What is a Star - Optics Institute of Southern California
... The properties of a main sequence star can be understood by considering the various physical processes acting in the interior. First is the hydrostatic balance, also called hydrostatic equilibrium. This determines the density structure of the star as the internal pressure gradient balances against t ...
... The properties of a main sequence star can be understood by considering the various physical processes acting in the interior. First is the hydrostatic balance, also called hydrostatic equilibrium. This determines the density structure of the star as the internal pressure gradient balances against t ...
Discussion Activity #11a
... helium, carbon, and so on) in a high-mass star is NOT true? A. As each stage ends, the reactions that occurred in previous stages continue in shells around the core. B. Each successive stage creates an element with a higher atomic number and atomic mass number. C. As each stage ends, the core shrink ...
... helium, carbon, and so on) in a high-mass star is NOT true? A. As each stage ends, the reactions that occurred in previous stages continue in shells around the core. B. Each successive stage creates an element with a higher atomic number and atomic mass number. C. As each stage ends, the core shrink ...
Geography
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
Revision on Universe 1-The nearest planet to the sun is
... 10-The day is shorter than night in …… ………………season Put ( T ) or ( F ) 1-In winter and summer seasons, the day hours are equal to the night hours ...
... 10-The day is shorter than night in …… ………………season Put ( T ) or ( F ) 1-In winter and summer seasons, the day hours are equal to the night hours ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
... recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has been made, you find that the maximum occurred a few minutes l ...
Some Basic Principles from Astronomy
... ladder, a concept we will return to when we talk about Cosmology • The first step to understanding how to measure the Cosmos is to ask “What can I easily measure?” The answer to this question is: time, and angles (though the former was not possible until the invention of timekeeping devices, like wa ...
... ladder, a concept we will return to when we talk about Cosmology • The first step to understanding how to measure the Cosmos is to ask “What can I easily measure?” The answer to this question is: time, and angles (though the former was not possible until the invention of timekeeping devices, like wa ...
RR animation
... and consequently, they were once stars with similar or slightly less mass than the Sun, around 0.8 solar masses. RR Lyrae stars pulse in a manner similar to Cepheid variables, so the mechanism for the pulsation is thought to be similar, but the nature and histories of these stars is thought to be ra ...
... and consequently, they were once stars with similar or slightly less mass than the Sun, around 0.8 solar masses. RR Lyrae stars pulse in a manner similar to Cepheid variables, so the mechanism for the pulsation is thought to be similar, but the nature and histories of these stars is thought to be ra ...
Lecture 1
... star (Star A), out to the Distant Stars. Which of the distant stars would appear closest to Star A in your night sky in January. Circle this distant star and label it Jan. Repeat Question 1 for July and label the distant star “July”. In the box below, the same distant stars are shown as you would se ...
... star (Star A), out to the Distant Stars. Which of the distant stars would appear closest to Star A in your night sky in January. Circle this distant star and label it Jan. Repeat Question 1 for July and label the distant star “July”. In the box below, the same distant stars are shown as you would se ...
Space Interactive Internet Scavenger Hunt
... discovered, making it only a hypothetical possibility. Scientists believe it would take a star such as the sun over 14 billion years to reach the black dwarf stage, a period of time greater than the estimated age of the universe. If black dwarfs were to exist they would be invisible and scientists c ...
... discovered, making it only a hypothetical possibility. Scientists believe it would take a star such as the sun over 14 billion years to reach the black dwarf stage, a period of time greater than the estimated age of the universe. If black dwarfs were to exist they would be invisible and scientists c ...
neutron star - Adams State University
... elements back out into space: Material for the next generation of stars! The Crab Nebula Remains of a supernova explosion observed by Chinese, Japanese, and Arabic astronomers in 1054. (Why not Europeans?) ...
... elements back out into space: Material for the next generation of stars! The Crab Nebula Remains of a supernova explosion observed by Chinese, Japanese, and Arabic astronomers in 1054. (Why not Europeans?) ...
Lesson 4d Models of the Solar System
... Venus has phases (like the moon) and appears to change size Jupiter has objects orbiting it (moons) There are dark spots on the sun The sun rotates and the spots on the ...
... Venus has phases (like the moon) and appears to change size Jupiter has objects orbiting it (moons) There are dark spots on the sun The sun rotates and the spots on the ...
STUDY GUIDE:
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
Quiz 2 review sheet - Rice Space Institute
... up, the core collapses again and starts burning Carbon into iron. The fusion in the core even goes deeper, changing Fe into heavier elements. But since iron is the most stable element, additional fusion takes energy not releases it, so the core collapses faster and the explosion even more incredible ...
... up, the core collapses again and starts burning Carbon into iron. The fusion in the core even goes deeper, changing Fe into heavier elements. But since iron is the most stable element, additional fusion takes energy not releases it, so the core collapses faster and the explosion even more incredible ...
Astronomy 200 Problem Set No
... Plot apparent magnitudes on the vertical axis with dim at the bottom and bright at the top. Plot temperature along the horizontal axis with hot to the left and cool to the right. Note that this is similar to the form of an HR diagram but until we know the distance to the Pleiades, we cannot convert ...
... Plot apparent magnitudes on the vertical axis with dim at the bottom and bright at the top. Plot temperature along the horizontal axis with hot to the left and cool to the right. Note that this is similar to the form of an HR diagram but until we know the distance to the Pleiades, we cannot convert ...
Parallels: Proto-Planetary Disks and rings
... Jupiters’. These planets, although similar in radius to Jupiter, orbit their stars so close that they are tidally locked in place with one side in permanent daylight and the other in perpetual darkness. The close proximity to their star means it can get incredibly hot. The hottest thus far is WASP-1 ...
... Jupiters’. These planets, although similar in radius to Jupiter, orbit their stars so close that they are tidally locked in place with one side in permanent daylight and the other in perpetual darkness. The close proximity to their star means it can get incredibly hot. The hottest thus far is WASP-1 ...
Events: - Temecula Valley Astronomers
... Now, look back at Jupiter again. To the left or east of Jupiter is the constellation Leo. Leo (The Lion) is our spring constellation that enters the beginning of the ‘Galaxy Constellations’ well into the summer months. The “head”, “shoulders” and “Chest” of Leo forms what looks like a “sickle” or re ...
... Now, look back at Jupiter again. To the left or east of Jupiter is the constellation Leo. Leo (The Lion) is our spring constellation that enters the beginning of the ‘Galaxy Constellations’ well into the summer months. The “head”, “shoulders” and “Chest” of Leo forms what looks like a “sickle” or re ...
sa`d al-malik - WordPress.com
... he pleaded with Zeus to be allowed to help them and was given permission to send down rain. Eventually he was glorified as Aquarius, god of rain, and placed amongst the stars. http://www.heavens-above.com/myth.aspx?con=aqr ...
... he pleaded with Zeus to be allowed to help them and was given permission to send down rain. Eventually he was glorified as Aquarius, god of rain, and placed amongst the stars. http://www.heavens-above.com/myth.aspx?con=aqr ...
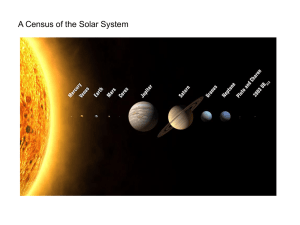
5-SolarSystem
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E di ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the excliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E di ...
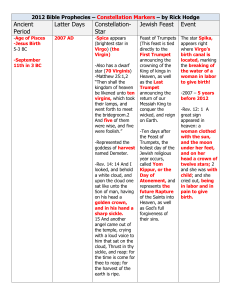
Constellation Markers - The Roger Sherman Society
... in the night sky and second brightest star in the constellation of Orion; diameter is 8oo times larger than our Sun, and its mass is 20 times greater. Betelgeuse is shrinking—in a big way. In the last 15 years it has lost 15% of its diameter! If Betelgeuse turns into a supernova, it would be visible ...
... in the night sky and second brightest star in the constellation of Orion; diameter is 8oo times larger than our Sun, and its mass is 20 times greater. Betelgeuse is shrinking—in a big way. In the last 15 years it has lost 15% of its diameter! If Betelgeuse turns into a supernova, it would be visible ...
Solar System Astrometry
... suggest the existence of a region of comet-like objects beyond the outer planets. The first observational support for it came in 1992 when David Jewitt of the University of Hawaii and Jane Luu of the University of California, Berkeley discovered a 200-kilometer-wide object circling the Sun beyond th ...
... suggest the existence of a region of comet-like objects beyond the outer planets. The first observational support for it came in 1992 when David Jewitt of the University of Hawaii and Jane Luu of the University of California, Berkeley discovered a 200-kilometer-wide object circling the Sun beyond th ...
Lecture02-ASTA01 - University of Toronto
... Asterisms • In addition to the 88 official constellations, the sky contains a number of less formally defined groupings known as asterisms. • For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism you probably recognize that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear) ...
... Asterisms • In addition to the 88 official constellations, the sky contains a number of less formally defined groupings known as asterisms. • For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism you probably recognize that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear) ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.