The Stellar Cycle
... • To make elements heavier than iron extra energy must be provided. • Supernova temperatures drive nuclei into each other at such high speeds that heavy elements can be made. • Gold, Silver, etc., -- any element heavier than iron, were all made during a supernova. We were all once fuel for a stellar ...
... • To make elements heavier than iron extra energy must be provided. • Supernova temperatures drive nuclei into each other at such high speeds that heavy elements can be made. • Gold, Silver, etc., -- any element heavier than iron, were all made during a supernova. We were all once fuel for a stellar ...
LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
... pressure and gravity, it becomes a star (its next stage of life). Vocabulary: Nebula-A diffuse mass of interstellar dust and gas. Protostar-Very dense regions (or cores) of molecular clouds where stars are in the process of forming. ...
... pressure and gravity, it becomes a star (its next stage of life). Vocabulary: Nebula-A diffuse mass of interstellar dust and gas. Protostar-Very dense regions (or cores) of molecular clouds where stars are in the process of forming. ...
Part A
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19)
... Brown dwarfs: Stars with M < 0.1M0 never get hot enough to ignite H. They just cool off and fade forever. Hard to detect because so faint, but by now 100s have been discovered. (Read Discovery 19-1, p. 511). It is still unknown whether brown dwarfs, which can be as low-mass as 0.01 Msun or even less ...
... Brown dwarfs: Stars with M < 0.1M0 never get hot enough to ignite H. They just cool off and fade forever. Hard to detect because so faint, but by now 100s have been discovered. (Read Discovery 19-1, p. 511). It is still unknown whether brown dwarfs, which can be as low-mass as 0.01 Msun or even less ...
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Astronomy 1
... nearly 7,000 light years across. The stars are very hot and show up in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum. The image was made with a telescope carried aboard a space shuttle. ...
... nearly 7,000 light years across. The stars are very hot and show up in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum. The image was made with a telescope carried aboard a space shuttle. ...
Stellar Structure - McMurry University
... sequence” because of similarities to the hydrogen burning phase: – Energy is again produced in the core (but using a different fuel). – Pressure-Temperature thermostat is very effective again: star’s size/temperature stays very stable. ...
... sequence” because of similarities to the hydrogen burning phase: – Energy is again produced in the core (but using a different fuel). – Pressure-Temperature thermostat is very effective again: star’s size/temperature stays very stable. ...
Document
... nearly 7,000 light years across. The stars are very hot and show up in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum. The image was made with a telescope carried aboard a space shuttle. ...
... nearly 7,000 light years across. The stars are very hot and show up in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum. The image was made with a telescope carried aboard a space shuttle. ...
Glossary Annual Motion – the Earth`s orbital motion around the sun
... Binary Stars – when two relatively close stars revolve around each other, often appearing as single stars because they are so far away from Earth Black Hole – an intense gravitational field created when a star runs out of fuel and collapses. Nothing, not even light can escape its pull Blue Moon – th ...
... Binary Stars – when two relatively close stars revolve around each other, often appearing as single stars because they are so far away from Earth Black Hole – an intense gravitational field created when a star runs out of fuel and collapses. Nothing, not even light can escape its pull Blue Moon – th ...
Stellar Evolution
... Star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core Leads to a very different fate Path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line Stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova ...
... Star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core Leads to a very different fate Path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line Stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova ...
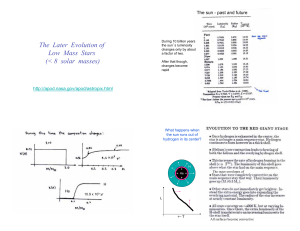
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin helium shell. These pulses grow more violent with time. Also, and probably more importantly, the outer layers of the star get so large and cool owing to the high luminosity, that they form ...
... persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin helium shell. These pulses grow more violent with time. Also, and probably more importantly, the outer layers of the star get so large and cool owing to the high luminosity, that they form ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... e) Population I star Cepheids (called Type I or classical Cepheids) have a slightly different period-luminosity relationship than the Population II star cepheids (called Type II Cepheids or W Virginis stars). 3. Lower mass versions of Cepheids exist called RR Lyrae type variables, which change in br ...
... e) Population I star Cepheids (called Type I or classical Cepheids) have a slightly different period-luminosity relationship than the Population II star cepheids (called Type II Cepheids or W Virginis stars). 3. Lower mass versions of Cepheids exist called RR Lyrae type variables, which change in br ...
Document
... AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin helium shell. These pulses grow more viole ...
... AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin helium shell. These pulses grow more viole ...
ph507lecnote06
... Most stars have properties within the shaded region known as the main sequence. The points plotted here are for stars lying within about 5 pc of the Sun. The diagonal lines correspond to constant stellar radius, so that stellar size can be represented on the same diagram as luminosity and temperatur ...
... Most stars have properties within the shaded region known as the main sequence. The points plotted here are for stars lying within about 5 pc of the Sun. The diagonal lines correspond to constant stellar radius, so that stellar size can be represented on the same diagram as luminosity and temperatur ...
HOU Supernova Light Curves
... In the spring of 1994 several HOU students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various HOU images had been requested throughout February and March, and in early April, two girls at Oil City High School in Pennsylvania received an important phone call. They had se ...
... In the spring of 1994 several HOU students were studying M51, the spiral galaxy also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy. Various HOU images had been requested throughout February and March, and in early April, two girls at Oil City High School in Pennsylvania received an important phone call. They had se ...
Stellar Evolution
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant Hydrogen in the core completely converted into He: → “Hydrogen burning” (i.e. fusion of H into He) ceases in the core. ...
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant Hydrogen in the core completely converted into He: → “Hydrogen burning” (i.e. fusion of H into He) ceases in the core. ...
Classification and structure of galaxies
... Globular Clusters • millions to hundreds of millions of stars • old! 6 to 13 billion years • mostly red giants and dwarfs • stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely); stars don’t drift apart • surround our disk as a halo Image at http://hubblesite.org/n ...
... Globular Clusters • millions to hundreds of millions of stars • old! 6 to 13 billion years • mostly red giants and dwarfs • stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely); stars don’t drift apart • surround our disk as a halo Image at http://hubblesite.org/n ...
Star Life Cycle Web Activity
... From this point on you may click on the Yellow Right Arrow at the bottom of each page. Or Click on Equilibrium of a Star. Read the web page and the summary of a typical cycle of stars given here. Stars repeat a cycle of reaching equilibrium and then losing it after burning out one fuel source…then ...
... From this point on you may click on the Yellow Right Arrow at the bottom of each page. Or Click on Equilibrium of a Star. Read the web page and the summary of a typical cycle of stars given here. Stars repeat a cycle of reaching equilibrium and then losing it after burning out one fuel source…then ...
1. a) Astronomers use the parallax method to measure
... use almost the same method anytime we measure the masses of astronomical objects. What quantities would an astronomer have to measure to determine the mass of a cluster of galaxies? (Your method should include all of the mass, not just the mass of the luminous matter.) We measure masses by seeing ho ...
... use almost the same method anytime we measure the masses of astronomical objects. What quantities would an astronomer have to measure to determine the mass of a cluster of galaxies? (Your method should include all of the mass, not just the mass of the luminous matter.) We measure masses by seeing ho ...
Unit8TheUniverse
... B. Large mass stars: shorter lives, may become neutron stars (pulsars) or blackholes C. Stars come in a variety of sizes and colors. D. The Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram (H-R) is a graph plotting a star’s luminosity (brightness) vs. its temperature, showing the stages of a star’s evolution. ...
... B. Large mass stars: shorter lives, may become neutron stars (pulsars) or blackholes C. Stars come in a variety of sizes and colors. D. The Hertzsprung- Russell Diagram (H-R) is a graph plotting a star’s luminosity (brightness) vs. its temperature, showing the stages of a star’s evolution. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.