Astronomy 103 – Midterm 2 – October 29, 2014
... 24. Once the luminosity of a star is known, what has to be measured in order to find the star’s radius? a) parallax angle to find distance b) color to find distance c) color to find surface temperature d) parallax angle to find surface temperature ...
... 24. Once the luminosity of a star is known, what has to be measured in order to find the star’s radius? a) parallax angle to find distance b) color to find distance c) color to find surface temperature d) parallax angle to find surface temperature ...
Binary Star - Armagh Observatory
... diameter is about 100 times bigger than it was originally, and has become cooler (the surface temperature is under 6,500 K). They are frequently orange in colour. Betelgeuse is a red giant. It is about 20 times as massive as the Sun, but about 14,000 times brighter than the Sun, and about 600 light- ...
... diameter is about 100 times bigger than it was originally, and has become cooler (the surface temperature is under 6,500 K). They are frequently orange in colour. Betelgeuse is a red giant. It is about 20 times as massive as the Sun, but about 14,000 times brighter than the Sun, and about 600 light- ...
The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... I is measured in Watt/m2 . So, a star that is 10 times farther away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less ...
... I is measured in Watt/m2 . So, a star that is 10 times farther away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less ...
Astronomy
... revolution takes about 365 days • The various positions of the Earth in relation to the Sun will cause seasons in some parts of the world • Solstices – Sun is directly on the Tropic of Cancer or Tropic of Capricorn • Equinoxes – Sun is directly on the Equator ...
... revolution takes about 365 days • The various positions of the Earth in relation to the Sun will cause seasons in some parts of the world • Solstices – Sun is directly on the Tropic of Cancer or Tropic of Capricorn • Equinoxes – Sun is directly on the Equator ...
The Milky Way
... nm • T = 3 x 10 6/500 = 6000 K • 10,000 F • Wein’s Law gives the surface temperature ...
... nm • T = 3 x 10 6/500 = 6000 K • 10,000 F • Wein’s Law gives the surface temperature ...
PREVIEW-Reading Quiz 06 - Chapter 12
... What characteristic of a giant or an asymptotic giant branch star lead to their eventual loss of around 50% of their mass? ...
... What characteristic of a giant or an asymptotic giant branch star lead to their eventual loss of around 50% of their mass? ...
Lecture 6
... cut in half, how much brighter would the sun appear in our sky? a. 2x brighter b. 4x brighter c. 8x brighter d. 16x brighter Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
... cut in half, how much brighter would the sun appear in our sky? a. 2x brighter b. 4x brighter c. 8x brighter d. 16x brighter Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
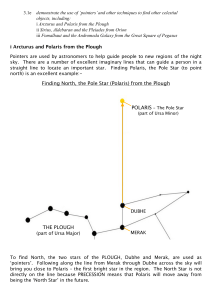
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
Stellar Evolution - Academic Computer Center
... • When a star uses up the Hydrogen in its core it can no longer support itself against gravity. • The core compresses and temperatures begin to rise. • Temperatures may get high enough outside the core to begin The life cycle of a star like the Sun Hydrogen fusion there instead. • The pressure from ...
... • When a star uses up the Hydrogen in its core it can no longer support itself against gravity. • The core compresses and temperatures begin to rise. • Temperatures may get high enough outside the core to begin The life cycle of a star like the Sun Hydrogen fusion there instead. • The pressure from ...
Milky Way
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
Chapter 13: The Death of Stars
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
Brock physics - Brock University
... 22. A star that is cool and very luminous must have (a) a very great distance. (b) a very large radius. (c) a very small mass. (d) a very small radius. 23. Stars with masses in excess of 50 solar masses are very common. (a) True. (b) False. 24. The spectroscopic binaries are detected (a) as separate ...
... 22. A star that is cool and very luminous must have (a) a very great distance. (b) a very large radius. (c) a very small mass. (d) a very small radius. 23. Stars with masses in excess of 50 solar masses are very common. (a) True. (b) False. 24. The spectroscopic binaries are detected (a) as separate ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... mark of Leo the Lion, representing the Lion’s head and mane. Brightest of Leo’s stars is Regulus, the ‘prince’ and one of the four ‘royal stars’, Second-brightest among Leo’s stars is Denebola (‘tail of the lion’), well to the east (right, for an observer facing north) of the ‘question mark’. Accord ...
... mark of Leo the Lion, representing the Lion’s head and mane. Brightest of Leo’s stars is Regulus, the ‘prince’ and one of the four ‘royal stars’, Second-brightest among Leo’s stars is Denebola (‘tail of the lion’), well to the east (right, for an observer facing north) of the ‘question mark’. Accord ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • A shock wave travels through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
... • A shock wave travels through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
Jeopardy 2015
... 100 billion stars The Milky Way Contains which of the following: 100,000 stars 100 million stars 100 Billion stars ...
... 100 billion stars The Milky Way Contains which of the following: 100,000 stars 100 million stars 100 Billion stars ...
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... (b) (i) Spectral class shows the surface temperature of a star. The spectral classes are arranged as O, B, A, F, G, K, M if stars are arranged from the highest surface temperature to the lowest surface temperature (1A). W is of the class B while X and Y are of the same class K. Thus, W has a higher ...
... (b) (i) Spectral class shows the surface temperature of a star. The spectral classes are arranged as O, B, A, F, G, K, M if stars are arranged from the highest surface temperature to the lowest surface temperature (1A). W is of the class B while X and Y are of the same class K. Thus, W has a higher ...
celestial equator
... Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and even Uranus. Occasionally, a bright comet is visible. On certain nights of the year there are many meteors (shooting stars) to be seen. Sometimes man-made debris falls back to Earth and burns up in the atmosphere. Space Shuttle fuel tank reentry, April, 1984. Lava from Kil ...
... Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and even Uranus. Occasionally, a bright comet is visible. On certain nights of the year there are many meteors (shooting stars) to be seen. Sometimes man-made debris falls back to Earth and burns up in the atmosphere. Space Shuttle fuel tank reentry, April, 1984. Lava from Kil ...
space I have Who has
... Who has the level of the universe that contains the sun, eight major planets, and various smaller bodies? ...
... Who has the level of the universe that contains the sun, eight major planets, and various smaller bodies? ...
PHYS 1470 3.0 W16/17 Highlights of Astronomy Assignment #1
... a) If Betelgeuze’s Hour Angle, HA, is +3h 11m 00s what is the Local Sidereal Time, LST? b) If the Local Sidereal Time is 4h 10m 00s what is the Hour Angle of Betelgeuze? c) From which direction did Betelgeuze rise? In which direction will Betelgeuze set? d) Search the web to find Betelgeuze’s declin ...
... a) If Betelgeuze’s Hour Angle, HA, is +3h 11m 00s what is the Local Sidereal Time, LST? b) If the Local Sidereal Time is 4h 10m 00s what is the Hour Angle of Betelgeuze? c) From which direction did Betelgeuze rise? In which direction will Betelgeuze set? d) Search the web to find Betelgeuze’s declin ...
Star Life Cycle – Web Activity
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... small telescopes, the primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow G-class star. The two stars are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. The rear and tail of the lion is formed by a trio of stars consisting of beta (β) (Denebola), delta (δ) (Zosma) and th ...
... small telescopes, the primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow G-class star. The two stars are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. The rear and tail of the lion is formed by a trio of stars consisting of beta (β) (Denebola), delta (δ) (Zosma) and th ...
Lecture 13
... The nearby star 'Sirius A' has a surface temperature T~10,000 K and a flux of arriving radiation at Earth (integrated over all wavelengths) of : ...
... The nearby star 'Sirius A' has a surface temperature T~10,000 K and a flux of arriving radiation at Earth (integrated over all wavelengths) of : ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.