Colour-magnitude diagram of an open cluster
... lifetimes than low-mass stars. The Sun will run out of fuel after about 1010 years; a star that is 10× more massive than the Sun will only live for about 10 million years! The point where the main sequence ends (the main sequence turn-off ) is thus a good indicator of the age of a star cluster. In ...
... lifetimes than low-mass stars. The Sun will run out of fuel after about 1010 years; a star that is 10× more massive than the Sun will only live for about 10 million years! The point where the main sequence ends (the main sequence turn-off ) is thus a good indicator of the age of a star cluster. In ...
MS Word version
... The following sequence of directions are steps an instructor might choose to follow in demonstrating the Eclipsing Binary Simulator in a classroom situation. We provide these suggestions with appropriate questions (shown in bold italics) to pose to the class as an aid in promoting interactivity. We ...
... The following sequence of directions are steps an instructor might choose to follow in demonstrating the Eclipsing Binary Simulator in a classroom situation. We provide these suggestions with appropriate questions (shown in bold italics) to pose to the class as an aid in promoting interactivity. We ...
Scientists discover surprising importance of `I Love Q` for
... The Love number relates to the deformability of a star when squished. The larger the number, the more deformed the star is. The third quantity, "Q," refers to the changing shape of a star. ...
... The Love number relates to the deformability of a star when squished. The larger the number, the more deformed the star is. The third quantity, "Q," refers to the changing shape of a star. ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... your journey of a few weeks, you spend some time observing the stars. Which of the statements below would represent one of your observations? A) The northern stars were above the horizon less time each succeeding night. B) The region of the sky that was circumpolar increased each night. C) Polaris w ...
... your journey of a few weeks, you spend some time observing the stars. Which of the statements below would represent one of your observations? A) The northern stars were above the horizon less time each succeeding night. B) The region of the sky that was circumpolar increased each night. C) Polaris w ...
STAR FORMATION
... • The core of the contracting cloudlet heats up -- but still not hot enough to begin nuclear fusion. • This protostellar period lasts for < 1 percent of the star's total life on the Main Sequence (i.e. ~3x107 yr for the Sun, whose total lifespan is ~ 10 billion yr.) • Much luminosity is generated in ...
... • The core of the contracting cloudlet heats up -- but still not hot enough to begin nuclear fusion. • This protostellar period lasts for < 1 percent of the star's total life on the Main Sequence (i.e. ~3x107 yr for the Sun, whose total lifespan is ~ 10 billion yr.) • Much luminosity is generated in ...
V = 3 d3 = 4188.8 pc N = ρV = 0.1 pc χ 4188.8 pc = 419
... Since more massive stars have shorter lifetimes, we conclude that stars more massive than about 1.9 times the mass of the Sun will have lifetimes that are too short to allow intelligent life to evolve. Answer c) Stars with mass greater than about 1.9 times the mass of the Sun. For the following thre ...
... Since more massive stars have shorter lifetimes, we conclude that stars more massive than about 1.9 times the mass of the Sun will have lifetimes that are too short to allow intelligent life to evolve. Answer c) Stars with mass greater than about 1.9 times the mass of the Sun. For the following thre ...
SAP_Paper1_FutureOfUniverse
... We don’t often think about how imperfect and fallible our timekeeping systems are, but in the next 50 thousand years the length of the day used for astronomical timekeeping will reaches about 86,401 SI seconds, due to lunar tides decelerating the Earth's rotation. Under the present-day timekeeping s ...
... We don’t often think about how imperfect and fallible our timekeeping systems are, but in the next 50 thousand years the length of the day used for astronomical timekeeping will reaches about 86,401 SI seconds, due to lunar tides decelerating the Earth's rotation. Under the present-day timekeeping s ...
11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... carbon and oxygen with a thin surface layer of hydrogen and helium. There is far too little gas to ever combust, however. White dwarfs simply continue to cool and reach a core temperature of around 20,000 K. ...
... carbon and oxygen with a thin surface layer of hydrogen and helium. There is far too little gas to ever combust, however. White dwarfs simply continue to cool and reach a core temperature of around 20,000 K. ...
Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... – When we say the Sun is 8 light-minutes away, we are expressing not only its distance from Earth, but also that we see the Sun as it was 8 minutes ago – We never see in the present • When we see objects, we see them as they were when they were younger ...
... – When we say the Sun is 8 light-minutes away, we are expressing not only its distance from Earth, but also that we see the Sun as it was 8 minutes ago – We never see in the present • When we see objects, we see them as they were when they were younger ...
The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
... that wheel about the sun, had become very erratic. Ogilvy had already called attention to a suspected retardation in its velocity in December. Such a piece of news was scarcely calculated to interest a world the greater portion of whose inhabitants were unaware of the existence of the planet Neptun ...
... that wheel about the sun, had become very erratic. Ogilvy had already called attention to a suspected retardation in its velocity in December. Such a piece of news was scarcely calculated to interest a world the greater portion of whose inhabitants were unaware of the existence of the planet Neptun ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
Lecture11
... the cloud is still in free-fall. Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, until it becomes ~30% larger tha ...
... the cloud is still in free-fall. Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, until it becomes ~30% larger tha ...
370KB - NZQA
... Rigel is a blue-white supergiant star, approximately 75 times the size of the Sun. Explain in detail the three life stages of Rigel in terms of gravity, mass, fuel source and use, and ...
... Rigel is a blue-white supergiant star, approximately 75 times the size of the Sun. Explain in detail the three life stages of Rigel in terms of gravity, mass, fuel source and use, and ...
1. - TeacherWeb
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
Planets Beyond the Solar System
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to ...
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to ...
Planets Beyond the Solar System
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to ...
... ice (water). There are approximately 2 x 1021 kg of water on Earth. Assuming this water came from asteroid impacts with the Earth, how many comets would have to hit the Earth in a time of 500 million years in order to ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
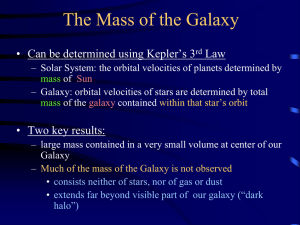
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Astronomical Knowledge Questionnaire (Student
... The Earth’s tilted axis means that one hemisphere has more direct sunlight and longer days making it summer while the other hemisphere experiences winter. The Sun moves to make one side of the Earth hot for six months making summer while the other side of the Earth is cool and experiences winter ...
... The Earth’s tilted axis means that one hemisphere has more direct sunlight and longer days making it summer while the other hemisphere experiences winter. The Sun moves to make one side of the Earth hot for six months making summer while the other side of the Earth is cool and experiences winter ...
Class 1: From Astrology to Astronomy
... What the Ancients Saw • All noticed that the stars seemed to be fixed on a giant sphere that turned about the earth (The “Starry Vault”) • The sun and moon moved across the sphere on similar path. ...
... What the Ancients Saw • All noticed that the stars seemed to be fixed on a giant sphere that turned about the earth (The “Starry Vault”) • The sun and moon moved across the sphere on similar path. ...
The Sun and the Origin of the Solar System
... – Contraction of core, raises the temperature – Ignites He shell around the core – Eventually the core stabilizes – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
... – Contraction of core, raises the temperature – Ignites He shell around the core – Eventually the core stabilizes – Envelope is ejected as a "planetary nebula" – The core remains as a "white dwarf" ...
Chapter 7
... As a result, the theories we developed to explain the formation of a solar system fit our system. Since the 1990’s we have discovered hundreds of extrasolar planets. How does our theory match these newly discovered worlds? ...
... As a result, the theories we developed to explain the formation of a solar system fit our system. Since the 1990’s we have discovered hundreds of extrasolar planets. How does our theory match these newly discovered worlds? ...
Shining Light on the Stars: The Hertzsprung-Russell
... Our Sun is located here on the diagram, and as before, the 122 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are too faint to be seen without a telescope? We immediately see that these two groups of ...
... Our Sun is located here on the diagram, and as before, the 122 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are too faint to be seen without a telescope? We immediately see that these two groups of ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.