Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... Astronomers use the Greek letter “λ” (pronounced “lambda”) as a symbol for wavelength. Wavelengths are measured in units of Angstroms, or “Å” for short. 1Å = 10-10 m = 0.1 nm. ...
... Astronomers use the Greek letter “λ” (pronounced “lambda”) as a symbol for wavelength. Wavelengths are measured in units of Angstroms, or “Å” for short. 1Å = 10-10 m = 0.1 nm. ...
Precession of the Equinoxes and its Importance in Calendar Making
... ent path of the Sun in the celestial sphere remains the same, the moon and the planets show some deviations in their motions. The moon and the planets move to some extent towards north and south of the ecliptic. This deviation for the moon does not exceed much more than 5 degrees, while the planets ...
... ent path of the Sun in the celestial sphere remains the same, the moon and the planets show some deviations in their motions. The moon and the planets move to some extent towards north and south of the ecliptic. This deviation for the moon does not exceed much more than 5 degrees, while the planets ...
ppt
... 65 Myr (Cretaceous-Tertiary) 202 Myr (Triassic-Jurassic) 250 Myr (Permian-Triassic) 367 Myr (Late Devonian) 438 Myr (Ordovician-Silurian) ...
... 65 Myr (Cretaceous-Tertiary) 202 Myr (Triassic-Jurassic) 250 Myr (Permian-Triassic) 367 Myr (Late Devonian) 438 Myr (Ordovician-Silurian) ...
... around 280 parts per million (ppm) to around 380 ppm now. Studies of ice core show that concentrations of CO2 have not been so high for nearly half a million years. At the current rate of increase, they will have reached 800 ppm by the end of the 21st century! Beyond 550 ppm it would not be liveable ...
Supermassive black holes
... rather random orbital orientations. Disk stars are younger, more metal rich and orbit in the same orientation, excepting some up and down motion ...
... rather random orbital orientations. Disk stars are younger, more metal rich and orbit in the same orientation, excepting some up and down motion ...
Distance Measures: Parallax
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
Chapter 7: The Galaxy, structure and content File
... thin disc). The term is associated with stars, not gas. It consists of moderately metalpoor, older stars, with [Fe/H] close to −0.6. The system is rotationally supported, but hvφ i is slightly smaller than for the thin disc, a consequence of the stars showing a velocity dispersion that is larger tha ...
... thin disc). The term is associated with stars, not gas. It consists of moderately metalpoor, older stars, with [Fe/H] close to −0.6. The system is rotationally supported, but hvφ i is slightly smaller than for the thin disc, a consequence of the stars showing a velocity dispersion that is larger tha ...
Distance Measures: Parallax
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
... One of the most difficult problems in astronomy is determining the distances to objects in the sky. There are four basic methods of determining distances: radar, parallax, standard candles, and the Hubble Law. Each of these methods is most useful at certain distances, with radar being useful nearby ...
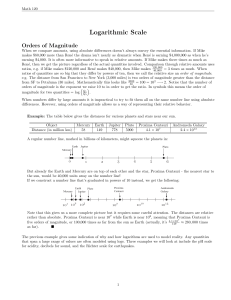
Logarithmic Scale
... But already the Earth and Mercury are on top of each other and the star, Proxima Centauri - the nearest star to the sun, would be 40,000 units away on the number line! If we construct a number line that’s graduated in powers of 10 instead, we get the following: Mercury ...
... But already the Earth and Mercury are on top of each other and the star, Proxima Centauri - the nearest star to the sun, would be 40,000 units away on the number line! If we construct a number line that’s graduated in powers of 10 instead, we get the following: Mercury ...
2015.09.20
... Twenty-Fifth Sunday in Ordinary Time: 9/20/15—5:00 PM, 7:00, & 8:30 AM I have here a bottle of Brasso for cleaning brass products, a container of flying insect spray, and a can of Comet cleanser. One thing they all have in common is that these products are great in doing the things they are designed ...
... Twenty-Fifth Sunday in Ordinary Time: 9/20/15—5:00 PM, 7:00, & 8:30 AM I have here a bottle of Brasso for cleaning brass products, a container of flying insect spray, and a can of Comet cleanser. One thing they all have in common is that these products are great in doing the things they are designed ...
sections 7-8 instructor notes
... The primary opacity source in the atmospheres of B and A-type stars is atomic hydrogen, which makes its presence obvious in the flux distributions of such stars with discrete discontinuities in the stellar continua at λ912Å (the Lyman discontinuity), λ3647Å (the Balmer discontinuity), and λ8206Å (t ...
... The primary opacity source in the atmospheres of B and A-type stars is atomic hydrogen, which makes its presence obvious in the flux distributions of such stars with discrete discontinuities in the stellar continua at λ912Å (the Lyman discontinuity), λ3647Å (the Balmer discontinuity), and λ8206Å (t ...
Student Paper (Klongcheongsan)
... consisted of 70.6% hydrogen, 27.3% helium, and 2.1% heavier elements (also called “metal” in this context) when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium began some 4.5 billion years ago. The values of luminosity and effective temperature at that time placed the sun on a curve that is known as the zero ...
... consisted of 70.6% hydrogen, 27.3% helium, and 2.1% heavier elements (also called “metal” in this context) when nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium began some 4.5 billion years ago. The values of luminosity and effective temperature at that time placed the sun on a curve that is known as the zero ...
Communication with Extraterrestrial Intelligence (CETI)
... with which we have long been familiar (Gold 1998). All these biological adaptations must inform our searches for life elsewhere in the universe. Mindful of the adaptability of life to extreme environments, we should reconsider our own solar system (where we may have some hope of systematic in situ s ...
... with which we have long been familiar (Gold 1998). All these biological adaptations must inform our searches for life elsewhere in the universe. Mindful of the adaptability of life to extreme environments, we should reconsider our own solar system (where we may have some hope of systematic in situ s ...
milano2006_popov - X-Ray
... Sergei Popov, Mikhail Prokhorov (SAI MSU) IASF, Milano. 14 December 2006 ...
... Sergei Popov, Mikhail Prokhorov (SAI MSU) IASF, Milano. 14 December 2006 ...
Galaxies - Mike Brotherton
... b) Type Ia supernovae (collapse of an accreting white dwarf in a binary system): Type Ia supernovae have well known standard luminosities Compare to apparent magnitudes Find its distances Both are “Standard-candle” methods: Know absolute magnitude (luminosity) compare to apparent magnitude f ...
... b) Type Ia supernovae (collapse of an accreting white dwarf in a binary system): Type Ia supernovae have well known standard luminosities Compare to apparent magnitudes Find its distances Both are “Standard-candle” methods: Know absolute magnitude (luminosity) compare to apparent magnitude f ...
3rd EXAM VERSION A key - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... D. The immense radiation output from the quasar carries away energy. The mass of the black hole gets smaller until it evaporates. 28. Observations indicate that blazers are A. quasars that have absorbed or merged with a smaller galaxy within a cluster B. distant spiral galaxies undergoing an intense ...
... D. The immense radiation output from the quasar carries away energy. The mass of the black hole gets smaller until it evaporates. 28. Observations indicate that blazers are A. quasars that have absorbed or merged with a smaller galaxy within a cluster B. distant spiral galaxies undergoing an intense ...
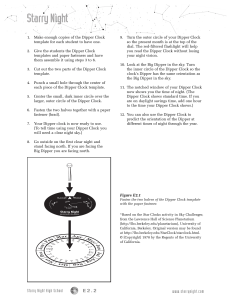
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.