![Global Warming_Notes_for_Test_Review[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009490554_1-1d4a9735243ab8423aa4808909f160ae-300x300.png)
Global Warming_Notes_for_Test_Review[1]
... 9. In most places around the world, there are four high tides and four low tides present each day. False – Two high tides and two low tides each day 10. A shooting star is often a star that passes through our atmosphere. False A shooting star is not a star. It is really a meteor. 11. The space betwe ...
... 9. In most places around the world, there are four high tides and four low tides present each day. False – Two high tides and two low tides each day 10. A shooting star is often a star that passes through our atmosphere. False A shooting star is not a star. It is really a meteor. 11. The space betwe ...
Galaxies - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... Galaxies contain millions or billions of stars held together by gravity Gravity holds galaxies together in clusters Clusters of galaxies can form even larger groups called superclusters How do we see galaxies? We can see our own Milky Way without the use of a telescope Spyglasses let us see further ...
... Galaxies contain millions or billions of stars held together by gravity Gravity holds galaxies together in clusters Clusters of galaxies can form even larger groups called superclusters How do we see galaxies? We can see our own Milky Way without the use of a telescope Spyglasses let us see further ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
The Characteristics of Stars
... more energy each second than the Sun. So why does the Sun appear so much brighter than Sirius in the night sky? The Sun appears brighter because it is much closer to Earth than Sirius. Sirius is approximately 9 ly from Earth, whereas the Sun is only 0.000 016 ly away. You may have noticed that lumin ...
... more energy each second than the Sun. So why does the Sun appear so much brighter than Sirius in the night sky? The Sun appears brighter because it is much closer to Earth than Sirius. Sirius is approximately 9 ly from Earth, whereas the Sun is only 0.000 016 ly away. You may have noticed that lumin ...
Intro Lecture: Stars - University of Redlands
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
ppt - UCL
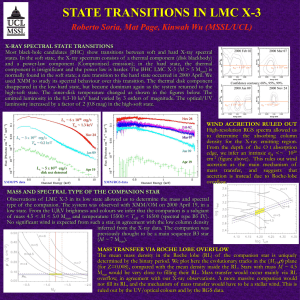
... type of the companion. The system was observed with XMM/OM on 2000 April 19, in a low state. From the U,B,V brightness and colours we infer that the companion is a subgiant of mass 4.5 < M < 5.0 Msun and temperature 15500 < Teff < 16500 (spectral type B5 IV). No significant wind is expected from suc ...
... type of the companion. The system was observed with XMM/OM on 2000 April 19, in a low state. From the U,B,V brightness and colours we infer that the companion is a subgiant of mass 4.5 < M < 5.0 Msun and temperature 15500 < Teff < 16500 (spectral type B5 IV). No significant wind is expected from suc ...
Teacher`s Guide The Solar Empire: A Star is Born
... Activity: Imagine that you are a terra-forming engineer. Which planet in our solar system would you choose to alter to a more Earth-like state? Research the atmosphere of this planet, then develop a plan to make it livable. ...
... Activity: Imagine that you are a terra-forming engineer. Which planet in our solar system would you choose to alter to a more Earth-like state? Research the atmosphere of this planet, then develop a plan to make it livable. ...
February 2008
... bright and it was easy to mark it’s yearly arrival. On January 1st this year, Sirius was right at due South at midnight. Sirius is twice as large as the Sun and has double it’s mass. It produces more than 20 times the light as the Sun. That isn’t really super bright, but since Sirius is only 8.6 lig ...
... bright and it was easy to mark it’s yearly arrival. On January 1st this year, Sirius was right at due South at midnight. Sirius is twice as large as the Sun and has double it’s mass. It produces more than 20 times the light as the Sun. That isn’t really super bright, but since Sirius is only 8.6 lig ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... brighter than star C. If star C were a 9TH magnitude star, then star D would have magnitude -1. 14. The star Deneb has an apparent magnitude of 1.25 and an absolute magnitude of -8.5. What two statements can you make about it, based on this data? Several statements can be made from these data. First ...
... brighter than star C. If star C were a 9TH magnitude star, then star D would have magnitude -1. 14. The star Deneb has an apparent magnitude of 1.25 and an absolute magnitude of -8.5. What two statements can you make about it, based on this data? Several statements can be made from these data. First ...
Stargazing Rules 01162013
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
Small images
... interesting systems can be created in which one star is a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, with another more ordinary star spilling matter onto it. Classical novae Type Ia supernovae X-ray binaries ...
... interesting systems can be created in which one star is a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, with another more ordinary star spilling matter onto it. Classical novae Type Ia supernovae X-ray binaries ...
Word doc - UC
... constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transited ...
... constellation Cygnus, monitoring their brightness photometrically every 30 minutes for four years. It was searching for any minute decreases in brightness that might indicate one or more planets transiting (passing in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transited ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... • Step 3 - Fusion stops, temperature drops • Step 4 - Core contracts (gravity pulling atoms in) • Step 5 - Increased temperature (more atoms, more collisions) and density in the core reinitiates nuclear fusion, equilibrium is achieved, and the cycle begins again ...
... • Step 3 - Fusion stops, temperature drops • Step 4 - Core contracts (gravity pulling atoms in) • Step 5 - Increased temperature (more atoms, more collisions) and density in the core reinitiates nuclear fusion, equilibrium is achieved, and the cycle begins again ...
Chapter 12 Stellar Evolution
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
Some 250 years ago, the philosopher Immanuel Universal
... in this artist’s impression. The Kepler space telescope (left) could yield even more. ...
... in this artist’s impression. The Kepler space telescope (left) could yield even more. ...
Wadhurst Astronomical Society Newsletter May 2017
... We were told about another active galaxy called a Starburst Galaxy where it is thought a nearby interacting galaxy is causing intense star formation far faster than in our galaxy, with many more supernovae being created seen in infra-red and x-ray wavelengths, so that there must be a great deal of a ...
... We were told about another active galaxy called a Starburst Galaxy where it is thought a nearby interacting galaxy is causing intense star formation far faster than in our galaxy, with many more supernovae being created seen in infra-red and x-ray wavelengths, so that there must be a great deal of a ...
Universe Now - Course Pages of Physics Department
... • Cataclysmic or explosive variable stars: – Stars that irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor. – Nova or dwarf nova: occurs in semidetached binaries where a white dwarf star is accreting matter from an ordinary companion star. When the accreted layer is about half a meter thick, the t ...
... • Cataclysmic or explosive variable stars: – Stars that irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor. – Nova or dwarf nova: occurs in semidetached binaries where a white dwarf star is accreting matter from an ordinary companion star. When the accreted layer is about half a meter thick, the t ...
Orion- The Swordsman of the Sky - A Winter Constellation from the
... however does require a telescope to see it. The Orion Nebula also holds fainter objects, which require magnification to see them, such as the Horse Head Nebula. You have to imagine, and possibly take your finger to join the dots, but you can virtually see the shoulders of Orion. The left shoulder s ...
... however does require a telescope to see it. The Orion Nebula also holds fainter objects, which require magnification to see them, such as the Horse Head Nebula. You have to imagine, and possibly take your finger to join the dots, but you can virtually see the shoulders of Orion. The left shoulder s ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
stars
... • Stars change over their lifespan just like animals change throughout their life. • Nebula-a large cloud of gas and dust spread out over a large volume of space. • They can have different appearances bright or dark ...
... • Stars change over their lifespan just like animals change throughout their life. • Nebula-a large cloud of gas and dust spread out over a large volume of space. • They can have different appearances bright or dark ...
TAURUS ZODIAC CONSTELLATION In Greek mythology, Taurus
... modest telescope.[19] The name of the star Aldebaran most likely comes from the fact that it follows the Pleiades during the nightly motion of the celestial sphere across the sky. Astronomers estimate that the cluster has approximately 500-1,000 stars, all of which are around 100 million years old. ...
... modest telescope.[19] The name of the star Aldebaran most likely comes from the fact that it follows the Pleiades during the nightly motion of the celestial sphere across the sky. Astronomers estimate that the cluster has approximately 500-1,000 stars, all of which are around 100 million years old. ...
Earth and Space - Sun, Moon and Stars
... communicate information from careful observations and simple investigation through a variety of methods. ...
... communicate information from careful observations and simple investigation through a variety of methods. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.