Candidate`s registration number: Desk number: ………………….. Date
... a good place to build large telescopes. ...
... a good place to build large telescopes. ...
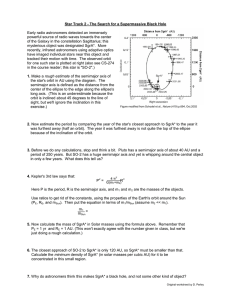
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tracked their motion with time. The observed orbi ...
... powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tracked their motion with time. The observed orbi ...
2nd Semester Exam Study Guide
... - light shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum; shows that the star is moving toward Earth 6. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe is expanding and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. 7. After the Big Bang occurred, many atoms of hydrogen and helium formed when tempera ...
... - light shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum; shows that the star is moving toward Earth 6. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe is expanding and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. 7. After the Big Bang occurred, many atoms of hydrogen and helium formed when tempera ...
Earth-sized planet found just outside solar system
... Alpha Centauri B is very similar to the Sun but slightly smaller and less bright. The newly discovered planet, with a mass of a little more than that of the Earth, is orbiting about six million kilometres away from the star, much closer than Mercury is to the Sun in the Solar System. The orbit of th ...
... Alpha Centauri B is very similar to the Sun but slightly smaller and less bright. The newly discovered planet, with a mass of a little more than that of the Earth, is orbiting about six million kilometres away from the star, much closer than Mercury is to the Sun in the Solar System. The orbit of th ...
Section 7.3 - CPO Science
... travels through space in one year. • A light year is a unit of distance, not time. ...
... travels through space in one year. • A light year is a unit of distance, not time. ...
Quiz # 2
... Bonus. The spectrum of a star shows an equivalent set of dark absorption lines to those of the Sun, but with one exception. Every line appears at a slightly longer wavelength, shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. What conclusion can be drawn from this observation? A) A cloud of cold gas and ...
... Bonus. The spectrum of a star shows an equivalent set of dark absorption lines to those of the Sun, but with one exception. Every line appears at a slightly longer wavelength, shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. What conclusion can be drawn from this observation? A) A cloud of cold gas and ...
Properties of Stars
... All stars are different. Some are small. Some are large. Every star is at a different stage in its life journey. Some have died and gone supernova, others are just dwindling white dwarfs that are cooling. Some stars are just being born in their nebulas. Some have turned into black holes or supergian ...
... All stars are different. Some are small. Some are large. Every star is at a different stage in its life journey. Some have died and gone supernova, others are just dwindling white dwarfs that are cooling. Some stars are just being born in their nebulas. Some have turned into black holes or supergian ...
Neutron Stars
... Upper mass limit of Neutron Stars • In Neutron stars the gravity is balanced by two forces. – Degenerate neutron pressure – Strong nuclear force. ...
... Upper mass limit of Neutron Stars • In Neutron stars the gravity is balanced by two forces. – Degenerate neutron pressure – Strong nuclear force. ...
16. Properties of Stars
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
Document
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... the stars by sketching the position and the shape of the moon and the bright stars in the sky. Document changes as the days go by. • Time: Once you know how to do it, this takes several minutes per observation. • Commitment: Do this over several, not necessarily consecutive days, exact time does not ...
... the stars by sketching the position and the shape of the moon and the bright stars in the sky. Document changes as the days go by. • Time: Once you know how to do it, this takes several minutes per observation. • Commitment: Do this over several, not necessarily consecutive days, exact time does not ...
Our Universe
... • demonstrates that an object is moving away from us and everything else • is evidence of the “push” from the initial Big ...
... • demonstrates that an object is moving away from us and everything else • is evidence of the “push” from the initial Big ...
What stars do Summary: Nuclear burning in stars •
... Pauli exclusion principle cannot have two electrons in same place with exactly same energy. ...
... Pauli exclusion principle cannot have two electrons in same place with exactly same energy. ...
Measuring the distance to Galaxies
... variables can be determined by parallax (a method you will learn in this course) The inverse square law and the periodluminosity relationship of Henrietta Leavitt enables the distance of all observable Cepheid variables to be determined ...
... variables can be determined by parallax (a method you will learn in this course) The inverse square law and the periodluminosity relationship of Henrietta Leavitt enables the distance of all observable Cepheid variables to be determined ...
Evidence of the Big Bang and Structure of the Universe
... Along with the Earth rotating on its axis and revolving around the sun, the Earth is also revolving around the center of the Milky Way galaxy Period of Revolution Around the Milky Way: 220 million years Neighbor: Andromeda Galaxy Takes 2 million years for the light from Andromeda to reach us Androme ...
... Along with the Earth rotating on its axis and revolving around the sun, the Earth is also revolving around the center of the Milky Way galaxy Period of Revolution Around the Milky Way: 220 million years Neighbor: Andromeda Galaxy Takes 2 million years for the light from Andromeda to reach us Androme ...
Basic Properties of the Stars
... absolute magnitudes that correlated with their spectral types. In a plot of MV vs. spectral type most stars traced out a band from the upper left of the diagram to the lower right. Astronomers call this the main sequence. They noted, however, that at a given temperature there were stars on the main ...
... absolute magnitudes that correlated with their spectral types. In a plot of MV vs. spectral type most stars traced out a band from the upper left of the diagram to the lower right. Astronomers call this the main sequence. They noted, however, that at a given temperature there were stars on the main ...
The First Star at Night
... realised that this was indeed the case. The main point, however, as I have mentioned, is that Venus is not a star. So, having digressed somewhat, what is the first star visible in the evenings? Currently, and unsurprisingly, it is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Sirius is also known as ...
... realised that this was indeed the case. The main point, however, as I have mentioned, is that Venus is not a star. So, having digressed somewhat, what is the first star visible in the evenings? Currently, and unsurprisingly, it is Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky. Sirius is also known as ...
Stellar Evolution
... where most stars lie; it has a diagonal pattern from the lower right to the upper left. ...
... where most stars lie; it has a diagonal pattern from the lower right to the upper left. ...
Exam 1 Monday, September 22nd, Chs 1-3
... A) a spherically shaped collection of about 1 million stars that is about 100 light-years in diameter B) a spiral galaxy with a disk about 100,000 light-years in diameter and containing between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars C) a spherically shaped collection of stars including our solar system an ...
... A) a spherically shaped collection of about 1 million stars that is about 100 light-years in diameter B) a spiral galaxy with a disk about 100,000 light-years in diameter and containing between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars C) a spherically shaped collection of stars including our solar system an ...
Deep Space Objects
... that emit a beam of electromagnetic radiation are called pulsars. Astronomers use the beams of pulsars that happen to point toward us as highly precise measuring tools to make new discoveries from Earth. Ridiculously big stars may collapse with so much force that they actually tear a hole in the ‘s ...
... that emit a beam of electromagnetic radiation are called pulsars. Astronomers use the beams of pulsars that happen to point toward us as highly precise measuring tools to make new discoveries from Earth. Ridiculously big stars may collapse with so much force that they actually tear a hole in the ‘s ...
Unit 4 CSI Letter Solar System - Home of the Super Stingrays!!!
... Sun: The star at the center of our solar system Constellation: A pattern of stars that form an imaginary picture or design in the sky Galaxy: A huge system of gases, dust, and many stars Universe: Everything that exists in space ...
... Sun: The star at the center of our solar system Constellation: A pattern of stars that form an imaginary picture or design in the sky Galaxy: A huge system of gases, dust, and many stars Universe: Everything that exists in space ...
UNIT VIII/B: THE EARTH IN SPACE – STARS AND GALAXIES
... a. We have only recently been able to look at the universe over the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Our Universe contains objects that produce a vast range of radiation with wavelengths either too short or too long for our eyes to see. b. Some astronomical objects emit mostly infrared radiation, ot ...
... a. We have only recently been able to look at the universe over the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Our Universe contains objects that produce a vast range of radiation with wavelengths either too short or too long for our eyes to see. b. Some astronomical objects emit mostly infrared radiation, ot ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.