Eksamination in FY2450 Astrophysics Wednesday June 8
... Therefore the lines of neutral helium appear before those of ionized helium. Many students claim that what we see on the surface of the star is directly influenced by fusion processes producing new elements. Such ideas are wrong. Except for white dwarfs and neutron stars, it is only deep inside a st ...
... Therefore the lines of neutral helium appear before those of ionized helium. Many students claim that what we see on the surface of the star is directly influenced by fusion processes producing new elements. Such ideas are wrong. Except for white dwarfs and neutron stars, it is only deep inside a st ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Step 4: Middle-aged star • Red giant- very bright, once an average star, but is now close to end of life - Has expanded to many times its original size (heat causes it to expand) - Hydrogen core has turned to helium and eventually to carbon - Our sun will become a red giant star in about 5 ...
... Step 4: Middle-aged star • Red giant- very bright, once an average star, but is now close to end of life - Has expanded to many times its original size (heat causes it to expand) - Hydrogen core has turned to helium and eventually to carbon - Our sun will become a red giant star in about 5 ...
Electromagnetic Radiation from the Sun
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are ...
... 6. Why is information about many stars contained in absorption rather than emission spectra? If there is a cloud of gas at a cooler temperature directly between a denser source producing a continuous spectrum (i.e. a star) and a telescope, the gas will absorb light at specific wavelengths that are ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
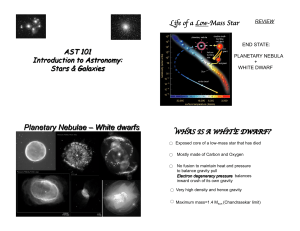
... 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula, and what does it have to do with planets? 4. What is a white dwarf star? 5. Why do high-mass stars go through more evolutionary stages ...
... 1. What kinds of nuclear reactions occur within a star like the Sun as it ages? 2. Where did the carbon atoms in our bodies come from? 3. What is a planetary nebula, and what does it have to do with planets? 4. What is a white dwarf star? 5. Why do high-mass stars go through more evolutionary stages ...
giant molecular clouds
... Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...
... Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...
Star - AUSD Blogs
... watched this happen in AD 1054, not knowing what it was they saw. Five centuries later, in 1572, a supernova blazed in Cassiopeia so brilliantly that it was visible in the daylight sky. There have been three more in the thousand years that passed since. Our mission was to visit the remnants of such ...
... watched this happen in AD 1054, not knowing what it was they saw. Five centuries later, in 1572, a supernova blazed in Cassiopeia so brilliantly that it was visible in the daylight sky. There have been three more in the thousand years that passed since. Our mission was to visit the remnants of such ...
Ch 19 Directed Reading
... 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense that light cannot escape its gravity is called a _____________________________. ...
... 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense that light cannot escape its gravity is called a _____________________________. ...
May 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... brightest star in the sky. In 1933, at the start of the Chicago World’s Fair, it was thought that Arcturus was 40 light years from Earth. (We now know it is closer to 37 light years.) In 1933, it had been 40 years since the last World’s Fair at Chicago (1893), so the promoters of the 1933 fair used ...
... brightest star in the sky. In 1933, at the start of the Chicago World’s Fair, it was thought that Arcturus was 40 light years from Earth. (We now know it is closer to 37 light years.) In 1933, it had been 40 years since the last World’s Fair at Chicago (1893), so the promoters of the 1933 fair used ...
11.3 Measuring Distances in Space
... are the smallest objects at 10-18 m while our universe is estimated to be 1026 m. This is a total difference of 1044 from smallest to largest things in our ...
... are the smallest objects at 10-18 m while our universe is estimated to be 1026 m. This is a total difference of 1044 from smallest to largest things in our ...
StarType
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
Big Bang and Life Cycle of Stars
... Fusion happening at the core of the star is combines Hydrogen to make helium. Define Fusion in your journal ...
... Fusion happening at the core of the star is combines Hydrogen to make helium. Define Fusion in your journal ...
Alien Earths Floorplan (3,000 sq. ft) Major Exhibit Areas
... 1. Something (perhaps a supernova) triggers the gravitational collapse of a nearby interstellar cloud. The cloud naturally heats up and spins faster as it collapses. Collisions between particles flatten the cloud into a disk. 2. The Sun and planets start to form in this spinning, flattened disk (pro ...
... 1. Something (perhaps a supernova) triggers the gravitational collapse of a nearby interstellar cloud. The cloud naturally heats up and spins faster as it collapses. Collisions between particles flatten the cloud into a disk. 2. The Sun and planets start to form in this spinning, flattened disk (pro ...
Night sky
... Precession causes celestial coordinates to change slowly with time. When observing, one must have coordinates for the correct epoch. ...
... Precession causes celestial coordinates to change slowly with time. When observing, one must have coordinates for the correct epoch. ...
Unit I – The Size, Shape and Motion of the Earth
... perspective on Earth, we then expect to see nearby stars shifting back and forth much more dramatically than the more remote stars. Very distant stars will scarcely budge. (In reality, the stars are so remote that the annual shifts are barely detectable, even for the very nearest stars of all.) ...
... perspective on Earth, we then expect to see nearby stars shifting back and forth much more dramatically than the more remote stars. Very distant stars will scarcely budge. (In reality, the stars are so remote that the annual shifts are barely detectable, even for the very nearest stars of all.) ...
constellations are not real!
... 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but less than 100 of them appear on the charts. f. Some 6th magnitude stars can be seen by the “keen of sight” in constellations such as the Dolphin, Cup, and the Fishes. g. For anything fain ...
... 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but less than 100 of them appear on the charts. f. Some 6th magnitude stars can be seen by the “keen of sight” in constellations such as the Dolphin, Cup, and the Fishes. g. For anything fain ...
Oct5
... • Unstable radioactive isotopes of elements, such as Uranium-235, decay at constant, known rates over time (its half-life, which is over 700 million years). • When a molten rock cools, radioactive isotopes and their daughters get frozen in the rock. • For example, when lava cools, it has no lead co ...
... • Unstable radioactive isotopes of elements, such as Uranium-235, decay at constant, known rates over time (its half-life, which is over 700 million years). • When a molten rock cools, radioactive isotopes and their daughters get frozen in the rock. • For example, when lava cools, it has no lead co ...
Skywatch Astro Ed Dec13
... reality the brighter of the two stars. Sirius appears brighter because it is so much closer. Viewed through binoculars in a dark sky, Sirius is a breathtaking sight, sparkling with the fire of a brilliant diamond. Of course, I wouldn’t be forgiven if I didn’t mention brilliant Venus in the western s ...
... reality the brighter of the two stars. Sirius appears brighter because it is so much closer. Viewed through binoculars in a dark sky, Sirius is a breathtaking sight, sparkling with the fire of a brilliant diamond. Of course, I wouldn’t be forgiven if I didn’t mention brilliant Venus in the western s ...
No Slide Title
... The sun is the center of our galaxy. The moon is part of our galaxy. There is one star in each galaxy. Our solar system makes up most of our galaxy. ...
... The sun is the center of our galaxy. The moon is part of our galaxy. There is one star in each galaxy. Our solar system makes up most of our galaxy. ...
How Far is far ?
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
Name: pd: ______ Date: Constellation Scavenger Hunt! Google Sky
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Massive Stars • Mass of massive stars 6x that of sun • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the ...
... Massive Stars • Mass of massive stars 6x that of sun • Take same path as medium-sized stars except for after red giant stage they do not become white dwarfs • Carbon atoms continue to fuse creating heavier elements like oxygen & nitrogen • Core of massive star so hot that fusion continues until the ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.