manual 1-6 ()
... over the run. Once you find the value of m, you can solve for b. The value of b can also be determined by inspection.) ALGEBRA and RATIOS Understanding astronomical sizes and distances can be difficult as they are often so large that they go beyond our everyday comprehension. One way to appreciate t ...
... over the run. Once you find the value of m, you can solve for b. The value of b can also be determined by inspection.) ALGEBRA and RATIOS Understanding astronomical sizes and distances can be difficult as they are often so large that they go beyond our everyday comprehension. One way to appreciate t ...
Space Unit notes
... Satellites are designed to perform one of four functions: Communication - provide ‘wireless’ technologies for a wide range of applications. Digital signals have resulted in clearer communications and more users. Observation and Research - A geosynchronous orbit is one that enables a satellite to re ...
... Satellites are designed to perform one of four functions: Communication - provide ‘wireless’ technologies for a wide range of applications. Digital signals have resulted in clearer communications and more users. Observation and Research - A geosynchronous orbit is one that enables a satellite to re ...
1 - ESO
... quantity “tau”? • For a variety of reasons, total disk mass is best measured at submillimeter wavelengths. But tau, which is a measure of far-IR excess emission, is much easier to measure and has been determined for an order of magnitude more stars than has dust mass. ...
... quantity “tau”? • For a variety of reasons, total disk mass is best measured at submillimeter wavelengths. But tau, which is a measure of far-IR excess emission, is much easier to measure and has been determined for an order of magnitude more stars than has dust mass. ...
Word version of Episode 704
... Discussion: Hubble’s observations Hubble measured 24 galaxies. 22 had red shifted light. He plotted recession speed v against distance d. Speed was much easier to measure (from the Doppler shift) than distance. There are real problems in setting a length scale. Different methods are used at the ever ...
... Discussion: Hubble’s observations Hubble measured 24 galaxies. 22 had red shifted light. He plotted recession speed v against distance d. Speed was much easier to measure (from the Doppler shift) than distance. There are real problems in setting a length scale. Different methods are used at the ever ...
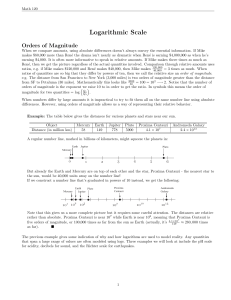
Logarithmic Scale
... Charles Richter introduced his scale in 1935 in order to differentiate between the magnitudes (and quantities) of earthquakes in southern California. The rough definition of the Richter scale is based in measuring the amplitude of the mark a quake registers on a seismograph and taking its log relative ...
... Charles Richter introduced his scale in 1935 in order to differentiate between the magnitudes (and quantities) of earthquakes in southern California. The rough definition of the Richter scale is based in measuring the amplitude of the mark a quake registers on a seismograph and taking its log relative ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... An orbiting telescope that collects light from celestial objects in visible, nearultraviolet, and near-infrared wavelengths. The telescope’s primary mirror is 2.4 meters (8 feet) wide. It orbits the Earth about every 96 minutes and is powered by sunlight collected with its two solar arrays. ...
... An orbiting telescope that collects light from celestial objects in visible, nearultraviolet, and near-infrared wavelengths. The telescope’s primary mirror is 2.4 meters (8 feet) wide. It orbits the Earth about every 96 minutes and is powered by sunlight collected with its two solar arrays. ...
Young Astronomers Digest
... Hi Young Astronomer digest, my friends and I have both agreed that this magazine’s the best! It practically covers everything that we need to know for astronomy. Interesting articles featured every month have awed me for the whole month…Plus, I was euphoric reading your July issue. The tips of buyin ...
... Hi Young Astronomer digest, my friends and I have both agreed that this magazine’s the best! It practically covers everything that we need to know for astronomy. Interesting articles featured every month have awed me for the whole month…Plus, I was euphoric reading your July issue. The tips of buyin ...
Comparison of the Phenomena of Light Refraction and Gravitational
... front of the light is rotated because dc’/dy is not zero. Changing the measure of time cannot affect the direction that individual objects move, however. This means that the light must continue to move in the same direction as before, that is, in a straight line. There is thus already an indication ...
... front of the light is rotated because dc’/dy is not zero. Changing the measure of time cannot affect the direction that individual objects move, however. This means that the light must continue to move in the same direction as before, that is, in a straight line. There is thus already an indication ...
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in
... - The situation has changed considerably with the adoption of the International Celestial Reference system (ICRS) by the IAU since 1998 and the IAU resolutions on reference systems that were adopted between 2000 and 2009. These correspond to major improvements in concepts and realizations of astrono ...
... - The situation has changed considerably with the adoption of the International Celestial Reference system (ICRS) by the IAU since 1998 and the IAU resolutions on reference systems that were adopted between 2000 and 2009. These correspond to major improvements in concepts and realizations of astrono ...
PDF
... suggested a significantly smaller distance of 118 parsecs as compared to the so far accepted ground-based 135 parsecs. One parsec is the distance to which the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun (called an astronomical unit), subtends an angle of one arcsecond. Distances have been always ver ...
... suggested a significantly smaller distance of 118 parsecs as compared to the so far accepted ground-based 135 parsecs. One parsec is the distance to which the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun (called an astronomical unit), subtends an angle of one arcsecond. Distances have been always ver ...
Improved pointing information for SCIAMACHY from in
... elevation. Top: The ASM mirror is not in the light path. The azimuth angle of the solar disk is changed by the orbital motion of the platform. At maximum intensity, the azimuth angle is 270◦ because that is the viewing direction of the sub-solar port in azimuth. ...
... elevation. Top: The ASM mirror is not in the light path. The azimuth angle of the solar disk is changed by the orbital motion of the platform. At maximum intensity, the azimuth angle is 270◦ because that is the viewing direction of the sub-solar port in azimuth. ...
Upper elementary students investigate seasonal constellations
... Sun, but our location in space is changing with respect to change in constellations to the notion of a flipbook, where the Sun. Other students believe that we see different conyou could observe the change of constellations over time stellations because, as we orbit the Sun, we move too far in a cont ...
... Sun, but our location in space is changing with respect to change in constellations to the notion of a flipbook, where the Sun. Other students believe that we see different conyou could observe the change of constellations over time stellations because, as we orbit the Sun, we move too far in a cont ...
SPA 302: THE EVOLUTION OF STARS LECTURE 1: BASICS OF
... stars emit at the IR and we do not see them at all. Hotter objects emit more energy at ALL wavelengths due to higher average energy of ALL photons. ...
... stars emit at the IR and we do not see them at all. Hotter objects emit more energy at ALL wavelengths due to higher average energy of ALL photons. ...
MS Word
... These telescopes are able to resolve the miniscule angular sizes of distant stars. In conjunction with a distance measured using trigonometric parallax you will be able to calculate their true size and compare your theoretical size with an experimental one. ...
... These telescopes are able to resolve the miniscule angular sizes of distant stars. In conjunction with a distance measured using trigonometric parallax you will be able to calculate their true size and compare your theoretical size with an experimental one. ...
Earth Science Practice Test
... Ceres, Pluto, and Eris are all dwarf planets. In what order would you put them in a list from fastest to slowest? A. Eris, Pluto, Ceres B. Pluto, Ceres, Eris C. Ceres, Eris, Pluto D. Ceres, Pluto, Eris ...
... Ceres, Pluto, and Eris are all dwarf planets. In what order would you put them in a list from fastest to slowest? A. Eris, Pluto, Ceres B. Pluto, Ceres, Eris C. Ceres, Eris, Pluto D. Ceres, Pluto, Eris ...
Stars PowerPoint
... stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through several methods. • Accurate measurements can show that its position shifts back and forth as it orbits the center of mass. • In an eclipsing binary, the orbital plane of a binary system can sometimes b ...
... stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through several methods. • Accurate measurements can show that its position shifts back and forth as it orbits the center of mass. • In an eclipsing binary, the orbital plane of a binary system can sometimes b ...
ASTR 330: The Solar System
... arisen by the action of comparatively small forces, such as wind and rain, acting over very long times (billions of years). • So successful was uniformitarianism, that it prevented scientists from recognizing the importance of catastrophic processes, e.g. the crater density of the Moon, which is und ...
... arisen by the action of comparatively small forces, such as wind and rain, acting over very long times (billions of years). • So successful was uniformitarianism, that it prevented scientists from recognizing the importance of catastrophic processes, e.g. the crater density of the Moon, which is und ...
C - ScienceWilmeth5
... length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will decrease. ...
... length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will decrease. ...