gravity
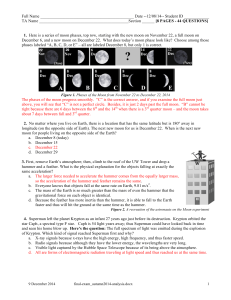
... age of a rock because index fossil species only existed for a relatively short time. What happened to the species that are now used as index fossils? A. They became extinct. B. They changed their diets. C. They hid in marine sediments. D. They migrated to new environments. F1 ...
... age of a rock because index fossil species only existed for a relatively short time. What happened to the species that are now used as index fossils? A. They became extinct. B. They changed their diets. C. They hid in marine sediments. D. They migrated to new environments. F1 ...
Mass
... Because the star is so far away, the scientist could not have the time to receive the radio signals from such a planet. B Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from ...
... Because the star is so far away, the scientist could not have the time to receive the radio signals from such a planet. B Because the star is so close that we should have received radio signals from the planet years ago. C Because the radio signals cannot penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere from ...
Some Facts and Hypotheses regard
... twenty years ago. The credit of the discovery of several hundreds of such stars is due chiefly to t,he labours of quite a few astronomers such as Dr. Chandler, J. E. Gore, and Dr. Roberts of the Cape Observatory. In view of the fact that this sort of work is highly interesting and is well within the ...
... twenty years ago. The credit of the discovery of several hundreds of such stars is due chiefly to t,he labours of quite a few astronomers such as Dr. Chandler, J. E. Gore, and Dr. Roberts of the Cape Observatory. In view of the fact that this sort of work is highly interesting and is well within the ...
Stars
... White Dwarfs When a stars core uses up its fuel it contracts even more and its outer layers ...
... White Dwarfs When a stars core uses up its fuel it contracts even more and its outer layers ...
Week 10
... On Earth, the parallax angle measured for the star Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcsecond ...
... On Earth, the parallax angle measured for the star Procyon is 0.29 arcseconds. If you were to measure Procyon’s parallax angle from Venus, what would the parallax angle be? (Note: Venus’ orbit is smaller than Earth’s orbit.) A. More than 0.29 arcseconds B. 0.29 arcseconds C. Less than 0.29 arcsecond ...
Stars
... Sun 4.5 Byr ago from the gravitational collapse of an interstellar cloud of gas and dust. The planets and Sun formed from the same reservoir of interstellar matter and are therefore composed of primarily the same elements. As the cloud collapsed under the force of gravity it began to spin rapidly an ...
... Sun 4.5 Byr ago from the gravitational collapse of an interstellar cloud of gas and dust. The planets and Sun formed from the same reservoir of interstellar matter and are therefore composed of primarily the same elements. As the cloud collapsed under the force of gravity it began to spin rapidly an ...
The Big Four:
... • Effects on matter/light outside the horizon – gravitational attraction of other bodies – “dark star” with mass 3M Sun • distinguish from normal star, white dwarf, neutron star ...
... • Effects on matter/light outside the horizon – gravitational attraction of other bodies – “dark star” with mass 3M Sun • distinguish from normal star, white dwarf, neutron star ...
The (Stellar) Parallax View
... is 17 light years away. So how do we measure the distances to the stars and galaxies? The most basic technique is called the Stellar Parallax method. Everyone has seen parallax in action, even if they don’t know the word. Parallax is the apparent movement of an object against a background due to a c ...
... is 17 light years away. So how do we measure the distances to the stars and galaxies? The most basic technique is called the Stellar Parallax method. Everyone has seen parallax in action, even if they don’t know the word. Parallax is the apparent movement of an object against a background due to a c ...
Lecture 12, PPT version
... The more massive is a star, the hotter and denser is the star in its core. The hotter and denser it is in a star’s core, the FASTER the conversion of hydrogen to helium happens. High-mass (> 8 Msun) stars are “gas guzzlers” Low-mass (< 2 Msun) are “economy cars” ...
... The more massive is a star, the hotter and denser is the star in its core. The hotter and denser it is in a star’s core, the FASTER the conversion of hydrogen to helium happens. High-mass (> 8 Msun) stars are “gas guzzlers” Low-mass (< 2 Msun) are “economy cars” ...
Exoplanet
... starlight. That's why many of the first planets discovered are Jupiter-class (300 times as massive as Earth), with orbits very close to their parent stars. ...
... starlight. That's why many of the first planets discovered are Jupiter-class (300 times as massive as Earth), with orbits very close to their parent stars. ...
Deducing Temperatures and Luminosities of Stars
... • Hotter Star emits MUCH more light per unit area ⇒ much brighter ...
... • Hotter Star emits MUCH more light per unit area ⇒ much brighter ...
Definitions of Magnitudes and Surface Brightness
... Astronomers are stuck with the antiquated old system of magnitudes and so a clear explanation of what this system is and how it relates to more sensible units is important. The magnitude scale is a logarithmic scale which in the first place related to stars. The larger the magnitude the fainter a st ...
... Astronomers are stuck with the antiquated old system of magnitudes and so a clear explanation of what this system is and how it relates to more sensible units is important. The magnitude scale is a logarithmic scale which in the first place related to stars. The larger the magnitude the fainter a st ...
Document
... in class) and the y axis is flux (don’t worry about those units!). Below each big plot is a zoomed-in view of the area of the spectrum around 6560 Ångstroms (i.e., 656 nm). Question 1 (1 point). Star #1 has a conspicuous Hα transition at 6563 Ångstroms. So, the zoomed-in view shows the Hα line for t ...
... in class) and the y axis is flux (don’t worry about those units!). Below each big plot is a zoomed-in view of the area of the spectrum around 6560 Ångstroms (i.e., 656 nm). Question 1 (1 point). Star #1 has a conspicuous Hα transition at 6563 Ångstroms. So, the zoomed-in view shows the Hα line for t ...
Sample Stellar Evolution TEST QUESTIONS
... 7. Nuclear fusion in stars is controlled by the dependence of density on mass. 8. The Sun has a core in which energy travels outward primarily by radiation. 9. Energy flows by radiation or convection inside stars but almost never by conduction. 10. Hydrostatic equilibrium refers to the balance betwe ...
... 7. Nuclear fusion in stars is controlled by the dependence of density on mass. 8. The Sun has a core in which energy travels outward primarily by radiation. 9. Energy flows by radiation or convection inside stars but almost never by conduction. 10. Hydrostatic equilibrium refers to the balance betwe ...
Basics – II. Time, Magnitudes and Spectral types
... or month, nor months in a year. This means that they all tend to either slowly get out of phase with the year or need some jiggling to stay in phase. ...
... or month, nor months in a year. This means that they all tend to either slowly get out of phase with the year or need some jiggling to stay in phase. ...
Review of the Principles of Stellar Parallax and Practice Problems
... Practice Problem 3: Star 1 has an absolute magnitude of 0. How many times more luminous is star 1 compared to the Sun? Note: the absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.8. ...
... Practice Problem 3: Star 1 has an absolute magnitude of 0. How many times more luminous is star 1 compared to the Sun? Note: the absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.8. ...
Star Formation: Interstellar Gas and Dust
... • What sets lower limit? • Collapsing gas cloud does not get hot enough in center to start p-p reaction. ...
... • What sets lower limit? • Collapsing gas cloud does not get hot enough in center to start p-p reaction. ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... smallest of these fragments contract further to form these pre-stars This catastrophic event is thought to be main source of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium A mass similar to that of the Sun, but only 1% of the Sun's diameter (approximately the diameter of the Earth). These form from massi ...
... smallest of these fragments contract further to form these pre-stars This catastrophic event is thought to be main source of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium A mass similar to that of the Sun, but only 1% of the Sun's diameter (approximately the diameter of the Earth). These form from massi ...
New Stars, New Planets?
... variations in the Doppler shifts of light emitted by stars. Such changes indicate a back and forth "wobbling" of the star's motion, perhaps due to gravity effects from an unseen, orbiting planet. Analysis of the light signal also permits estimates of the planet's mass and orbital characteristics to ...
... variations in the Doppler shifts of light emitted by stars. Such changes indicate a back and forth "wobbling" of the star's motion, perhaps due to gravity effects from an unseen, orbiting planet. Analysis of the light signal also permits estimates of the planet's mass and orbital characteristics to ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... attempt at stardom As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence t ...
... attempt at stardom As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence t ...
Stellar Evolution of Single Stars
... The HB is like a He main sequence, but its not exactly that due to the extra luminosity from the H burning shell. How much mass is lost up to this point??? From now on the calculations get more uncertain due to this and other factors. The position of a star on the HB depends on the composition (“bra ...
... The HB is like a He main sequence, but its not exactly that due to the extra luminosity from the H burning shell. How much mass is lost up to this point??? From now on the calculations get more uncertain due to this and other factors. The position of a star on the HB depends on the composition (“bra ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.