Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... compact, these regions spin and shrink and begin to form a flattened disk. The disk has a central concentration of matter called a protostar. • The protostar continues to contract and increase in temperature for several million years. Eventually the gas in the region becomes so hot that its electron ...
... compact, these regions spin and shrink and begin to form a flattened disk. The disk has a central concentration of matter called a protostar. • The protostar continues to contract and increase in temperature for several million years. Eventually the gas in the region becomes so hot that its electron ...
Galaxy5
... • The gas collided and sunk to the center. The Milky Way was built up piece-meal in this fashion. • Today, galaxy interactions between the primary spiral galaxy and its satellites are much less frequent, because there are few satellites remaining. • The Milky Way is in the process of eating a satell ...
... • The gas collided and sunk to the center. The Milky Way was built up piece-meal in this fashion. • Today, galaxy interactions between the primary spiral galaxy and its satellites are much less frequent, because there are few satellites remaining. • The Milky Way is in the process of eating a satell ...
public_lector_10
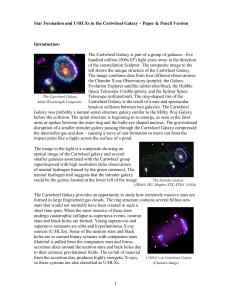
... The blue image shows young star-forming regions and is affected by dust obscuration. The NIR image shows mainly the old stars and is unaffected by dust. Note how clearly the central bar can be seen in the NIR image ...
... The blue image shows young star-forming regions and is affected by dust obscuration. The NIR image shows mainly the old stars and is unaffected by dust. Note how clearly the central bar can be seen in the NIR image ...
Giant “Pulsar” Studies with the Compact Array Abstract
... Not Just Cool, But Ultracool Dwarfs I have completed a survey of all 15 known ultracool dwarfs within 10 pc in the Southern hemisphere with CABB at the ATCA. Our sample was chosen from stars that straddle the hydrogen-burning star and brown dwarf divide, with spectral types ranging from M7 to L. Sin ...
... Not Just Cool, But Ultracool Dwarfs I have completed a survey of all 15 known ultracool dwarfs within 10 pc in the Southern hemisphere with CABB at the ATCA. Our sample was chosen from stars that straddle the hydrogen-burning star and brown dwarf divide, with spectral types ranging from M7 to L. Sin ...
Australian National Flag Day
... • Gamma Crucis (also Gacrux) - is a red giant star approximately 88 lightyears away in the constellation of Crux. • Delta Crucis – is a star about 360 light-years from Earth, the faintest of the four bright stars that form the constellation Crux. • Epsilon Crucis - is an orange giant, located about ...
... • Gamma Crucis (also Gacrux) - is a red giant star approximately 88 lightyears away in the constellation of Crux. • Delta Crucis – is a star about 360 light-years from Earth, the faintest of the four bright stars that form the constellation Crux. • Epsilon Crucis - is an orange giant, located about ...
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
... formed in large fragmented gas clouds. The ring structure contains several billion new stars that would not normally have been created in such a short time span. When the most massive of these stars undergo catastrophic collapse as supernova events, neutron ...
... formed in large fragmented gas clouds. The ring structure contains several billion new stars that would not normally have been created in such a short time span. When the most massive of these stars undergo catastrophic collapse as supernova events, neutron ...
Thermonuclear supernovae and cosmology
... SNe known, surveys find hundreds SNe a year; new dedicated surveys under way. Most distant SNIa: z=1.914 (10Gyr. 04/13: CANDELS, HST). ...
... SNe known, surveys find hundreds SNe a year; new dedicated surveys under way. Most distant SNIa: z=1.914 (10Gyr. 04/13: CANDELS, HST). ...
two dozen compact sources and a massive disk
... NGC 6334 Star Forming Complex (G351.4-0.6) • Confusing nomenclature: Radio sources A, C, D, E, F (Rodriguez+ 1982) Far-infrared sources: I, II, III, IV (McBreen+ 1979, Gezari 1982) ...
... NGC 6334 Star Forming Complex (G351.4-0.6) • Confusing nomenclature: Radio sources A, C, D, E, F (Rodriguez+ 1982) Far-infrared sources: I, II, III, IV (McBreen+ 1979, Gezari 1982) ...
ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... • The study of young binaries began with Joy & van Biesbrock (1944) who found 5 visual binaries among the newly recognized T Tauri stars. • In 1962, George Herbig added another 24 T Tauri binaries, demonstrating that binaries among young stars are not uncommon. • Observations of young binaries remai ...
... • The study of young binaries began with Joy & van Biesbrock (1944) who found 5 visual binaries among the newly recognized T Tauri stars. • In 1962, George Herbig added another 24 T Tauri binaries, demonstrating that binaries among young stars are not uncommon. • Observations of young binaries remai ...
The Dynamics-Based Approach to Studying Terrestrial Exoplanets
... 5. The planet-to-star contrast is much larger than that for the Earth-Sun system. In the Rayleigh-Jeans limit, this ratio depends upon the relative surface areas and brightness temperatures of the planet and star. This ratio is 0.012% (M4V) and 0.11% (M8V), compared to 0.00044% for the Earth-Sun sys ...
... 5. The planet-to-star contrast is much larger than that for the Earth-Sun system. In the Rayleigh-Jeans limit, this ratio depends upon the relative surface areas and brightness temperatures of the planet and star. This ratio is 0.012% (M4V) and 0.11% (M8V), compared to 0.00044% for the Earth-Sun sys ...
mufon ufo symposium -1974
... F5V to F7V have more stars rotating slowly indicating the possibility of planets. From approximately F8 on, all main sequence stars are rotating slowly, probably indicating planets. According to Carl Sagan, F8 is the point where intelligent life would have time to emerge. So main sequence stars fro ...
... F5V to F7V have more stars rotating slowly indicating the possibility of planets. From approximately F8 on, all main sequence stars are rotating slowly, probably indicating planets. According to Carl Sagan, F8 is the point where intelligent life would have time to emerge. So main sequence stars fro ...
Effects of Mutual Transits by Extrasolar Planet
... light curves. We show that, especially for small separation cases, geometrical blocking of one faint object by the other transiting a parent star causes an apparent increase in light curves and characteristic fluctuations appear as an important evidence of mutual transits. We show also that extrasol ...
... light curves. We show that, especially for small separation cases, geometrical blocking of one faint object by the other transiting a parent star causes an apparent increase in light curves and characteristic fluctuations appear as an important evidence of mutual transits. We show also that extrasol ...
Star formation in galaxies over the last 10 billion
... Astronomers can look back in time: light from very distant galaxies took billions of years to reach us. Looking far is looking back ...
... Astronomers can look back in time: light from very distant galaxies took billions of years to reach us. Looking far is looking back ...
Brown et al. 2008 Studying Resolved Stellar
... One of the core goals of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is to determine the history of star formation and metal enrichment in the Universe. JWST will pursue this goal primarily by searching for luminous objects at very high redshift. An important complement to the high-redshift observations w ...
... One of the core goals of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is to determine the history of star formation and metal enrichment in the Universe. JWST will pursue this goal primarily by searching for luminous objects at very high redshift. An important complement to the high-redshift observations w ...
Stellar Physics 2
... B. Neutron stars are stars with a mass below the Chandrasekhar Mass limit and its electrons have become relativistic. C. Neutron stars are stars with a mass above the Chandrasekhar Mass limit, its electrons are yet to become relativistic. ...
... B. Neutron stars are stars with a mass below the Chandrasekhar Mass limit and its electrons have become relativistic. C. Neutron stars are stars with a mass above the Chandrasekhar Mass limit, its electrons are yet to become relativistic. ...
Introduction
... This movement of the star can be accurately measured using the Doppler effect. The shift produced by a planetary object is of the order of tens or hundreds of m/s (the amplitude of the Sun’s movement due to Jupiter is ∼12.5 m/s, due to Saturn ∼4 m/s, and due to the Earth ∼8 cm/s; 51 Peg b moves the ...
... This movement of the star can be accurately measured using the Doppler effect. The shift produced by a planetary object is of the order of tens or hundreds of m/s (the amplitude of the Sun’s movement due to Jupiter is ∼12.5 m/s, due to Saturn ∼4 m/s, and due to the Earth ∼8 cm/s; 51 Peg b moves the ...
Space astrometry 2: Scientific results from Hipparcos
... • spiral-arm shocks: Pleiades group (Asiain et al 1999, Famaey et al 2005, Gieles et al 2007) • resonance due to rotating bar: Hercules stream (Dehnen 1998) • other moving groups: • Castor: 0.2 Gyr (Barrado y Navascues 1998, Montes et al 2001) • Ursa Major: 0.3 Gyr (Eggen 1998, Chupina et al 2001, K ...
... • spiral-arm shocks: Pleiades group (Asiain et al 1999, Famaey et al 2005, Gieles et al 2007) • resonance due to rotating bar: Hercules stream (Dehnen 1998) • other moving groups: • Castor: 0.2 Gyr (Barrado y Navascues 1998, Montes et al 2001) • Ursa Major: 0.3 Gyr (Eggen 1998, Chupina et al 2001, K ...
San Pedro Mártir observations of microvariability in obscured quasars
... campaign, we conclude that we cannot confirm microvariability in this source. J1430+1339 was observed on March 28 and March 30, 2011. During the two observing nights, both the target and the comparison star exhibited very contradictory results from ANOVA. We were unable to find a comparison star tha ...
... campaign, we conclude that we cannot confirm microvariability in this source. J1430+1339 was observed on March 28 and March 30, 2011. During the two observing nights, both the target and the comparison star exhibited very contradictory results from ANOVA. We were unable to find a comparison star tha ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.