Chapter 6 Physics
... 2. Assuming that a rocket is aimed above the horizon, does it matter which way it is aimed for it to escape from Earth? (Neglect air resistance.) 3. Determine the elevation in kilometres above the surface of Uranus where the gravitational field strength has a magnitude of 1.0 N/kg. 4. Ganymede, one ...
... 2. Assuming that a rocket is aimed above the horizon, does it matter which way it is aimed for it to escape from Earth? (Neglect air resistance.) 3. Determine the elevation in kilometres above the surface of Uranus where the gravitational field strength has a magnitude of 1.0 N/kg. 4. Ganymede, one ...
Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe (ES) V.4
... travel times, big bang, red shift. Tools: Telescopes, binoculars, spectroscopes Real-world contexts: Observations of other stars, star clusters, nebulas, and galaxies, observations of other potential planetary systems, accounts of possible travel to other star systems. ...
... travel times, big bang, red shift. Tools: Telescopes, binoculars, spectroscopes Real-world contexts: Observations of other stars, star clusters, nebulas, and galaxies, observations of other potential planetary systems, accounts of possible travel to other star systems. ...
powerpoint version
... 4500 K to 6000 K. Visible as red flash during solar eclipse. Corona: starts about 2000 km from the solar surface, rapid temperature rise to 500,000 K then slower rise to well over one million K. Probably heated by electric currents due to changing magnetic fields. Total energy in corona is small des ...
... 4500 K to 6000 K. Visible as red flash during solar eclipse. Corona: starts about 2000 km from the solar surface, rapid temperature rise to 500,000 K then slower rise to well over one million K. Probably heated by electric currents due to changing magnetic fields. Total energy in corona is small des ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... Planets traveled in smaller circular paths as they traveled around the Earth (epicycles and deferents) Popular model of universe for 1,500 years. ...
... Planets traveled in smaller circular paths as they traveled around the Earth (epicycles and deferents) Popular model of universe for 1,500 years. ...
Dead Earth – Lesson 2 – Solar System
... distance from the Sun, and what other objects exist in the Solar system I will be successful if I can : Explain how the conditions on a planet change as the distance from the Sun increases ...
... distance from the Sun, and what other objects exist in the Solar system I will be successful if I can : Explain how the conditions on a planet change as the distance from the Sun increases ...
Astronomy
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
6th Grade Review II - pams
... • The sun creates energy through fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in its core/center. • The seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth’s axis. • The moon appears to go through phases, because one side is always lit. • The phases of the moon are: new, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, fu ...
... • The sun creates energy through fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in its core/center. • The seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth’s axis. • The moon appears to go through phases, because one side is always lit. • The phases of the moon are: new, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, fu ...
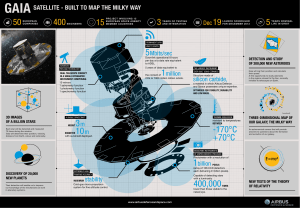
3m 10m -170°C +70°C 400,000
... Gaia will log their position and calculate their speed. A first opportunity to study asteroids in the regions closest to the Sun, normally invisible to telescopes on Earth. ...
... Gaia will log their position and calculate their speed. A first opportunity to study asteroids in the regions closest to the Sun, normally invisible to telescopes on Earth. ...
Subject- Geography Class- VI Chapter 1
... STARS: A star is a huge, bright ball of burning gas that is held together by gravity. Stars contain mostly hydrogen as well as helium and smaller amounts of other elements. The Sun is the closest star to Earth. THE SUN: The Sun is a star and the biggest object in the Solar System, it burns brightly ...
... STARS: A star is a huge, bright ball of burning gas that is held together by gravity. Stars contain mostly hydrogen as well as helium and smaller amounts of other elements. The Sun is the closest star to Earth. THE SUN: The Sun is a star and the biggest object in the Solar System, it burns brightly ...
Year 8 Science Home Learning Booklet
... (b) The diagram below shows the position of the Earth and the Sun when the astronomer made her observations. She noticed that Regulus was directly overhead at midnight. On the diagram, draw an arrow from the Earth to show the direction in which she looked to see ...
... (b) The diagram below shows the position of the Earth and the Sun when the astronomer made her observations. She noticed that Regulus was directly overhead at midnight. On the diagram, draw an arrow from the Earth to show the direction in which she looked to see ...
PHY 121 Astronomy
... see any parallax on the stars. They started with the wrong premise that the stars are on a sphere which is not too large in its diameter and so the stars were assumed to be much closer than they actually are. Starting with this wrong assumption, they concluded that the appearance of the constellatio ...
... see any parallax on the stars. They started with the wrong premise that the stars are on a sphere which is not too large in its diameter and so the stars were assumed to be much closer than they actually are. Starting with this wrong assumption, they concluded that the appearance of the constellatio ...
Document
... • RR Lyrae variables used like this to find our place in the Galaxy. • Distances that can be reached depend on the intrinsic brightness of the standard candle – and the limiting magnitude of your telescope ...
... • RR Lyrae variables used like this to find our place in the Galaxy. • Distances that can be reached depend on the intrinsic brightness of the standard candle – and the limiting magnitude of your telescope ...
Gravity
... that the force of gravity near the surface of the Earth is pretty much constant in magnitude and direction. The green lines are gravitational field lines. They show the direction of the gravitational force on any object in the region (straight down). In a uniform field, the lines are parallel and ev ...
... that the force of gravity near the surface of the Earth is pretty much constant in magnitude and direction. The green lines are gravitational field lines. They show the direction of the gravitational force on any object in the region (straight down). In a uniform field, the lines are parallel and ev ...
CHAPTER 4 FINAL REVIEW QUESTIONS MULTIPLE CHOICE
... is the book that first described the heliocentric solar system. b. ...
... is the book that first described the heliocentric solar system. b. ...
Today`s Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... Aristarchus: Used geometry of eclipses to show Sun bigger than Earth (and Moon smaller), so guessed that Earth orbits the Sun. Also guessed Earth spins on its axis once a day => apparent motion of stars. Aristotle: But there's no wind or parallax. ...
... Aristarchus: Used geometry of eclipses to show Sun bigger than Earth (and Moon smaller), so guessed that Earth orbits the Sun. Also guessed Earth spins on its axis once a day => apparent motion of stars. Aristotle: But there's no wind or parallax. ...
Distance Measurement
... The apparent change in the direction of the remote object due to a change in the vantage point of the observer is called parallax. ...
... The apparent change in the direction of the remote object due to a change in the vantage point of the observer is called parallax. ...
Space Part1
... What happens during a solar eclipse? Where must the Moon be for a solar eclipse to take place? ...
... What happens during a solar eclipse? Where must the Moon be for a solar eclipse to take place? ...
Perspectives of the Earth, Moon and Sun
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...