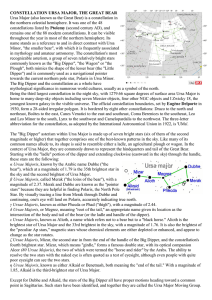
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
The Night Sky 12-07
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
... The bright winter stars are visible setting in the west as total darkness falls about two hours after sunset. Sirius, the well-known brightest star, puts on a show by scintillating rapidly in the heavier air near the horizon. Up in the southwest above Sirius is Procyon, another bright white star. Hi ...
Earth Science: Chapter 7: Stellar Evolution: Spring 2017: Student
... Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebula. The name planetary is actually misnamed by an early a ...
... Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebula. The name planetary is actually misnamed by an early a ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... NGC6205 (M13) (5.9) gc. Arguably one of the outstanding objects in the northern hemisphere. Just visible to the naked eye from dark sites it appears as a fuzzy blob in binoculars. It stands high power well and the outer edges begin to resolve into individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasi ...
... NGC6205 (M13) (5.9) gc. Arguably one of the outstanding objects in the northern hemisphere. Just visible to the naked eye from dark sites it appears as a fuzzy blob in binoculars. It stands high power well and the outer edges begin to resolve into individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasi ...
Document
... is based on the Doppler shift in the star's light as the star moves towards or away from us. ...
... is based on the Doppler shift in the star's light as the star moves towards or away from us. ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
Great Astronomers of the 20th Century
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
Star Life Cycle - GSHS Mrs. Francomb
... • After millions to billions of years, depending on their initial masses, stars run out of their main fuel - hydrogen. • Without the outward pressure generated from these reactions to counteract the force of gravity, the outer layers of the star begin to collapse inward toward the core. • Just as du ...
... • After millions to billions of years, depending on their initial masses, stars run out of their main fuel - hydrogen. • Without the outward pressure generated from these reactions to counteract the force of gravity, the outer layers of the star begin to collapse inward toward the core. • Just as du ...
Badge Day - GBT
... 3. Wavemaker: How can you make a wave? How can you make the wavelength shorter? ...
... 3. Wavemaker: How can you make a wave? How can you make the wavelength shorter? ...
Mountain Skies
... these folks as the sky turns are the two dogs. The Dog Star Sirius, the brightest star in the nighttime sky, is in the southwest. Above Sirius is the lesser or little dog consisting of only two naked eye stars, Procyon and the much dimmer Gomiesa. ...
... these folks as the sky turns are the two dogs. The Dog Star Sirius, the brightest star in the nighttime sky, is in the southwest. Above Sirius is the lesser or little dog consisting of only two naked eye stars, Procyon and the much dimmer Gomiesa. ...
Star Of Wonder
... Saturnalia festival, when the Christian celebration could avoid attention and thus escape persecution. The Saturnalia can in turn be traced to the winter solstice, the time of the shortest and darkest days, a time when a festival of lights was needed to cheer the soul. Did the Magi see a meteor, the ...
... Saturnalia festival, when the Christian celebration could avoid attention and thus escape persecution. The Saturnalia can in turn be traced to the winter solstice, the time of the shortest and darkest days, a time when a festival of lights was needed to cheer the soul. Did the Magi see a meteor, the ...
PDF copy
... The discovery of the mechanism of fasting and feasting process is the breakthrough that many were looking forward to and given important inputs for further theoretical understanding of these binaries. Says Dr Bhalerao: “This allows us to better understand how massive stars form, to study how binarie ...
... The discovery of the mechanism of fasting and feasting process is the breakthrough that many were looking forward to and given important inputs for further theoretical understanding of these binaries. Says Dr Bhalerao: “This allows us to better understand how massive stars form, to study how binarie ...
Star Characteristics
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
Stars Unit
... Apparent Absolute Magnitude Magnitude What the star looks like from Earth… based on distance from earth ...
... Apparent Absolute Magnitude Magnitude What the star looks like from Earth… based on distance from earth ...
Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... The Beehive Cluster (M44) • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
... The Beehive Cluster (M44) • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... - Stars are classified by their size, brightness, color, temperature, spectrum and age. ...
... - Stars are classified by their size, brightness, color, temperature, spectrum and age. ...
Homework PHY121 (Astronomy
... Q: What characteristic do stars in a constellation or asterism share? A: Stars in a constellation or an asterism appear to be in about the same direction as seen from Earth. They are part of a grouping of stars on the celestial sphere which has a shape which suggested a particular object, animal or ...
... Q: What characteristic do stars in a constellation or asterism share? A: Stars in a constellation or an asterism appear to be in about the same direction as seen from Earth. They are part of a grouping of stars on the celestial sphere which has a shape which suggested a particular object, animal or ...
Document
... Notice that the X axis is spaced unevenly, and the number of Kelvins (degrees) between each line is not constant. This because it is a logarithmic scale. For example: each line between 2,000 and 3,000 represents 100 degrees; but each line between 6,000 and 7,000 represents 200 degrees; and differe ...
... Notice that the X axis is spaced unevenly, and the number of Kelvins (degrees) between each line is not constant. This because it is a logarithmic scale. For example: each line between 2,000 and 3,000 represents 100 degrees; but each line between 6,000 and 7,000 represents 200 degrees; and differe ...
Chapter 19 Notes Stars Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... Supernovae define a fundamentally different event – here, the entire star is disrupted in a vastly more energetic explosion. Two types of supernovae are have been identified by astronomers, based on a completely different set of circumstances. Oddly, each type produces about the same explosion e ...
... Supernovae define a fundamentally different event – here, the entire star is disrupted in a vastly more energetic explosion. Two types of supernovae are have been identified by astronomers, based on a completely different set of circumstances. Oddly, each type produces about the same explosion e ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
STARS In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.