Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year… • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million km. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris). • and rotates in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year… • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million km. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris). • and rotates in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
Cosmo: Student`s Workbook
... She was able to use parallax and Intensity vs distance graphs to measure the distance of these ...
... She was able to use parallax and Intensity vs distance graphs to measure the distance of these ...
S1-4-03 - Celestial Navigation
... Show students the northern circumpolar constellations. Note that depending on where you live, some constellations are visible all year round and some constellations are seasonal. If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, the constellations that circle around the North Star are visible all year. These ...
... Show students the northern circumpolar constellations. Note that depending on where you live, some constellations are visible all year round and some constellations are seasonal. If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, the constellations that circle around the North Star are visible all year. These ...
Formation of the Solar System
... Our solar system and the stars visible in our sky comprise an extremely small portion of our galaxy. Our galactic centre cannot be seen in optical light due to heavy obscuration from foreground stars and interstellar matter; we can only see about a tenth of the way toward the centre. In a dark rural ...
... Our solar system and the stars visible in our sky comprise an extremely small portion of our galaxy. Our galactic centre cannot be seen in optical light due to heavy obscuration from foreground stars and interstellar matter; we can only see about a tenth of the way toward the centre. In a dark rural ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... Accretion in binary systems can also take the form of a wind from the surface of one star, as opposed to a thin accretion stream flowing through the inner Lagrange point. Then the second star accumulates matter from the first star as ...
... Accretion in binary systems can also take the form of a wind from the surface of one star, as opposed to a thin accretion stream flowing through the inner Lagrange point. Then the second star accumulates matter from the first star as ...
White Dwarfs - University of Maryland Astronomy
... Surface rotation speed ~ 60,000 km/s. ~ 20% speed of light. ~ escape speed from NS. Anything else would be torn to pieces! ...
... Surface rotation speed ~ 60,000 km/s. ~ 20% speed of light. ~ escape speed from NS. Anything else would be torn to pieces! ...
Tips on taking Astro sights
... obtained from astronomical observations is not so reliable as one obtained from terrestrial bearings. The transferred position line If two position lines are obtained at approximately the same moment, the ship's position is decided by their point of intersection. If there is an appreciable interval ...
... obtained from astronomical observations is not so reliable as one obtained from terrestrial bearings. The transferred position line If two position lines are obtained at approximately the same moment, the ship's position is decided by their point of intersection. If there is an appreciable interval ...
doppler effect
... If a star is moving at 558,000 miles per second, where is its spectral line located now if it was originally at 4861 Å and the object is moving away? SHOW YOUR WORK ...
... If a star is moving at 558,000 miles per second, where is its spectral line located now if it was originally at 4861 Å and the object is moving away? SHOW YOUR WORK ...
302 Final Review
... 51. After a super giant star goes supernova it can turn into one of two things, a neutron star or a black hole. Matching Match each item with the correct definition below. a. black hole e. b. Reflecting f. c. fusion g. d. Refracting h. ...
... 51. After a super giant star goes supernova it can turn into one of two things, a neutron star or a black hole. Matching Match each item with the correct definition below. a. black hole e. b. Reflecting f. c. fusion g. d. Refracting h. ...
Planets and Stars Differences and Similarities
... Planets the Solar System’s Best Friend In our Solar System there are 8 planets Mercury. Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune. Theses planets in some ways are very similar to the stars but in other way they might be more different then you might think. In our solar system we have planets ...
... Planets the Solar System’s Best Friend In our Solar System there are 8 planets Mercury. Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune. Theses planets in some ways are very similar to the stars but in other way they might be more different then you might think. In our solar system we have planets ...
Document
... We also see gas and dust absorbing light in other galaxies… …as dark dust lanes when we see a galaxy edge-on Sombrero Galaxy ...
... We also see gas and dust absorbing light in other galaxies… …as dark dust lanes when we see a galaxy edge-on Sombrero Galaxy ...
Astronomy_Main_Lesson_Book_Contents
... iv. Moons of Jupiter v. Negative consequences for the Aristotelian/Ptolemaic model and its support for the Copernican Explanation of Retrograde Motion with drawing Kepler’s Three Laws a. 1 - Orbits of planets are ellipses with the Sun at one foci b. 2 – Line between planet and Sun sweeps out equal a ...
... iv. Moons of Jupiter v. Negative consequences for the Aristotelian/Ptolemaic model and its support for the Copernican Explanation of Retrograde Motion with drawing Kepler’s Three Laws a. 1 - Orbits of planets are ellipses with the Sun at one foci b. 2 – Line between planet and Sun sweeps out equal a ...
Lesson 3: Calculating distances to stars
... The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will appear bright, and if the star is far away i ...
... The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will appear bright, and if the star is far away i ...
Earth in Space - Learning Outcomes
... 10. (a) Explain what is meant by the term „escape velocity‟. (b) Derive an expression for the escape velocity in terms of the mass and radius of a planet. (c) (i) Calculate the escape velocity from both the Earth and from the Moon. (ii) Using your answers to (i) comment on the atmosphere of the Eart ...
... 10. (a) Explain what is meant by the term „escape velocity‟. (b) Derive an expression for the escape velocity in terms of the mass and radius of a planet. (c) (i) Calculate the escape velocity from both the Earth and from the Moon. (ii) Using your answers to (i) comment on the atmosphere of the Eart ...
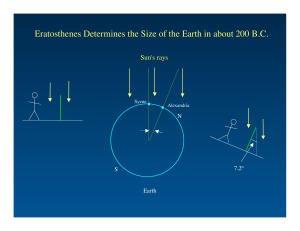
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
Lifetime of Stars/ Fusion powers the stars—11 Oct
... life or does it last forever? – What powers the sun? – Where does carbon come from? – How long does the sun live? – What happens to the sun when it dies? ...
... life or does it last forever? – What powers the sun? – Where does carbon come from? – How long does the sun live? – What happens to the sun when it dies? ...
Document
... If on the equator, we see the whole sky once per day In between, we see part of the sky all day long and part only some of the day ...
... If on the equator, we see the whole sky once per day In between, we see part of the sky all day long and part only some of the day ...
Chapter 34: Cosmology FYI 1. Radar Ranging 2. Triangulation idea
... by atoms moving with stars or galaxies. Which statements are true? a. You can actually see little red atoms that have been shifted to the left. They have small beady red eyes and cannot be trusted. b. The spectral colors emitted by the atoms moving with most of those objects are shifted toward highe ...
... by atoms moving with stars or galaxies. Which statements are true? a. You can actually see little red atoms that have been shifted to the left. They have small beady red eyes and cannot be trusted. b. The spectral colors emitted by the atoms moving with most of those objects are shifted toward highe ...
Lecture 4, PPT version
... system. The ancient Greeks (for the most part) were completely convinced that we lived in a geocentric system. The ancient Greeks weren’t stupid people! They had reasons for their beliefs. They also didn’t have telescopes. ...
... system. The ancient Greeks (for the most part) were completely convinced that we lived in a geocentric system. The ancient Greeks weren’t stupid people! They had reasons for their beliefs. They also didn’t have telescopes. ...
005 Astrophysics problems
... 10. (a) Explain what is meant by the term ‘escape velocity’. (b) Derive an expression for the escape velocity in terms of the mass and radius of a planet. (c) (i) Calculate the escape velocity from both the Earth and from the Moon. (ii) Using your answers to (i) comment on the atmosphere of the Eart ...
... 10. (a) Explain what is meant by the term ‘escape velocity’. (b) Derive an expression for the escape velocity in terms of the mass and radius of a planet. (c) (i) Calculate the escape velocity from both the Earth and from the Moon. (ii) Using your answers to (i) comment on the atmosphere of the Eart ...
AST 111 – Introduction to Astronomy
... d. originated just after the telescope was invented. e. was devised by Galileo. 4. If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it a. as it looked 1,000 light-years ago. b. as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer. c. as it looked 1,000 years ago. d. as it would appear to o ...
... d. originated just after the telescope was invented. e. was devised by Galileo. 4. If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it a. as it looked 1,000 light-years ago. b. as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer. c. as it looked 1,000 years ago. d. as it would appear to o ...
October 2014 - Hermanus Astronomy
... A recent study led by Olivier Mousis from the University of Franche-Comté in France examined how Titan’s methane rainfall would interact with icy materials within underground reservoirs. They found that the formation of materials called clathrates changes the chemical composition of the rainfall run ...
... A recent study led by Olivier Mousis from the University of Franche-Comté in France examined how Titan’s methane rainfall would interact with icy materials within underground reservoirs. They found that the formation of materials called clathrates changes the chemical composition of the rainfall run ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.